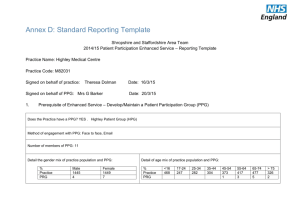
Sex Differences
chromosomal sex
gonadal sex
ENVIRONMENT
hormonal sex
morphological sex
differences in physiology and behavior
Reproduction
• Hormonal control of reproductive processes
– Female reproductive function
• Fertility
• Pregnancy, parturition, and lactation (?)
– Male reproductive function
• Development
– Sex determination and differentiation
• Chromosomal-gonadal-hormonal-morphological…
• Behavioral Endocrinology
– Aggression
– Pair Bonding
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology
Primordial
follicle
primary follicle
secondary follicle
preantral follicle
graafian follicle
ovulation
Corpus luteum formation
Secondary
follicle
Pre-antral follicle
Pause
until fertilization
Graafian Follicle
28 days
time
Follicular Phase
Luteal Phase
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology
Hormonal Control of the menstrual cycle
GnRH
LH
1.
2.
3.
4.
Androgen Synthesis (thecal cells)
Moves primary oocyte out of
meiosis I
Luteinization of follicular cells
Ovulation
FSH
1.
2.
3.
Follicular development
Conversion of androgens to
estrogens (granulosa cells)
Induce Inhibin secretion from
granulosa cells
Steroidogenesis: follicular phase
LH
thecal
cell
granulosa
cell
T
TE2
?
T
inhibin
LH
FSH
FSH
T E2
E2
HPG axis
HPG axis
Steroidogenesis: late follicular,
early luteal phase
LH
Corpus luteum formation
Luteinize:
Change function,
start producing progesterone
P4
+E2
HPG axis
Menstrual Cycle
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology
The Pill
• Carl Djurassi
– Invented the first oral contraceptive in 1951
– FDA approved in 1957
• Two types
– Combination of estrogens and progestins
– Progestins only (depo provera—shot)
• Actions:
• Benefits
• Risks
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
• Amenorrhea—lack of menstrual cycle
– Primary amenorrhea
– Secondary amenorrhea
• Pregnancy
• Menopause
– Premature menopause
• Strenuous exercise
• Anorexia Nervosa
• Premenstrual Syndrome
• Endometriosis
• Excessive Androgen Production
– Can be due to ovarian or adrenal problem
• Infertility…and treatment
Causes of infertility
Ovary stimulation
Normal ovary with graafian follicle
Hyperstimulated ovary
Hormonal Control of Follicle Stimulation
month before stimulation
stimulation month
Pregnancy
test
Lupron
The pill
Gonal-F
embryo transfer
egg retrieval
hCG: starts ovulation
Synthetic FSH stimulates follicles
Lupron shuts down your own LH and FSH secretion
(suppresses your own hormones)
Pill suppresses ovulation
Multi-cell stage…
8-cell stage embryos
bean 1
bean 2
bean 1?
bean 2?
% live births per transfer
60
% success
50
40
own eggs
30
donor eggs
20
10
0
25
30
35
40
45
50
age
Note: these women are all pre-menopausal
Types of IVF
Use your own eggs collected that
cycle
Use frozen embryos collected
from you previously
13%
8%
Use fresh eggs or embryos from
3%
donor
Use frozen embryos from donor
1%
Gestational carrier
75%
Female Reproduction: fertility
• Anatomy
– Ovarian cycle
• Hormonal Control
– HPG axis
• Contraceptives
• Pathophysiology