Cells
advertisement

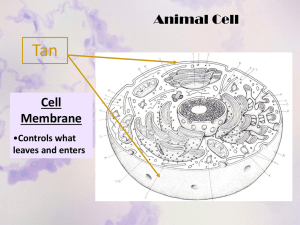
Cells Structure and Function Cell Vocabulary Make a flashcard for these terms: 1. Cell 2. Cell theory 3. Cell membrane 4. Cell wall 5. Nucleus 6. Cytoplasm 7. Prokaryote 8. Eukaryote 9. Organelle 10. Ribosome 11. Endoplasmic reticulum 12. Gogi apparatus 13. Lysosome 14. Vacuole 15. Chloroplast 16. Mitochondria 17. Lipid bilayer 18. Selective permeability 19. Diffusion 20. Active transport Cell Theory •All living things are composed of cells. •Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. •New cells are produced from existing cells. Cell Shape and Size • Press your pen to your paper to create dot. • How many cells do you think would fit within that dot???? Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic •These 2 types of cells differ in complexity and general structure Prokaryotic Cells •Lack internal membrane-bound structures •Unicellular organisms •About 1/10th the size of a Eukaryotic cell. •Example: bacteria Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell •Multicellular organisms •Membrane bound organelles •Mostly animal cells •Present in all living things, except bacteria Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic POGIL Plant and Animal Cells • Look at p. 176 in your textbook. • Take a moment to look at the cells. • What structures do plant cells have that animal cells do not?? Plant and Animal Cell Mystery Basic Parts of a Cell •Despite cell diversity, ALL cells have 3 basic parts: 1)Cell Membrane and/or Cell Wall 2)Cytoplasm 3)Nucleus Cell Wall •Cell Wall provides support and protection for the cell. •Found in plants and many prokaryotes •Very outside edge of the cell Cytoplasm •The region of the cell that is within the plasma membrane •Includes the fluid, cytoskeleton, and all organelles (except nucleus). Cytoplasm Nucleus • Cells carry coded information in the form of DNA. • In some cells DNA floats freely inside the cell • In other cells the DNA is found in a membranebound organelle: the NUCLEUS • Most functions of a cell are controlled by the nucleus. • The NUCLEOLUS is a small structure within the nucleus where ribosomes are assembled. Control Center Basic Parts Video Clip Nucleus Video Clip INTERACTIVE •Draw a cell and label all 3 basic parts •You do NOT need to include all the organelles Cell Organelles • • • • • • • Plasma Membrane Nucleus Mitochondria Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Cytoskeleton The Cell Song! • Available on Youtube and Itunes Cell Organelle POGIL Ribosomes (not an organelle - but important) • Present in the cytoplasm. • Present with Rough ER. • No membrane present. • Each cell contains thousands • Make proteins Ribosome Video Clip Endoplasmic Reticulum • System of tubes and sacs • Moves materials around in cell • Smooth type: lacks ribosomes • Rough type (pictured): ribosomes embedded in surface http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum • Transports materials throughout the cell. • Digests lipids. • Produces proteins. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • Covered with ribosomes. • Produces proteins. • Transports materials throughout the cell. Video Clip Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies or Golgi Apparatus •Protein 'packaging plant' •Move materials within the cell •Move materials out of the cell http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/structures.html Golgi Apparatus Video Clip Central Vacuole (Plant Cell Only) • Most plant cells have one large one. • Filled w/ fluid. • Helps maintains turgor pressure and shape of cell. Chloroplast (Plant Cell Only) • Contains chlorophyll. • Makes plants green. • Uses light energy to make ATP & sugars. • Photosynthesis takes place here. Mitochondria Video Clips Mitochondria, aka “Mighty-Chondria” • This organelle processes energy for a cell. It makes ATP by breaking down glucose to Carbon dioxide. • (ATP = energy) • Involved in cellular respiration • Controls level of water and other materials in cell • Recycles and decomposes proteins, fats, and carbohydrates • Mitochondria even have their own DNA! Let’s hear that Cell Song Again… A quick review of cell organelles • 3 Facts from the Brainpop on Cell Structures INTERACTIVE Cell City Cell Memory Chart Cell Coloring! • Quiz on Eukaryotic cell at next meeting!! • Plant and Animal Cell Coloring sheet Movement through the Membrane • Cell’s outer boundary • Covers a cell’s surface and acts as a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell • All materials enter and exit through the plasma membrane • Membrane is SEMIPERMEABLE: allows only certain materials in and out. Plasma Membrane Movement through a membrane video Clip Cell Homeostasis • Cell membranes help organisms maintain homeostasis by controlling what substances may enter or leave cells. • There are two main ways of transporting materials into and out of a cell: Passive Transport and Active Transport Passive Transport •Passive transport occurs when substances cross the cell membrane without any energy by the cell •Transport with NO Energy—riding a bike downhill •Diffusion and Osmosis are the primary methods of Passive Transport Diffusion •Simplest form of passive transport •Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration •The difference in the concentration of molecules across a distance is called a CONCENTRATION GRADIENT •Molecules will move from one area to another until it reaches EQUILIBRIUM, or a balance. Sugar Cube Diffusion Osmosis • Osmosis is the passive (no energy required) transport of water across a cell membrane • Water moves from areas of high concentration to low concentration • When the concentration of solute molecules outside the cell is lower than inside the cell, the solution outside the cell is HYPOTONIC to the cell. In this situation water diffuses INTO the cell until equilibrium is established. Osmosis •If the solution outside the cell is higher than the inside the cell the solution is HYPERTONIC and the water diffuses out of the cell to reach equilibrium •When the concentrations are equal=ISOTONIC Osmosis Video Clip Gummy Bear Osmosis Lab Active Transport •When cells need to transport materials from an area of low concentration to high concentration (the opposite of what would naturally happen) it is called ACTIVE TRANSPORT, the cell needs to use ENERGY. Endocytosis •The process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles. Exocytosis • Process by which a substance is released from a cell Endo and Exo video clip