Chapter 16: Control of Gene Expression
advertisement

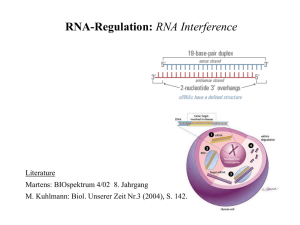
Control of Gene Expression Chapter 16 Genes and Development Proteins can determine the DNA sequence by binding the major groove of DNA. Proteins binding the minor groove cannot determine the exact sequence of bases. Prokaryotic gene regulation Lac Operon Prokaryotic gene regulation Trp Operon Biosynthesis of the amino acid typtophan Therefore, the regulation is the opposite of the lac operon. Eukaryotic gene regulation Enhancer (DNA sequence) Looping Activator (protein) ATP ADP + Pi ATP -dependent remodeling factor 1. Nucleosome sliding 2. Remodeled nucleosome 3. Nucleosome displacement 4. Histone replacement RNA Polymerase II microRNA gene Pri-microRNA Nucleus Pre-microRNA Drosha Exportin 5 Cytoplasm Dicer Mature miRNA RISC mRNA RISC mRNA cleavage mRNA RISC Inhibition of translation RISC Exogenous dsRNA, transposon, virus Repeated cutting by dicer siRNAs siRNA in RISC Ago + RISC mRNA Cleavage of target mRNA Ago RISC RNA polymerase II DNA 3´ 5´ Primary RNA transcript 1. Initiation of transcription Most control of gene expression is achieved by regulating the frequency of transcription initiation. Cut intron 5´ cap Exons Introns 3´ poly-A tail Mature RNA transcipt 2. RNA splicing Gene expression can be controlled by altering the rate of splicing in eukaryotes. Alternative splicing can produce multiple mRNAs from one gene. Large subunit 3´ poly-A tail Nuclear pore mRNA Small subunit 3´ 5´ 3. Passage through the nuclear membrane Gene expression can be regulated by controlling access to or efficiency of 5´ cap transport channels. 4. Protein synthesis Many proteins take part in the translation process, and regulation of the availability of any of them alters the rate of gene expression by speeding or slowing protein synthesis. P P Completed polypeptide chain 6. Posttranslational modification Phosphorylation or other chemical modifications can alter the activity of a protein after it is produced. RISC 5. RNA interference Gene expression is regulated by small RNAs. Protein complexes containing siRNA and miRNA target specific mRNAs for destruction or inhibit their translation. 23