Sex organs and Hormonal
Control
Unit 2
The Continuation of Life
Lesson Aims:
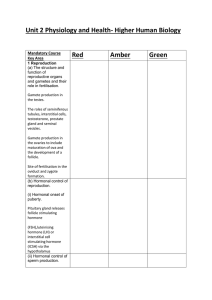
• To revise the structure and function of the
male reproductive system
• To learn about sperm production and hormonal
control
• To revise the structure and function of the
female reproductive system
• To learn about egg production and hormonal
control
Fertilisation video clip
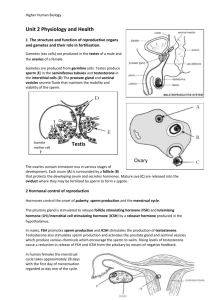
Male Reproductive System
• Made up of testicles,
duct system, accessory
glands and penis
Functions:
• produce hormones
• produce sperm
• store sperm
• deposits sperm inside
vagina during sexual
intercourse
Sperm production
• Testosterone produced in interstitial cells stimulates
sperm production
• Sperm formed by meiosis in seminiferous tubules
Accessory Glands
• Seminal Vesicles
produce
prostaglandin and
fructose
• Prostate gland
secretes enzymecontaining liquid
Hormonal Control
FSH – Follicle
Stimulating Hormone
ICSH – Interstitial cellstimulating hormone
ICSH
ICSH
Female Reproductive System
• made up of uterus,
oviducts, ovaries and
vagina
Functions:
• produces ova
• receives sperm from
penis
• houses and provides
nutrients to the
developing zygote
(fertilized egg) and later
the embryo and foetus
• gives birth to the
offspring
Ovaries
• Ovum contained in
Graafian follicle
• Follice secretes
oestrogen
• Follicle develops into
corpus luteum after
ovulation
• Corpus luteum
secretes
progesterone
Graafian Follicle
Graafian
follicle
follicular
liquid
ovum
Hormonal Control
Continual Fertility vrs Cyclical Fertility
Continual Fertility in Males
• high level of testosterone has a negative
feedback effect on the secretion of FSH
and ICSH by the pituitary gland
• relatively constant levels of
testosterone, FSH and ICSH
Cyclic Fertility in Females
fluctuating levels of FSH, LH,
oestrogen and progesterone
only fertile for a few days before and
after ovulation
“What you should know”
• p9 from “ova, the female gametes…”
• to “progesterone retains the
endometrium”