Biology Slides
advertisement
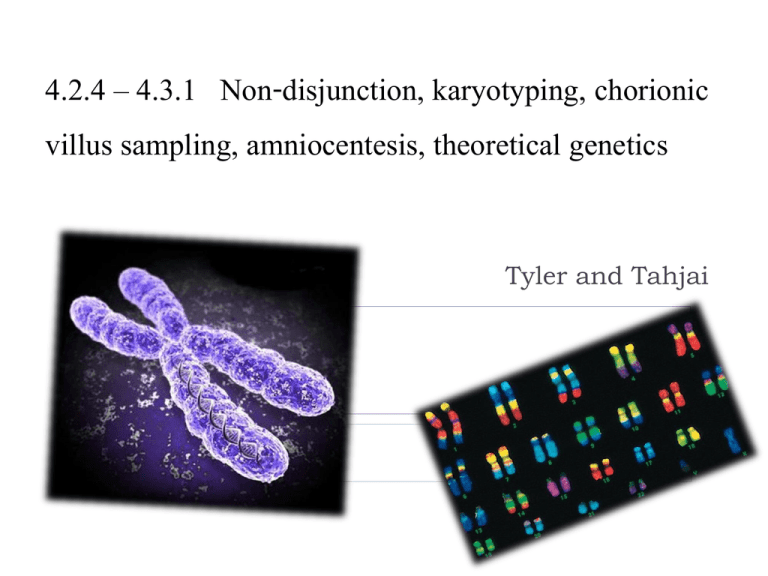
4.2.4 – 4.3.1 Non-disjunction, karyotyping, chorionic villus sampling, amniocentesis, theoretical genetics Tyler and Tahjai 4.2.4 Explain that non-disjunction can lead to changes in chromosome number, illustrated by reference to Down syndrome (trisomy 21). 4.2.4 Non-disjunction- failure of chromosomes to properly separate during Anaphase I Leads to aneuploidy or polyploidy within gametes Aneuploidy – having one extra chromosome or missing one chromosome Extreme cases can result in total non-disjunction, where all homologous pairs fail to separate Total non-disjunction causes polyploidy, where an organism has a complete extra set of chromosomes. (3n) 4.2.4 Synapsis- pairing up of homologous chromosomes during Prophase I Resulting pairs of homologous chromosomes are called tetrads or bivalents 4.2.4 Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) Down syndrome is present when there are 3 chromosomes of chromosome 21 Occurs from non-disjunction and aneuploidy in either parent gamete One 21 parent gamete will carry two copies of chromosome Causes of non-disjunction Non-disjunction can occur randomly, but age of female gametes/eggs influences chances Female gametes are produced before birth and are not used until ovulation, leaving egg cells to endure damage from environment over time Because sperm cells are constantly produced, the age of the male parent has less of an effect on non-disjunction A 20 year old woman’s egg cells will have collected 20 years of damage and with more years, comes more damage 4.2.5 State that, in karyotyping, chromosomes are arranged in pairs according to their size and structure 4.2.5 Karyotyping- the process of finding the chromosomal characteristics of a cell Process: Chromosomes within cell are stained with a dye to reveal structural banding Chromosomes are then photographed. Chromosomes are cut from picture, then paired and arranged based on size and structure 4.2.6 State that karyotyping is performed using cells collected by chorionic villus sampling or amniocentesis, for pre-natal diagnosis of chromosome abnormalities Chorionic Villus Sampling Amniocentesis 4.2.6 What is Chorionic Villus? Chorionic villi cells are stored within the placenta of the zygote and are used to analyze an organism’s chromosomes 4.2.6 Chorionic Villus Sampling Can be done 11-12 weeks into pregnancy Process of taking chorionic villi cells in order to obtain cells from original zygote tissue (chromosomes) 1% risk of miscarriage 4.2.6 Amniocentesis Can be done during 16th week of pregnancy Amniotic fluid sample is taken to obtain chromosomes The sample cells begin to divide and are photographed in order to produce karyotype 0.5% risk of miscarriage 4.2.7 4.3.1 Theoretical Genetics Definitions Genotype- the alleles of an organism Phenotype- includes all the characteristics of an organism Dominant Allele- one which has the same effect on the phenotype whether it is present in the homozygous or heterozygous state Recessive Allele- one which only has an effect on the phenotype when present in the homozygous state Codominant Alleles- a pair of alleles that both affect the phenotype when present in a heterozygote Locus- the particular position on homologous chromosomes of a gene Homozygous- having two identical alleles of a gene Heterozygous- having two different alleles of a gene Carrier- a heterozygous individual that has one copy of a recessive allele that causes a genetic disease in individuals that are homozygous for this allele Test Cross- testing a suspected heterozygote by crossing with a known homozygous recessive 4.3.1 Genotype- the alleles of an organism Phenotype- includes all the characteristics of an organism 4.3.1 Dominant Allele- one which has the same effect on the phenotype whether it is present in the homozygous or heterozygous state Recessive Allele- one which only has an effect on the phenotype when present in the homozygous state 4.3.1 Codominant Alleles- a pair of alleles that both affect the phenotype when present in a heterozygote Locus- the particular position on homologous chromosomes of a gene 4.3.1 Homozygous- having two identical alleles of a gene Heterozygous- having two different alleles of a gene 4.3.1 Carrier- a heterozygous individual that has one copy of a recessive allele that causes a genetic disease in individuals that are homozygous for this allele Test Cross- testing a suspected heterozygote by crossing with a known homozygous recessive Works Cited "Amniocentesis - What Is an Amniocentesis Video." How-to Videos: How-to and DIY Videos - About.com Videos. N.p., n.d.Web. 22 Feb. 2012. <http://video.about.com/pregnancy/Amniocentesis.htm>. "Chorionic Villus Sampling - What Is Chorionic Villus Sampling - CVS Video." How-to Videos: How-to and DIY Videos - About.com Videos. N.p., n.d. Web. 22 Feb. 2012. <http://video.about.com/pregnancy/Chorionic-VillusSampling.htm>. "HowStuffWorks Videos "Conspiracy Test: Gulf War Illness Test Results" ."HowStuffWorks Videos "Video Channel" . N.p., n.d.Web. 22 Feb. 2012. <http://videos.howstuffworks.com/discovery/32199-conspiracy-test-gulfwar-illness-test-results-video.htm>. Karyotype game http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/traits/karyoty pe/