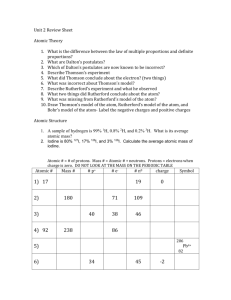
Physics and the Quantum Mechanical Model
Physics and the Quantum
Mechanical Model
Light and Atomic Spectra
What is Light??
• What do you think light is? Can you describe it??
• Isaac Newton (1642-1727) thought of light as consisting of particles.
• By the year 1900, however, most scientists accepted the idea that light was a wave phenomenon.
Light as a WAVE
• According to the wave model, light consists of electromagnetic waves.
• Electromagnetic Radiation – includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, x-rays, and gamma rays.
• All light travels at 3.0x10
8 m/s (or _____________)
The Wave Cycle
• Each complete wave cycle has several important parts
• The amplitude is the wave’s height from the origin to the crest
• The wavelength (denoted “λ”) is the distance between crests.
• The frequency (denoted “ν”) is the number of wave cycles to pass a given point in a specified amount of time
Wave Cycle
Wavelength and Frequency
• The frequency and wavelength are inversely related… meaning as one ____________ the other ____________.
• As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases.
• The product (multiplication) of these two values ALWAYS equals a constant (c) which is known as the ______________________.
Mathematical Relationship
c = λν
c = the speed of light (a constant), 3.0x10
8 m/s
(or 3.0x10
10 cm/s )
λ = wavelength
ν = frequency, units are cycles per second, or
Hertz (Hz)
Inverse Relationship
The Visible Spectrum
• When light passes through a prism, different wavelengths separate out into their own different colors.
• This phenomenal spectrum of colors can be seen in a rainbow.
• These colors you can see are known as the
VISIBLE SPECTRUM. (ROYGBIV)
The Visible Spectrum
Question??
Which part of the visible spectrum has the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency??
Violet
Atomic Emission Spectrum
• Each element emits light when excited with electricity while in its gas/vapor phase.
• The atoms become “excited” when the absorb the electrical energy, and the “relax” when that energy is then released again. This release emits a “spark” of light, unique to that particular element, known as the Atomic Emission Spectrum.
Atomic Emission Spectrum
Practice
• Calculate the wavelength of the yellow light emitted by a sodium lamp if the frequency of the radiation is 5.10x10
14 Hz (5.10x10
14 s -1 )
Practice
**use Figure 13.10, page 373**
• What is the wavelength of radiation with a frequency of 1.50x10
13 s -1 ? Does this radiation have a longer or shorter wavelength than red light??
Practice
**use Figure 13.10, page 373**
• What frequency is radiation with a wavelength of 5.00 x10 -6 cm? In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this radiation??
*careful with your units!!*
Homework:
• Read Chapter 13, section 3
(page 372-382)
• Complete (on a separate sheet to turn in) Page 386,
#32-38