10.09.12.HistVar
advertisement

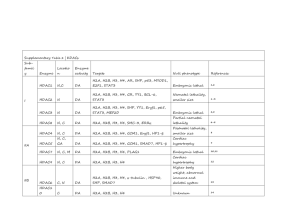
Bio 483 October 9, 2012 Overview of Histone Variants Shelley Berger Shelley Berger Biology; CDB; Genetics The Wistar Institute Penn Epigenetics Program University of Pennsylvania bergers@upenn.edu Lecture Outline What are histone variants? Review nuclesome structure wrt replacement Discuss H2A: macroH2A, H2A.Bbd, H2Ax, H2AZ H3: CENPA, H3.3 testes histone variants Consideration of following issues: - sequence variation - nucleosome structure - genome function - location within the genome - physiological function Core vs. variant histones N globular C H3 H4 H2A H2B Are there additional histones? H3 H4 H2A H2B H1 H3 H4 H2A H3 ‘tail’ H2B Luger and Richmond, Nature 1997 New nucleosome formation: after replication H3/H4 tetramer binds to DNA 2 dimers H2A/H2B bind H3/H4 tetramer How to replace? 1. During replication assemble with variant histones 2. H2A/H2B dimer exchange 3. Disassembly of nucleosome during DNA damage repair, transcription H2A DNA repair Gene activation Gene repression X chrom inact H2B Gene activation H3 H4 Centromere identity H2A Chromatin compaction by macroH2A Chromatin destabilization by H2A.Bbd H2A H2Ax Histone H2Ax in DNA damage pathway DNA damage leads to complex repair pathways Molecular details of DNA repair H2Ax evolutionary conservation H2Ax phosphorylation is an early step in the repair process Histone H2AZ in gene regulation Histone H2AZ (= HTZ1): What is its localization in the genome? What genomic process does it regulate? How does it affect NCP structure and positioning? Genome-wide view of H2AZ at promotors TSS Promoter TSS Gene ORF H2AZ tends to occur in one nuc up- and one nuc down-stream of the TSS Does it regulate transcription? Nuc “Depleted” Region H2AZ is released as genes are activated Its release is required for full activation Is there a difference in nucleosome stability? Association of H2A/H2AZ with chromatin H2AZ is more loosely bound to chromatin (although NCP structure very similar) What is the localization of H2AZ around active/inactive genes? Active genes less enriched than inactive H2AZ What is its localization in the genome? Inactive promoters What genomic process does it regulate? Poises genes for activation How does it affect NCP structure and positioning? Destablizes NCP: correlates with depletion of one NCP over the TSS How is it incorporated? …a digression ATP-dependent Nucleosome Remodeling Nucleosomes can be changed in detailed association with DNA, position, presence Activities of ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes ATP ADP + Pi ATP Remodeler Evolutionary Tree of SWI2/SNF2 Remodelers ino80-sc ISW1-Sc ISW2-Sc SNF2L-Hs SNF2H-Hs ISWI-Dm CHD5-Hs CHD4-Hs CHD3-Hs MI2-Dm CHD1-Sc CHD2-Hs CHD1-Hs CHD-Dm STH1-Sc SWI2-I Brahma-Dm BRG-1-Hs BRM-Hs INO80 ISWI CHD SWI/SNF ATP dependent remodelers and Histone Variant deposition Swr1 H2AZ Start with H2A NCPs What do ATP-dependent remodeling complexes do? 1. Directly alter NCP position 2. Exchange histones and histone variants: New paradigm! Model for H2AZ Biochem. Cell Biol vol 84 2006 Instability of H2AZ NCPs allows high temp to turn on/off genes in plants Histone H3 and its Variants Replication Coupled deposition (only S phase) CenpA Replication independent Deposition (not strictly during S phase) Histone H3.1 and H3.3 H3/H3.1 H3.3 H4 H3.3 is very similar to H3.1 H3.3 is more ancient What genomic processes do H3.1/H3.3 regulate? Replication Dependent: Either H3.1 or H3.3 Replication Independent: Only H3.3 H3.3 localizes with RNAPII and K4me H3.3 H3.1 K4me2 RNAP genes How are H3.1 and H3.3 deposited in RC and RI pathways? H3.1 H3.3 p150 p60 HIRA IP-Western Two different chaperone/ assembly factors Nucleosome assembly RC or RI Histone CENPA H3 CENPA H4 What are centromeres? Sequence complexity CENPA, an H3 variant, is in a specialized NCP at centromeres in all eukaryotes Targeting of CENPA to centromeres Mapping in vitro and in vivo defined a region in the histone fold as “CATD” Chaperone for Centromeric Localization Cell line expressing CENPA-TAP HJURP required for CENPA targeting to centromeres HJURP Knock Down cell line 1. OE CENPA did not restore targeting 2. H3-CATD recruited by HJURP No targeting of CENPA in HJURP KD Controversy regarding structure of the centromeric CENPA NCP Proposed structures: Is there a distinct structure? (CENPA-H4)2 is more compact Structure of CENPA NCP Structural features map to CATD! It forms a well behaved octamer Summary: H3 variants and their functions Cenp A HIRA CAF1 HJURP Spermatogenesis and chromatin compaction: key role for histone variants Testes-specific histone variants replace core histones following meiosis All histones (except H4) have testes variants A remarkable variety of histone variants to regulate the genome via location-specific nuclesome funtion H3 H4 H2A H2B H1 Penn Epigenetics Monthly Meeting Every month Thursday 4:00 pm Check website Website: Penn Epigenetics