Study Guide
advertisement

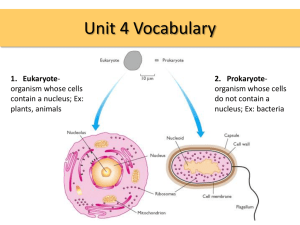
Name _________________________ 1 Semester Review st 1) Date _________________ Per.______ List the levels of classification in order. (Domain)-Kingdom-Phylum-Order-Family-Genus0-Species “King Phillip Came Over For Great Spaghetti/Grape Soda” 2) What are some characteristics of living organisms? Cellular organization, contains similar chemicals, use energy, reproduce, respond to their surroundings, and grow and develop. 3) What are the 5 levels of organization? Cells, Tissues, Organs, Organ Systems, Organism 4) How did the microscope help with the discovery of the cell theory? After the microscope was invented, it enabled scientists to view cells. 5) What is the Cell theory and who contributed to it? The cell theory is: All living things are made of cells. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. All cells are produced from other cells. 6) Explain the theory of Spontaneous Generation. An old theory proven to be untrue stating that non-living “things” turned into living organisms. 7) Fill in the table below Organelle or Structure Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi body Lysosome Ribosome Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Cell wall Cell membrane Vacuole 8) Function Direct’s cells activities, reproduction Carries products between organelles Receives and sends materials throughout cell Break down food particles and worn-out cell parts Produce proteins Produce cell’s energy Gel-like fluid that holds cell organelles Capture energy from sunlight produces food for the cell Rigid wall that protects and supports Protects the cell and regulates what enters and leaves Stores food, water, waste, and other materials What are the differences between an animal and plant cell? PLANT CELL—Has a Cell Wall and Chloroplast and can make its own food through Photosynthesis and respires. ANIMAL CELL--Doesn’t have a cell wall or chloroplast and can’t make their own food; Uses respiration for energy. 9) How does photosynthesis help living things? Photosynthesis provides oxygen for all living things and food in the form of glucose while it takes in carbon dioxide. 10) What is the cell cycle and list the 3 phases of the cell cycle. The cell cycle is the process of cell division resulting in 2 identical daughter cells Phases: Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis 11) Define mitosis and list the 4 phases of mitosis in order. Mitosis is the stage of the Cell Cycle when the cell’s nucleus divides into two new nuclei. One copy of the DNA is distributed into each of the two daughter cells. Mitosis stages are Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. 12) What are active and passive transport and how do they maintain homeostasis and give 2 examples of each? Passive Transport is the movement of materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy. Active transport is the movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy. These processes maintain homeostasis by trying to maintain equilibrium so that the inside and outside of the cell have the same concentration of materials. Examples: 13) Passive= Diffusion and Osmosis Active= Engulfing and Protein Transport Define Osmosis and Diffusion and explain where and when they occur? OSMOSIS—The diffusion of water across a membrane. DIFFUSION—The movement of material from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until equilibrium has been reached. They occur across the cell membrane when the substance is unbalanced. 14) What is photosynthesis and write the equation? PHOTOSYNTHESIS--The process plants use to make food using the sun’s energy. 6 Co2 + 6 H2O light energy carbon dioxide water 15) C6 H12 O6 + 6 O2 a sugar oxygen What happens during respiration (equation)? RESPIRATION—The use of Oxygen to release energy from food. Oxygen + Glucose (O2 + SUGAR 16) Energy + Carbon Dioxide + Water E + CO2 + H2O) 22.5 What are chromosomes and what is their function? A double rod of condensed DNA; contains that genes that carry genetic information. 17) What is meiosis? The process of making sex cells that have ½ the number of chromosomes as the body cells. 18) How many chromosomes does each human cell begin and end with for: A. MITOSIS---Begin with 46 and end with 46 because they are exact copies. B.MEIOSIS---Begin with 46 and end with 23 because the # is split in ½. 19) Define: Phenotype - The physical characteristics of an organism. **What the organism looks like. Genotype - The genetic make-up of an organism. **The genes/alleles for a trait. Probability - The likelihood that a particular event will occur. Mutation – Any permanent change to DNA. Allele - A form of a trait or gene. Dominant allele - An allele that masks or covers-up recessive alleles. **It always shows itself. ***Capital Letter. Recessive allele - An allele that only expresses itself when with another recessive allele. **Will be coveredup by a dominant. ***Lowercase Letter. 27) What is a Punnett square? A tool used to predict the probability of possible allele combinations from a genetic cross. 28) Make a Punnett square for 2 guinea pigs that have the genotype Bb (black) & bb (white). How many offspring will be black and how many offspring will be white. b b B b Bb bb Bb bb BLACK= 2/4 or 50% WHITE= 2/4 or 50% 29) Who is the father of genetics and why? Gregor Mendel is the “Father of Genetics” because of his work on Pea Plants to determine the rules of inheritance and how they apply to heredity. 30) Describe the structure of DNA. DNA is a double helix. 31) Match the following terms with their genotypic description? a. BB 1. _a_Homozygous Dominant or Purebred Dominant b. Bb 2. _c__Homozygous Recessive or Purebred Recessive c. bb 3. _b__Heterozygous or Hybrid 32) Cytosine pairs with _Guanine__ and Thymine pairs with _Adenine__. In RNA Adenine pairs with Uracil. 33) What is the relationship between chromosomes, DNA, and genes? A gene is a section of DNA and DNA is coiled up to form chromosomes, which are housed in the nucleus of the cell. 35. Farmers who grow corn plants want the plants that produce the most ears of corn and are most resistant to insects and disease. What process would a farmer use to produce corn plants with these desired traits? Hybridization 36. Thad is a potato farmer who is trying to produce potatoes with only large traits. Which selective breeding would be BEST for him to use to produce only large potatoes? Inbreeding 37. Which body systems work together to enable you to move? A certain kind of cell produces a substance that breaks down proteins so they can be absorbed by the body. What body system is the cell MOST LIKELY a part of? Digestive system 38. What body system is in charge of transportation of substances around the body to get to the body cells? Circulatory System 39. The scientific name for bread mold is Rhizopus stonifer. Which classification group is Rhizopus? Genus What classification group is Rhizopus stonifer? Species E) E. R. C) Nucleus G) Ribosomes F) Golgy Bodies LO 27-28 Word Bank: a. Cytoplasm b. Mitochondria c. Nucleus d. Lysosome e. Endoplasmic Reticulum f. Golgi Bodies g. Ribosomes h. Cell membrane Match Definitions: 40._f__Packages and sends protein. 41._g__Produces protein. 42._h__Controls what moves in/out of cell 43._c__Controls the functions/reproduction of the cell 44._b__Releases energy for the cell 45._d__Digests/recycles material for cell 46._a__Gel-like fluid that the organelles float in 47._e__Moves materials around the cell