Cornell Notes
advertisement
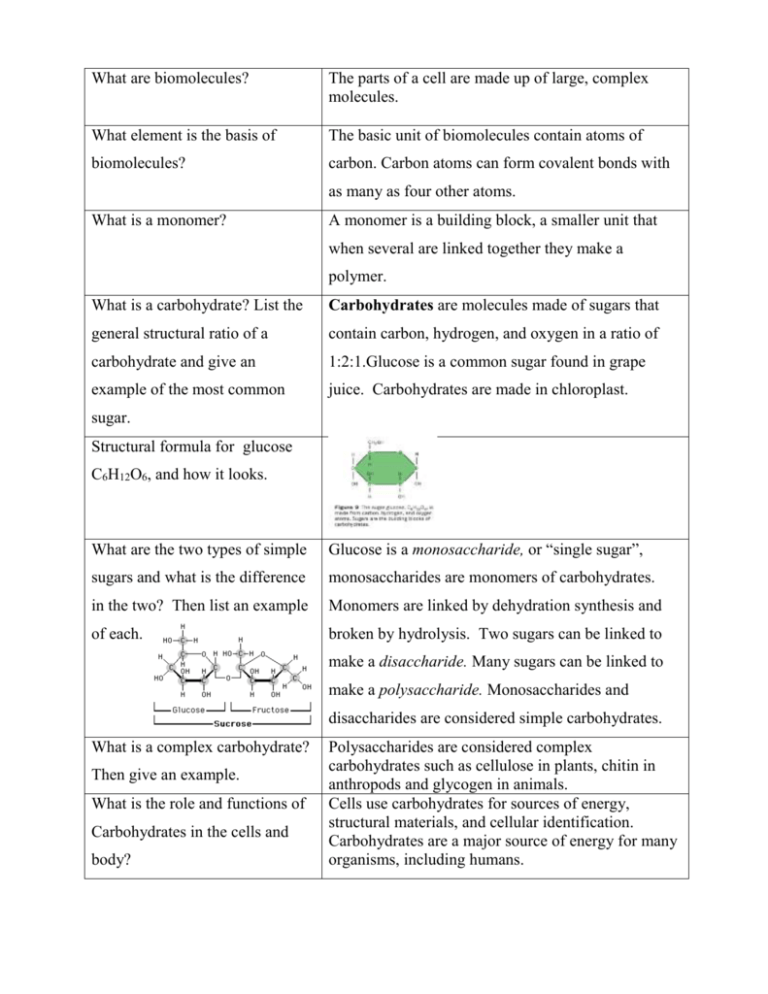
What are biomolecules? The parts of a cell are made up of large, complex molecules. What element is the basis of The basic unit of biomolecules contain atoms of biomolecules? carbon. Carbon atoms can form covalent bonds with as many as four other atoms. What is a monomer? A monomer is a building block, a smaller unit that when several are linked together they make a polymer. What is a carbohydrate? List the Carbohydrates are molecules made of sugars that general structural ratio of a contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of carbohydrate and give an 1:2:1.Glucose is a common sugar found in grape example of the most common juice. Carbohydrates are made in chloroplast. sugar. Structural formula for glucose C6H12O6, and how it looks. What are the two types of simple Glucose is a monosaccharide, or “single sugar”, sugars and what is the difference monosaccharides are monomers of carbohydrates. in the two? Then list an example Monomers are linked by dehydration synthesis and of each. broken by hydrolysis. Two sugars can be linked to make a disaccharide. Many sugars can be linked to make a polysaccharide. Monosaccharides and disaccharides are considered simple carbohydrates. What is a complex carbohydrate? Then give an example. What is the role and functions of Carbohydrates in the cells and body? Polysaccharides are considered complex carbohydrates such as cellulose in plants, chitin in anthropods and glycogen in animals. Cells use carbohydrates for sources of energy, structural materials, and cellular identification. Carbohydrates are a major source of energy for many organisms, including humans. What are Lipids and what are the Lipids are another class of biomolecules, which 4 lipid categories? includes fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. Lipids consist of chains of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to hydrogen atoms. This structure makes lipids repel water. Lipids are made in the smooth ER. What are the main functions of The main functions of lipids include storing energy lipids? and controlling water molecules. What is the function of fat in the The main purpose of fats is to store energy. Fats can body and types of fat? store energy even more efficiently than carbohydrates. Unsaturated fats: liquid at room temp, one or more double bonds between carbons in the fatty acids allows for “kinks” in the tails of most plant fats. Saturated fats: have only single C-C bonds in fatty acid tails solid at room temp, most animal fats like lard Structure of a fat molecule. Triglyceride (monomers: Glycerol + 3 fatty acids) What is the function of The structure of cell membranes depends on how this phospholipids? molecule interacts with water. (monomers: glycerol, 2 fatty acids and a phospholipid) What are proteins? Proteins are chains of amino acids(monomer) that twist and fold into certain shapes that determine what the proteins do. List 5 functions of proteins. Proteins may be involved in structure, support, movement, communication, transportation, and carrying out chemical reactions What are proteins made of? How A protein is a molecule made up of amino acids, do amino acids link together to building blocks that link to form proteins. Proteins form a long protein chain? are made at the ribosomes in cells. Every amino acid has an amino group (NH2) and a carboxyl(COOH) group. Units of amino acids can form links called peptide bonds. The side group or R-group gives an amino acid its unique properties. Twenty different amino acids are found in proteins, 8 are considered essential. What is the basic structure of a protein What are Nucleic Acids? A nucleic acid is a long chain of nucleotide units. What are the 3 parts of a A nucleotide (monomer) is a molecule made up of: a nucleotide? sugar, a base, and a phosphate group. What are the 2 most common Nucleotides of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, Nucleic Acids and how are DNA contain the sugar deoxyribose. Nucleotides of & RNA different? Draw the DNA ribonucleic acid, or RNA, contain the sugar ribose. structure and label the 3 parts? DNA and RNA are made in the nucleus of cells. What are the functions of Nucleic Nucleic acids store and transmit hereditary Acids in the body? information. ATP Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is also nucleic acid that has three phosphate groups and supplies energy to cells. ATP is made in the mitochondria.