RESPIRATORY SUPPORT
advertisement

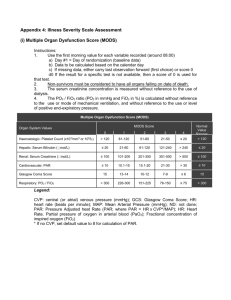
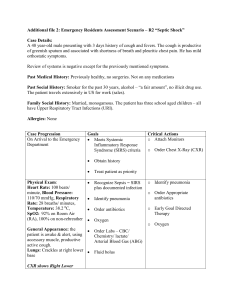
RESPIRATORY SUPPORT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Oxygen therapy Mechanical stimulator Nasal CPAP / SIMV-CPAP BI-PAP Mechanical ventilation Respiratory Assessment • Is the patient Ventilating well? >>> Normal PCO2 – Normal ventilatory effort – Increase work of breathing • Able to compensate • Is patient getting exhausted >> Impending respiratory failure • Is the patient oxygenating well? >> Normal Pa O2 – Assess oxygen requirement – A-a gradient Vs PaO2/FiO2 >> Hypoxic respiratory failure? Respiratory Assessment 1. Mental Status (Is patient being sedated) 2. RR (according to age) 3. Work of breathing (retraction, nasal flaring, paradoxic breathing) 4. Chest movement-Air-entry 5. Adventitious sounds (Stridor-wheezes, crackles) 6. Oxygen requirements 7. Cardiovascular status, (Compensatory mechanisms: HR, BP, perfusion) 8. Peak Flow 9. ABG Respiratory Mechanics • Flow • Compliance (degree of stiffness) Compliance = Volume Pressure • Resistance = = Pressure Flow • Time Constance ARF In the absence of intracardiac shunt. • Pa02 < 50 mm Hg • PC02 > 50 mmHg • Increase PaO2/Fio2 < 200 (Normal >400) • Increase A-a gradient (>300) (PaO2 60 on FiO2 of 0.6 = 100) Indication for Intubation • For Airway protection – Facial Trauma – Alter mental status – Recurrent Apnea • Respiratory Failure – Hypoventilatory – Hypoxic – Mix • Cardiovascular instability- Shock INDICATION FOR INTUBATION AND MECHANICAL VENTILATION IN STATUS ASTHMATICUS 1. Alter sensorium / Coma 2. Inability to speak 3. Increasing pulsus paradosus 4. Signs of exhautioon (decreasing pulsus paradosus 5. Respiratory or cardiac arrest 6. Diaphoresis in the recumbent position 7. Acute Barotrauma 8. Severe Lactic Acidosis (specially in infants) 9. Silent chest despite respiratory effort 10. Refractory hypoxemia (PaO2 < 60 mmHg on maximal O2) 11. Increasing PaCO2 (50 mmHg and rising > 5 mmHg/hr) General Principles Approaches to Lung Protection • Small tidal volumes/pressure limitation – Prevent Barotrauma – Prevent Volutrauma • Recruitment maneuvers, with – Higher PEEP levels – Ventilation in the prone position OXYGEN THERAPY “Low Flow Oxygen < 35 %” Nasal Cannula: No more than 3L/min Each L/min delivers ~ 4 % Oxygen > RA At low flows, no need to humidify Simple Mask Use for an emergency/ transport Deliver ~ 30% at 6-8 L/min OXYGEN THERAPY “Moderate Amount= >35% < 50%) VENTURY MAST: 28% TO 50 % AEROSOLIZED MASK 25% TO 100% Oxygen Delivery High Flow Non re-breathing mask •high flow delivered system with reservoir, • It deliver between 80 to 100% FiO2. • This delivering System is use mainly for transport and for initially emergency care and patient stabilization. OXYHOOD 25 % TO 100% NASAL cpap NON INVASIVE VENTILATION BI-PAP HOW TO ORDER MECHANICAL STIMULATOR (Pt with recurrent apnea, in between O2 Sat 100% in RA) 1) Under order entry, SELECT Mechan2) Select Peds/Neo 3) Fill up the blanks as showed below HOW TO ORDER NCPAP (Nasal Continuous Positive airway pressure) (Pt with frequent apnea, intermittent desaturations) 1) Under order entry, SELECT Mechan2) Select Peds/Neo 3) Fill up the blanks as showed below HOW TO ORDER NCPAP /SIMV (Pt with frequent apnea, irregular respirations with intermittent desaturations, in between active) 1) Under order entry, SELECT Mechan2) Select Peds/Neo 3) Fill up the blanks as showed below HOW TO ORDER SIMV in the Bear cub ventilator. (Pt with frequent apnea, irregular respirations with intermittent desaturations, Patient is intubated 1) Under order entry, SELECT Mechan2) Select Peds/Neo 3) Fill up the blanks as showed below