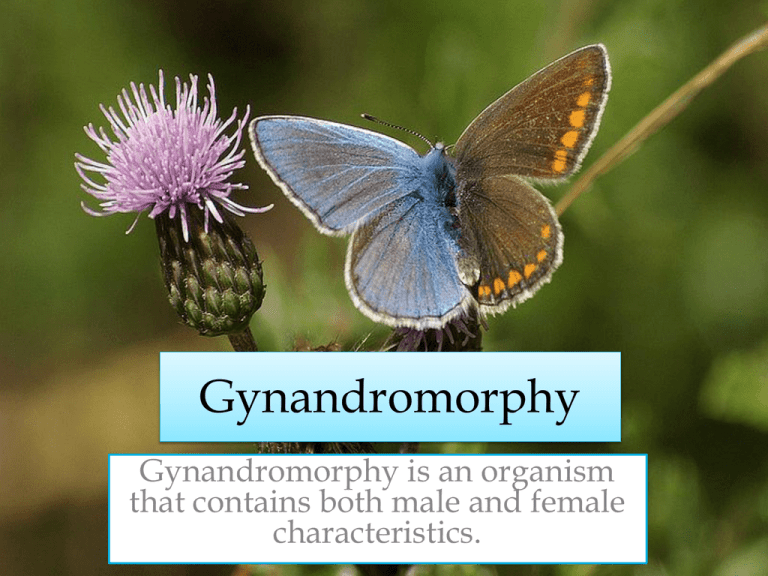
Gynandromorphy
Gynandromorphy is an organism
that contains both male and female
characteristics.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Clinton says chickens with this mix of cells are rare, but
maybe not as rare as people think. "If they are the same color,
for example, you might think well, that's a funny-looking
chicken. But you wouldn't think it's half-male and halffemale," he says.
Up until now, scientists who study sexual development
assumed that in birds and mammals hormones were by far
the more important signal. But the chicken study puts that in
doubt
Chickens have male and female sex chromosomes.
And these sex chromosomes tell a chicken which one to be.
The chickens were a mix of male and female cells
Only about 1 in 10,000 chickens are born as gynandromorphy
– Male features (a rooster's comb and a defensive leg spur)
– Female features (dainty, hen like features )
Found that the chickens' cells were normal. What was
strange, however, was that male cells made up one half of the
body, and female cells composed the other half.
The scientists believe gynandromorphy are created when a
chicken egg becomes fertilized by two sperm.
Chicken?
½ rooster
½ hen
Insect
Each cell division in insects
decides what a cell will become
The decisions that are made with
the earliest cell divisions are as
follows:
First division (of zygote) determines left and right sides
Second division - determines
front and back (at this point, there
would be four cells,
a front left, a front right, a back left
and a back right)
Third division - determines top
from bottom (at this point, there
would be eight cells,
a front upper left, a front lower left,
and so on)
Birds
Gynandromorphy are known to
exist in other bird species, such
as zebra finches, pigeons, and
parrots.
A clear example in birds is the
gynandromorphy Zebra Finch.
These birds have lateralized
brain structures in the face of a
common steroid signal,
providing strong evidence for a
non-hormonal primary sex
mechanism regulating brain
differentiation.
It's likely that this occurs in all
birds species, but it's not
always obvious because males
and females of many species
often look similar.
LOBSTER:
½ COOKED
½ ALIVE
• Half of the animal is mottled
brown, while the other is bright
orange—the color lobsters turn
after they've been boiled.
• lobsters usually sport a
combination of yellow, red, and
blue pigments. But the animals
grow symmetrically, with each
half of the body developing
independently of the other.
• half of the lobster's shell was
lacking the blue pigment, giving
it the appearance of having been
cooked to a turn
What is Gynandromorphy?
• The term "gynandromorphy" literally means part
female and part male
• Bilateral asymmetry: one side female and one side
male
• Mosaic: a case in which the two sexes aren't
defined as clearly.
• Bilateral gynandromorphy arises very early in
development, typically when the organism has
between 8 and 64 cells.
• Later the gynandromorphy is mosaic.