female hormone cycle
advertisement
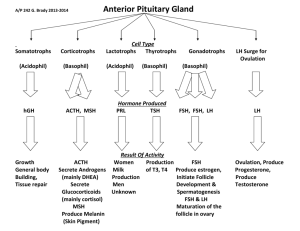
Follicle Stimulating Hormones (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)- released in the pituitary gland. Estrogen- Development of the female secondary sexual characteristics and control of the menstrual cycle. Progesterone- Regulates activity in female reproductive organs during menstrual cycle and pregnancy. The pituitary gland releases the FSH hormone. FSH is secreted into the blood stream and enters the ovaries where the follicle then produces an ovum (egg). The follicle then releases estrogen to prepare the release of the ovum and the uterine linen thickens. After about 2 weeks the production of FSH stops and LH is produced. LH is then transported through the blood stream to the ovaries to stimulate ovulation in the follicle. The remains of the follicle are then transported to the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland, where progesterone is secreted. The progesterone causes an ovum to travel to the uterus and the uterine wall. If the ovum is not fertilized the corpus luteum breaks down, the ovum degenerates and menstruation begins. Menstruation washes away the ovum and the uterine lining. If the ovum is fertilized it embeds to the uterine wall and the overall hormone levels rise. Where is FSH and LH produced? 2. What hormone does FSH cause the production of? 3. When is progesterone secreted and what is its function? 4. What happens when an ovum is not fertilized? 1.