Unit 4 Vocabulary: Cells
advertisement

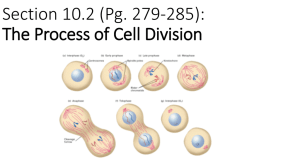
Unit 4 Vocabulary 1. Eukaryoteorganism whose cells contain a nucleus; Ex: plants, animals 2. Prokaryoteorganism whose cells do not contain a nucleus; Ex: bacteria Unit 4 Vocabulary 3. cell theory- Unit 4 Vocabulary 4. Robert Hooke- first scientist to view cells Unit 4 Vocabulary 5. organelle- specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell #6 Unit 4 Vocabulary 6. cell wall- provides structure for plant cells; barrier, helps control water content #7 Unit 4 Vocabulary 7. Cell/plasma membrane- forms boundary; semipermeable, acts as ‘gatekeeper’ by controlling what enters & exits the cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 8. nucleus- holds & protects the DNA; ‘control center’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 9. nucleolus- mix of proteins & nucleic acids; produces ribosomes Unit 4 Vocabulary 10. chromosomes/chromatin/DNA- the genetic material found in the nucleus Unit 4 Vocabulary 11. nuclear membrane- surrounds the nucleus to protect DNA Unit 4 Vocabulary 12. cytosol- fluid in cell, mostly water; where many cellular reactions take place cytoplasm- cytosol & organelles Cytoplasm/Cytosol Unit 4 Vocabulary 13. centriole- help to organize cell division; in animal cells only Unit 4 Vocabulary 14. endoplasmic reticulum (ER)- assembles lipids, proteins; ‘factory’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 15. ribosomes- synthesize proteins Unit 4 Vocabulary 16. chloroplast- conducts photosynthesis (produces sugar); ‘solar power plant’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 17. mitochondria- where cellular respiration takes place & energy is released; ‘powerhouse’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 18. lysosomes- vesicles filled with enzymes; break down and recycles molecules, old organelles; ‘recycling center’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 19. Golgi apparatus/body/complex- sac-like structures that sorts & packages materials; ‘packaging center’ of cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 20. vacuole- stores materials, especially water Unit 4 Vocabulary 21. microtubules- hollow tubes that aid in cell division and help cells maintain their shape; form cytoskeleton, the framework of the cell Unit 4 Vocabulary 22. vesicle- membrane-enclosed structures used for transport Moving substances into cell: Moving substances out of cell: Unit 4 Vocabulary 23. cell differentiation- process in which cells become specialized in structure and function Unit 4 Vocabulary 24. cancer- disorder in which some of the body’s cells lose the ability to control growth Unit 4 Vocabulary 25. nucleated- contains a nucleus Eukaryotic cells are nucleated because they contain nuclei. 26. synthesize- to make something or combine things together Ribosomes synthesize proteins. Unit 4 Vocabulary 27. unicellular- an organism composed of a single cell; ex: prokaryotes like bacteria 28. multicellular- an organism composed of many cells; ex: humans, trees Unit 4 Vocabulary 29. respiration- exchanging carbon dioxide and oxygen; breathing Your cells respire so that they have the oxygen necessary for breaking down glucose (cellular respiration) Unit 4 Vocabulary 30. plasmolysis- the shrinking of the cytoplasm of a plant cell due to water loss, causing gaps between the cell wall and cell membrane Unit 4 Vocabulary 31. osmosis- the diffusion of water across a membrane Unit 4 Vocabulary 32. diffusion- process where particles move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration 33. diffusion gradient- a difference in the concentration of particles from high to low Unit 4 Vocabulary 34. passive transport- the movement of materials across the cell membrane without using cellular energy; ex: diffusion Unit 4 Vocabulary 35. active transport- the movement of materials against a concentration difference; requires energy; ex: pumping calcium across a membrane Unit 4 Vocabulary 36. permeable- allows substances to pass through 37. impermeable- does not allow substances to pass through 38. differentially permeable/semipermeable- allows some things to pass through but not others, as with the cell membrane Unit 4 Vocabulary 39. isotonic- when solute concentrations are equal inside and outside of the cell and water moves in and out at the same rate; means ‘same strength’ Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Unit 4 Vocabulary 40. hypertonic- when the concentration of solutes is high outside of the cell, causing water to leave; means ‘above strength’ Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Unit 4 Vocabulary 41. hypotonic- when the concentration of solutes is lower outside of the cell, causing water to enter; means ‘below strength’ Animal Cell: Plant Cell: Unit 4 Vocabulary 42. secretion- the production and release of a useful substance; ex: a cell excreting a hormone Unit 4 Vocabulary The volume of a cell increases much faster than its surface area! This causes transport of molecules in and out of the cell to be too slow for the cell to survive! 43. surface area- the total area of the outside of an object 44. volume- the total amount of space inside an object 45. surface area : volume ratio- the amount of surface area per unit volume; helps explain why cells must be small Relative Surface Area: Relative Volume: Unit 4 Vocabulary 46. mitosis- type of cell division resulting in 2 identical cells 47. spindle- a fan-like system of microtubules that will help to separate duplicated chromosomes Unit 4 Vocabulary 48. chromatid- each DNA strand in a duplicated chromosome 49. centromere- where replicated DNA/chromosomes attach to each other Unit 4 Vocabulary 50. replication- the act of copying or reproducing something DNA is replicated during interphase. 51. interphase- the period of the cell cycle between cell divisions; includes cell growth and DNA replication Unit 4 Vocabulary 52. prophase- 1st phase of mitosis; DNA condenses into chromosomes and spindle fibers form 53. metaphase- 2nd phase of mitosis; chromosomes line up in center of cell, pulled by spindle fibers Unit 4 Vocabulary 54. anaphase- 3rd phase of mitosis; the chromosomes separate and move to opposite sides of the cell 55. telophase- 4th phase of mitosis; the chromosomes unwind and nuclear membranes reform Unit 4 Vocabulary 56. cytokinesis- division of the cytoplasm, splitting the cell in two Unit 4 Vocabulary 57. Why are cells so small? The volume of a cell increases much faster than its surface area. This causes passive transport of molecules in and out of the cell to be too slow for the cell to survive because the distance the molecules must travel has become very large. Unit 4 Vocabulary 58. What is the end product of mitosis? The end product of mitosis is two identical cells. Unit 4 Vocabulary 59. When would a cell undergo mitosis? A cell undergoes mitosis when its surface area to volume has become to great for the cell to rely on passive transport to survive. Mitosis begins after interphase, when the cell grows in size and replicates its DNA.