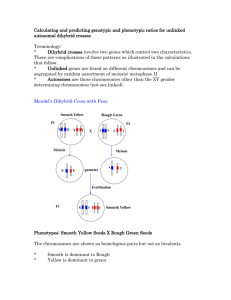
Calculate and predict the genotypic
and phenotypic ratio of offspring of
dihybrid crosses involving unlinked
autosomal genes.
Genotype-The genetic makeup of an organism
that includes their biological
characteristics.
Phenotype-The physical makeup of an
organism that includes their physical
characteristics
Possible phenotypes
Corresponding genotypes
Yellow
YY or Yy
green
yy
Round
RR or Rr
wrinkled
rr
YY = 2 dominant
Yy = one
dominant, one
recessive
yy = 2 recessive
Dihybrid Crosses involve two genes
which control two
characteristics.
We can use
dihybrid crosses
to calculate and
predict the
genotypic and
phenotypic ratio
of offspring
involving unlinked
autosomal genes.
Autosomal
Genes- A gene that
is not located on a sex
chromosome.
*When a gene is unlinked, they
are found on different
chromosomes and can be
segregated by Random
Assortment of meiosis, during
Metaphase II.
In order to calculate the genotypic and
phenotypic ratio:
› 1) Determine the parent’s genotypes
› 2) Make and solve dihybrid cross
› 3) Calculate and predict genotypic and
phenotypic ratios.
› http://www.siskiyous.edu/class/bio1/genetics/di
hybrid_v2.html
› http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/anim
ations/content/mendel/mendel.html
Distinguish between autosomes and sex
chromosomes.
Autosomes- General
chromosomes that carry
genetic instruction and any
chromosome other than a
sex chromosome; come in
pairs.
Sex chromosomes- Come in
pairs also, but there are two
types, X & Y. For humans, the
Y chromosome is the
“determining factor” as it
determines whether or not
the embryo is male or
female.
Explain how crossing over between nonsister chromatids of a homologous pair in
prophase I can result in an exchange of
alleles.
Crossing over, also
known as
recombination, is the
exchange of chromosome
segments between nonsister chromatids in
meiosis.
Alleles - an
alternative form of
a gene (one
member of a pair)
that are located at a
specific position on a
specific chromosom
e. The DNA codings
on an allele
determine traits that
are passed on from
parents to offspring.
During crossing over, “slices” of
homologous chromosomes’ DNA are
exchanged with non-sister chromatids of
a homologous pair. Because of this,
alleles are exchanged as the alleles from
one chromatid are being exchanged
with the alleles on a non-sister chromatid.
http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0072835125/126997
/animation5.html
"Dihybrid Cross." The Biology Project. Web. 09 Feb. 2012.
<http://www.biology.arizona.edu/mendelian_genetics/problem_set
s/dihybrid_cross/03t.html>.
http://library.thinkquest.org/20830/Textbook/Genetics.htm
http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/me
ndel/mendel.html
http://newton.dep.anl.gov/askasci/mole00/mole00388.htm
http://www.bookrags.com/research/crossing-over-gen-01/
http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/IB_Biology/Genetics,pt2
http://click4biology.info/c4b/10/gene10.2.htm#1
http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/dl/free/0072835125/126997/animation5.html
http://www.ibguides.com/biology/notes/dihybrid-crosseshl?PHPSESSID=8a17514703a1a528f6e35ae35079158d