HERE
advertisement
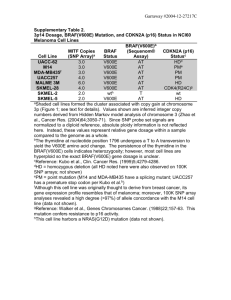
Emerging Concepts in the Diagnosis and Work-up of Thyroid Cancer APMG Pathologist, MD FCAP Thyroid Nodules • Found in 4-7% of U.S. adults – Approximately 5% are malignant. • Fine needle aspiration (FNA) mainstay of diagnosis • Bethesda system: – Six diagnostic categories – Correlate with risk of malignancy and recommended clinical management Bethesda Diagnostic Categories (2009) Papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) • Approximately 85% of thyroid cancers • Often (50-60%) harbor mutations in BRAF gene – Point mutation at codon 600 results in substitution of glutamate for valine (V600E) – Most common mutation in PTC • Mutation found more often in conventional and tall-cell variants PTC Variant % Positive for BRAF V600E Conventional PTC 60% Tall-cell PTC 77% Follicular variant PTC 12% BRAF V600E mutation leads to constitutive activation of the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway Atypia of Undetermined Significance • 10-15% of fine needle aspirations (FNAs) • 5-15% risk of malignancy • Often referred for diagnostic thyroidectomy – Low but defined risk of complications BRAF in diagnosis of PTC • BRAF V600E is VERY SPECIFIC (99.8%) for PTC. – BRAF mutation is very strong evidence of PTC • BRAF V600E is NOT SENSITIVE for PTC (49.5%) – Failure to detect a BRAF mutation does NOT rule out PTC. • Niche for BRAF testing in cases with indeterminate cytology? • BRAF testing can increase the ability of FNA biopsy to reach a diagnosis. Studies evaluating BRAF in thyroid FNAs BRAF and PTC prognosis • Numerous studies have found that PTC with mutated BRAF have more aggressive features – Extrathyroidal extension, regional metastasis, etc. – Even applies to small lesions (less than 1.0 cm) • However, excellent prognosis in general for PTC – Over 95% 10-year survival rate – Targeted therapy against BRAF unlikely to markedly improve survival BRAF testing • Predominantly occurs via PCR – Assay should have the ability to detect the mutation in the background of normal cells seen in the cytology • Can be performed on: – Residual cytology sample in preservative solution after cytological examination – Formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue blocks and slides Conclusions • BRAF testing can aid in diagnosing papillary thyroid carcinoma from cytology samples – Particularly useful with indeterminate cytology • Identifies PTC with more aggressive features. – May help identify patients needing surgery. • No current role in therapy selection – Full prognostic significance still unknown Questions? • Contact pathologist with questions or to request testing on a patient: APMG Pathologist, MD FCAP tlpath@domain.com (888) 555-1212