Cell Biology: How Cells Work - High School Presentation
advertisement

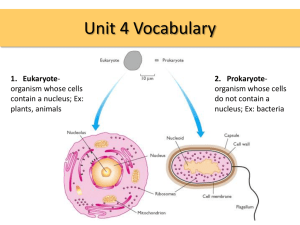
Chapter 23- How Cells Work BIG IDEA: Cells perform a wide variety of tasks in order to live and carry out their functions. 23.1 How Things Get in and out of Cells Cells need to be able to receive nutrients, and export wastes. Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of higher to lower concentration. Called “moving down a concentration gradient” Diffusion does NOT require cellular energy Ex: food coloring in water Osmosis is the diffusion of water. Facilitated diffusion- doesn’t require cell energy Most molecules cannot move across the membrane on their own. Need transport proteins Active transport requires cellular energy! Endocytosis Part of the cell membrane pinches in to form a vesicle that brings in nutrients. Exocytosis Vesicle inside the cell fuses w/ membrane, and releases it’s contents outside of the cell. 23.2 How Cells Reproduce Mitosis is a type of cell division in which 1 cell divides into 2. Resulting cells are genetically identical to the original cell. Cell Cycle: 1.Gap 1(G1)- Chromosomes condense, prepare for cell division. 2. Synthesis- chromosomes replicate 3. Gap 2(G2)- Builds machinery for cell division 4. Mitosis and Cytokinesis: cell divides completely Phases of Mitosis:(PMAT) Prophase: nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes condense Metaphase: Chromosomes line up in middle Anaphase: sister chromatids separate Telophase: New nuclear membrane forms around the product:2 cells -Cytokinesis= division of cells completely 23.3 Enzymes and the Chemical Reactions in cells Exothermic- chemical reactions that release heat Endothermic- chemical reactions that absorb heat Integrated Science: Chemistry Substrate: where reactants are brought together to react Enzyme-substrate complex: the reactants of enzymecatalyzed reactions Like a “lock and key” they must fit together completely Temperature, pH, and other factors can affect the activity of enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts (speed up reactions). -Enzymes lower the energy required to start a reaction. Integrated Science: Chemistry Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is cellular energy When the 3rd phosphate group is removed (making adenosine diphosphate [ADP]) cells get energy ATP in the Sodium-Potassium pump This pump uses active transport to pump in sodium and potassium out. -Important in how our brain cells work 23.4 Photosynthesis All life on Earth ultimately depends on photosynthesis for energy -Uses carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to produce oxygen and glucose (sugar) 23.5 How Cells get Energy When chemical bonds break to make glucose energy is released. -When it uses oxygen= cellular respiration Steps of cellular respiration: 1. Glycolysis 2. Kreb’s Cycle 3. Electron transport chain Fermentation When cells use energy without oxygen= anaerobic -Important in making wine and bread. - How our muscles allow us to continue to exercise without oxygen (Lactic acid is produced, and it is the burn you feel during a workout)