Molecular markers in pediatric glial neoplasms
advertisement

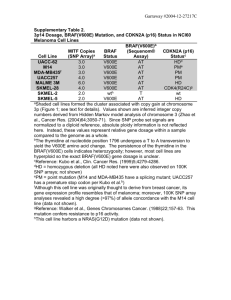
Molecular diagnostics in pediatric glial tumors Joon-Hyung Kim, MSIV Weill Cornell Medical College Key molecular alterations in pediatric glial tumors Tumor type Molecular phenotype Association Oligodendroglioma 1p/19q codeletion Adults > Peds Ganglioglioma BRAF V600E Peds > Adults PXA BRAF V600E Peds = Adults Mesenchymal histology Pilocytic astrocytoma BRAF-KIAA1549 Tumor location/resectability (Cerebellar > Non-cerebellar) DIPG 1q gain, 17p loss H3F3A, HIST1H3B mutations (K27M) Peds > Adults DIPG > Non-Brainstem pGBM pGBM H3F3A mutation Peds > Adults GBM > WHO I,II,III gliomas Peds > Adults Type of H3F3A mutation (G34R/V > K27M) ATRX, DAXX mutation ATRX mutation Anaplastic oligodendroglioma in adults (n=64) Progression Free Survival Overall Survival Snuderl et al. Clin Cancer Res 2009. 1p/19q codeletion 1p/19q codeletion with polysomy “relative deletion” No 1p/19q codeletion 1p and 19q deletions are infrequent in pediatric oligodendroglioma Series N Age 1p del 19q del 1p/19q del MGMT met IDH1 mut TP53 mut Pollack et al., 2003 8 NA 1 2 NA NA NA NA Raghavan et al. 2003 15 2-9 0 0 0 NA NA NA 11 10-18 2 0 3 NA NA NA Kreiger et al., 2005 13 5-18 1 0 0 NA NA NA Suri et al., 2011 7 3-18 0 0 0 5 0 0 Creach et al., 2012 15 1-18 NA NA 2 NA NA NA Total 69 1-18 4 (7.4%) 2 (3.7%) 5 (8.2%) 5 (71%) 0 0 Tumor type Molecular phenotype Association Oligodendroglioma 1p/19q codeletion Adults > Peds Ganglioglioma BRAF V600E Peds > Adults PXA BRAF V600E Peds = Adults Mesenchymal histology Pilocytic astrocytoma BRAF-KIAA1549 Tumor location/resectability (Cerebellar > Non-cerebellar) DIPG 1q gain, 17p loss H3F3A, HIST1H3B mutations (K27M) Peds > Adults DIPG > Non-Brainstem pGBM pGBM H3F3A mutation Peds > Adults GBM > WHO I,II,III gliomas Peds > Adults Type of H3F3A mutation (G34R/V > K27M) ATRX, DAXX mutation ATRX mutation BRAF V600E in Ganglioglioma in Children MacConaill et al. 2009 Schindler et al. 2011 BRAF V600E in Ganglioglioma and Pleomorphic Xanthoastrocytoma in Children < 18 years Pediatric Ganglioglioma % BRAF V600E MacConaill et al., 2009 57% (8/14) Dougherty et al., 2010 50% (9/18) Schindler et al., 2011 13% (3/24) Total 36% (20/56) Pediatric PXA • • Schindler et al., 2011 78% (28/36) Dias-Santagata et al, 2011 57% (4/7) Total 74% (32/43) Initially described in melanoma, colon and papillary thyroid carcinoma Vemurafenib (“V600E mutated BRAF inhibitor”) – FDA approved for late-stage or unresectable melanoma (Aug 2011) Tumor type Molecular phenotype Association Ganglioglioma BRAF V600E Peds > Adults PXA BRAF V600E Peds = Adults Mesenchymal histology Pilocytic astrocytoma BRAF-KIAA1549 Tumor location/resectability (Cerebellar > Non-cerebellar) Oligodendroglioma 1p/19q codeletion Adults > Peds DIPG 1q gain, 17p loss Peds > Adults H3F3A, HIST1H3B mutations (K27M) DIPG > Non-Brainstem pGBM H3F3A mutation Peds > Adults GBM > WHO I,II,III gliomas ATRX, DAXX mutation Peds > Adults ATRX mutation Type of H3F3A mutation (G34R/V > K27M) pGBM Unlike in adults, EGFR amplification, PTEN deletion, IDH1 mutations are rarely observed in pGBM. ` H3F3A mutations are exclusive to high grade tumors and occur in the pediatric setting. H3F3A, ATRX, and DAXX mutations distinguish pediatric from adult GBM. Schwartzentruber et al., 2012 Tumor type Molecular phenotype Association Ganglioglioma BRAF V600E Peds > Adults PXA BRAF V600E Peds = Adults Mesenchymal histology Pilocytic astrocytoma BRAF-KIAA1549 Tumor location/resectability (Cerebellar > Non-cerebellar) Oligodendroglioma 1p/19q codeletion Adults > Peds DIPG 1q gain, 17p loss Peds > Adults H3F3A, HIST1H3B mutations (K27M) DIPG > Non-Brainstem pGBM H3F3A mutation Peds > Adults GBM > WHO I,II,III gliomas ATRX, DAXX mutation Peds > Adults ATRX mutation Type of H3F3A mutation (G34R/V > K27M) pGBM H3F3A is located on chromosome 1q, a region of large-scale chromosomal gain in DIPG. Adults Peds Epigenome MGMT promoter methylation in adult GBM (associated with pseudoprogression s/p TMZ/RT and improved survival) H3.3-ATRX-DAXX chromatin remodeling pathway in pGBM Chromosome 1p/19q codeletion in adult OGD 1q gain, 17p loss in DIPG Gene Adult AA with EGFR amplification behaves like GBM EGFR amp, PTEN del are rare in pGBM/DIPG PDGFRA amp in DIPG Nucleotide Protein IDH1 mutation (R132H) in secondary GBM and LGG in adults BRAF mutation (V600E) in ganglioglioma and PXA BRAF-KIAA1549 in cerebellar PA PARP-1 overexpression in DIPG Tumor-derived Exosomes Electron microscopy of exosomes derived from U87 cells • Exosomes are small membrane vesicles (30-100 nm) derived from luminal membranes of multivesicular bodies and released constitutively by fusion with cell membrane • Released from tumor cells, exosomes mediate local and systemic cell communication through horizontal transfer of information, such as mRNA, miRNA, proteins, DNA Research questions: 1. Can exosomes in peripheral blood of glioma patients serve as biomarkers of tumor progression? 2. Can exosomes in patient plasma reliably predict parent tumor mutational status in brain? -IDH1 R132H mutation -BRAF V600E mutation DNA is present in tumor cell derived exosomes. ExoDNA exists predominantly as methylated, single stranded DNA gDNA exoDNA DNase - + - + 10kb 3kb gDNA S1 nuclease + - exoDNA-1 exoDNA-2 + + 10kb 3kb 1kb 1kb Anti-5’metCytosine Anti-DNA exoDNA gDNA Courtesy of Haiying Zhang and David Lyden Acknowledgements Neurosurgery • Jeffrey Greenfield, MD, PhD • Michael Kaplitt, MD, PhD • Philip Stieg, MD, PhD Pediatrics • David Lyden, MD, PhD Neurosurgery • Philip Gutin, MD Pathology • Jason Huse, MD, PhD Neuroradiology • Andrei Holodny, MD