CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
CFP 2
True/False Questions
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Video
Play Video
•
Open-ended &
True/False Questions
•
•
7 minutes
Play video from
Video Layout
2
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 1
Security Markets &
The Economic Environment
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 1 True/False
1. Examples of financial intermediaries are banks,
mutual funds, and insurance companies.
Play Jeopardy
music
Your answer
4
Module 1 True/False
2. The SEC requires private placements to make a
3.
4.
5.
6.
full disclosure.
Investment bankers do not issue securities, but
they do serve as advisers to firms that want to
raise capital.
Margin is a way to leverage return with very little
risk.
Brokerage commissions are determined by the
SEC.
Repurchase agreements are subject to market
risk because of their long-term maturities.
5
Module 1 True/False
7. To become a registered representative with FINRA,
8.
9.
a planner must pass one or more FINRA exams; to
become a registered investment adviser within a
state, an exam is also required.
Blue-sky laws make it possible for the SEC to
enforce securities laws and prevent market
manipulation, deception, misrepresentation of facts,
and fraudulent practices.
The Securities Act of 1933 requires that new
securities be registered with the SEC and that
adequate and accurate disclosure be provided to
buyers by the prospectus.
6
Module 1 True/False
10. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform Act created
an independent Consumer Financial Protection
Bureau, which oversees institutions that offer
financial products and services, both banks and
non-banks.
11. A registered investment adviser cannot charge
both fees and receive commissions.
12. Gains from the sales of capital assets can be
offset by capital losses, dollar for dollar.
13. A wash sale involves selling securities on which
capital losses can be realized and then buying
them back 30 days later.
7
Module 1 True/False
14. During periods of economic prosperity, security
prices tend to decline.
15. Three economic goals of the Federal Reserve
and the U.S. Treasury are full employment,
stable prices, and growth in the supply of money.
16. When the Fed purchases Treasury securities
(using the monetary policy tool of open market
operations), economic growth is stimulated and
stock prices rise.
17. When the federal government utilizes the fiscal
policy tool of increasing taxes, stock prices drop
because corporate earnings are reduced.
8
Module 1 True/False
18. For investment purposes, an important
component of industry analysis is business cycle
analysis, because the stocks of most industries
closely follow this cycle.
19. The supply of a product is influenced by the
product’s price, its production cost, and the level
of technology required to produce it.
20. When consumer confidence declines, consumer
spending typically declines.
9
Module 1 True/False
21. During the contraction phase of the economic
22.
23.
24.
25.
26.
cycle, the rate of inflation tends to be low.
During the recovery phase of the economic cycle,
real assets tend to underperform the market.
During the expansion phase of the economic
cycle, unemployment declines.
During the contraction phase of the economic
cycle, productivity increases.
Gross domestic product measures productivity.
The consumer price index is a measure of
inflation.
10
Module 1 True/False
27. Leading economic indicators forecast the direction
of the economy.
28. Form ADV Part 2 is written in narrative form, and
any changes made from the previous filing must
be summarized up front.
29. The overall maximum FDIC coverage an individual
has with any one covered bank is $250,000.
11
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 2
Investment Risk & Return
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 2 True/False
1. Total risk is comprised of systematic risk plus
2.
3.
unsystematic risk.
An investment portfolio of mutual funds from highly
correlated asset classes will have less risk than a
portfolio of mutual funds from asset classes that
are not highly correlated.
Client Oscar Moore should achieve his investment
goal of less volatility than there is in the general
market if, in his current portfolio of equally
weighted mutual funds, he increases the proportion
of funds with a beta of 0.7 and decreases the
proportion of funds with a beta of 1.3.
13
Module 2 True/False
4. Client Britt Smith, who owns a stock portfolio with
5.
a weighted beta of 1.4 and a mutual fund bond
portfolio with a weighted beta of 0.9, should
achieve her goal of lower risk if she shifts some of
the money in the mutual fund portfolio into the
stock portfolio.
Client Ron Price, who enjoys taking risks, should
achieve his goal of a higher return than the
general market if he increases his holdings of
Adam stock, which has a beta of 1.5, and
decreases his holdings of FSM stock, which has a
beta of 1.0.
14
Module 2 True/False
6. Systematic risk is a risk that affects whole classes
of securities.
7. Interest rate risk is the chance that investment
returns will be affected by changes in the level of
interest rates.
8. The U.S. government is said to be free of financial
risk because there is no uncertainty associated
with its income flows.
9. Some common stocks have more liquidity risk
than others because of a “thin” market.
10. If a stock’s return has a large standard deviation,
it suggests that the stock has little risk.
15
Module 2 True/False
11. If the returns on two stocks are highly and
12.
13.
14.
15.
positively correlated (i.e., the correlation
coefficient is +1.0), combining these stocks will
reduce the risk associated with the portfolio.
If a stock has a beta of 1.0, it is a risk-free stock.
Stocks with low betas generate better returns in
declining markets.
If a stock’s beta coefficient is 1.7, it implies that
the stock’s return tends to be less volatile than the
market’s return.
Systematic risk can be reduced through
diversification.
16
Module 2 True/False
16. A portfolio consisting of securities whose returns
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
are highly correlated is not truly diversified.
The coefficient of determination is the square root
of the correlation coefficient.
Purchasing power, market risk, and exchange rate
risk are all examples of systematic risk.
Business risk reflects the amount of debt
(leverage) that a company uses.
A weighted average standard deviation can only
be used when the correlation coefficient is 0.
A low beta always means that a stock is less risky
than the general market.
17
Module 2 True/False
22. The Jaguar Mutual Fund has a covariance of 45
with the S&P 500, and the Leopard Fund has a
covariance of 78 with the S&P 500. The Leopard
Fund should be chosen for diversification since it
has the higher covariance.
23. Oftentimes, the yield on Treasury bills is used for
the risk-free rate.
24. The market risk premium is the difference
between the return of the market and the risk-free
rate.
25. The Capital Asset Pricing Model allows an
investor to calculate required return, and it adjusts
the required return for risk by using beta.
18
Module 2 True/False
26. Correlations remain relatively stable over time,
and stay the same in both rising and falling
markets.
27. The lower the R-squared, the better when trying
to diversify; however, the higher the R-squared
the better when using beta.
28. An advisor can rely on long-term returns and risk
measurements when putting together a portfolio
for a client who is about to retire, since the
retirement period may last decades.
19
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 3
Modern Portfolio Theory
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 3 True/False
1. Portfolios that offer the highest return for a given
2.
3.
4.
5.
level of risk are “efficient.”
The efficient frontier contains all the combinations
of risk and return that represent the same level of
satisfaction.
Arbitrage is the act of buying a high-priced asset
in one market and simultaneously selling it in
another market at a lower price.
Arbitrage pricing theory is a multi-variable model
that is used to explain security returns.
An efficient capital market assumes that a security
cannot be overvalued or undervalued.
21
Module 3 True/False
6. The efficient market hypothesis assumes that an
7.
8.
9.
investor can outperform the market if the investor is
efficient in gathering information about a company.
The efficient market hypothesis suggests that, over a
period of time, an investor should earn a return that
is consistent with the amount of risk the investor
bears.
The weak form of the efficient market hypothesis
suggests that current security prices reflect all
historical security market information.
The strong form of the efficient market hypothesis
suggests that stock prices reflect all public and
private information.
22
Module 3 True/False
10. Empirical evidence tends to support the weak and
semi-strong forms of the efficient market
hypothesis.
11. The efficient market hypothesis implies that
technical analysis should work.
12. An investor’s optimal portfolio would be where an
investor’s indifference curve is tangent with the
efficient frontier.
13. The major difference between the Capital Market
Line (CML) and the Security Market Line (SML) is
that the CML uses beta as its measure of risk,
and the SML use standard deviation.
23
Module 3 True/False
14. The slope of the Security Market Line is
determined by the Capital Asset Pricing Model
(CAPM).
15. An underlying principal when calculating riskadjusted return is that an investor should be
rewarded with additional return when taking on
additional risk.
16. The four primary factors in Arbitrage Pricing
Theory are unexpected changes in inflation, GDP,
market risk premiums, and taxes.
17. Overlap occurs when an investor owns certain
securities in more than one mutual fund.
24
Module 3 True/False
18. Life cycle analysis has four major phases, and in
order they are the accumulation phase, consolidation
phase, spending phase, and gifting phase.
19. Monte Carlo is a type of value at risk (VAR)
methodology.
20. Tactical asset allocation is a strategy by which the
investor moves money into the areas of the market
with the best predicted opportunities, and it often
involves various forms of market timing.
21. A believer in the dividend yield anomaly would buy
stocks with high dividend rates, and a believer in the
neglected firm effect would avoid firms followed by
few analysts.
25
Module 3 True/False
22. The size effect anomaly explains how small stocks
23.
24.
25.
26.
tend to outperform large stocks over time, with
approximately the same level of risk.
In a truly efficient market, a security could not be
undervalued or overvalued.
Overconfidence and rationalization are two examples
of investor behavior that can lead to
underperformance.
Behavioral finance and the efficient market hypothesis
work well together, in that both believe investors are
rational.
The “random walk’ hypothesis states that security
prices are randomly determined, so analysis is futile.
26
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 4
Common Stock Valuation &
Performance Measurement
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 4 True/False
1. The longer an individual is invested in the stock
2.
3.
4.
market, the more the individual’s investments are
subject to drastic swings in the market.
An ex-dividend date is when a company
announces a certain date in the future on which it
will pay a specific dividend.
With a stock split, the book value per share
changes, but the book value of the firm remains
the same.
The risk/return trade-off in investments results
from the fact that, generally, as an investor’s
required rate of return increases, the amount of
risk that must be taken also increases.
28
Module 4 True/False
5. An advantage to a firm that offers a dividend
6.
7.
8.
9.
reinvestment plan is lower commissions.
An advantage to the investor in a dividend
reinvestment plan is the automatic savings.
If a general price index rises more rapidly than an
index of security prices, one could conclude that
stockholders gain purchasing power.
Small company stock is more risky than long-term
government bonds.
Long-term government bonds are less risky than
intermediate-term government bonds.
29
Module 4 True/False
10. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is
11.
12.
13.
14.
computed by adding the prices of one share of
each of the 30 stocks included in the index and
dividing the result by 30.
Two characteristics of the S&P 500 stock index
are that it is a price-weighted index and that it
tracks specific sectors of the stock market.
A higher dividend payout ratio implies a lower
growth rate.
If an investor buys a stock on the ex-dividend
date, that individual will receive the dividend.
Dividend reinvestment plans offer the advantage
of deferring federal income taxes.
30
Module 4 True/False
15. If a firm retains earnings, total equity increases.
16. The PSR is an asset utilization ratio.
17. The S&P 500 stock index is more sensitive to
changes in the prices of small stocks than to the
stock prices of large companies.
18. The required return includes the risk-free rate and
a risk premium.
19. The Treynor index assumes that portfolios are not
well-diversified.
20. The intrinsic value of a preferred stock paying a
$1.80 dividend with current interest rates at 6%,
would be $30.00.
31
Module 4 True/False
21. When constructing an Investment Policy
Statement, the return objective and risk tolerance
of the client are mutually exclusive of each other.
22. The Sharpe ratio is a comparative measure,
taking the excess return above the risk-free rate,
and then dividing by standard deviation. The
Sharpe ratio of one investment would be
compared with another, with the higher ratio being
chosen.
23. Alpha is an absolute measure, and is simply the
difference between the return of the portfolio and
the required return as calculated by CAPM.
32
Module 4 True/False
24. The purpose of an Investment Policy Statement
includes defining the asset allocation policy and
determining communication procedures.
25. The PEG ratio is the price to earnings ratio
divided by the dividend growth rate.
33
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 5
Security Analysis
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 5 True/False
1. A geometric average is calculated by adding the
2.
3.
4.
5.
share prices and then dividing by the total number
of prices.
A weighted-average return is calculated by
weighting each investment return by its weight in
the portfolio and adding together all weighted
returns.
The S&P 500 is a price-weighted average; the
DJIA is a value-weighted average.
The Value Line index includes a larger number of
stocks than does the S&P 500 index.
A major weakness of a holding period return is
that it fails to consider the timing of cash flows.
35
Module 5 True/False
6. When the annual rate of inflation is 8% and the
annual nominal return is 10%, the inflationadjusted return is 2%.
7. Most stock indexes, including the S&P 500 stock
index, are value weighted.
8. Modern portfolio theory reinforced the use of the
price-weighted method.
9. The geometric average return generally is higher
than the arithmetic average return.
10. The dollar-weighted return is the preferred return
to use when comparing the performances of two
or more portfolio managers.
36
Module 5 True/False
11. Bottom-up analysis focuses on company analysis.
12. An increase in assets financed by equity
13.
14.
15.
16.
increases the debt ratio.
Technical analysts use financial statements as the
basis for making investment decisions.
In general, rising interest rates result in rising
stock and bond prices.
High leverage in a profitable company results in a
lower return on equity (ROE).
Given the following annual returns: +12%, +18%,
- 7%, the geometric return is +7.12%.
37
Module 5 True/False
17. Beatrice purchases 100 shares of Lookout
Industries at $60 per share using 50% margin.
She sells the stock 7 months later for $72 per
share. Ignoring interest charges, her holding
period return was 20%.
18. Samuel purchases a painting for $5,000. At the
end of the first year, he spends $1,200 on
restoration; and at the end of the third year, he
sells the painting for $8,000. His IRR was 9.48%.
19. The difference between the total present value of
cash flows and the amount of the initial cash
outlay (the cost of the investment) is called the net
present value.
38
Module 5 True/False
20. If the net present value of a potential investment
is negative or zero, it should be avoided; if it is
positive, it should be purchased.
21. If all else remains equal, the impact of a company
using debt instead of equity to raise capital will
result in a higher return on equity.
22. Contrary opinion rules state that if too many
investor advisors are bearish, the contrarian
should be bullish.
23. Contrary investors looking at the put/call ratio will
be bullish if the ratio of call options increases
relative to put options.
39
Module 5 True/False
24. The general stages of the life cycle of a company
are development, growth, expansion, maturity,
and decline.
25. The D Group has assets of $350 million, and
liabilities of $150 million. Current earnings are $25
million, so its return on equity is 12.5%.
26. The retention rate is the percentage of earnings
paid out in dividends.
40
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 6
Features of Fixed-Income
Securities
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 6 True/False
1. Bonds are referred to as fixed-income securities
2.
3.
because the amount to be received at maturity is
a fixed amount.
Reinvestment risk is the risk that there will not be
an opportunity to reinvest the coupon interest
payments and the face value of a bond
investment at an acceptable rate when these
amounts are received.
Default risk is the risk that the issuer will fail to
pay either the coupon interest payments or the
face value of a bond when it is due.
42
Module 6 True/False
4. In general, the smaller the yield differences are
5.
6.
7.
between Treasury bonds and corporate bonds, the
more attractive corporate bonds are because they do
not have a risk of default.
Standard & Poor’s bond ratings BB through C
indicate to a potential investor that bonds with these
ratings are investment-grade bonds.
As a bond that is selling at a premium moves closer
to maturity, it decreases in price and moves toward
face value.
Before common dividends are paid in any given year,
owners of cumulative preferred stock are paid any
back dividends that might have been missed in
previous years.
43
Module 6 True/False
8. Treasury notes and bonds pay coupon interest
semiannually and are available through Federal
Reserve banks or brokerage firms.
9. Interest income from Treasury securities is
taxable as ordinary income at all levels—federal,
state, and local.
10. The Treasury Direct System allows individual
investors to purchase original-issue Treasury
securities without going through a broker or
financial institution (and thus paying a
commission).
44
Module 6 True/False
11. General obligation bonds are issued by states,
counties, cities, special districts, towns, and
school districts, and they are backed by the
issuer’s general taxing powers.
12. Full faith and credit general obligation municipal
bonds are backed by pledged revenues from fees
and charges that are accumulated outside the
general fund of a municipality.
13. Municipal revenue bonds are issued to finance
specific projects and are secured by revenues to
be generated by the projects.
45
Module 6 True/False
14. Government National Mortgage Association
securities (GNMAs) are called pass-through
securities because funds invested in these
securities go directly to homeowners for their
mortgages.
15. Investors in GNMAs receive monthly payments
containing only the interest paid on the mortgages
held.
16. GNMAs are called self-liquidating investments
because funds paid by homeowners are pooled to
repay investors the principal amount at the end of
the investment period.
46
Module 6 True/False
17. The governing document of a bond issue is the
bond indenture, which is the contract between the
trustee and the bondholders.
18. A difference between a term bond and a serial
bond is the number of maturity dates under the
original issue.
19. Interest earned on U.S. Treasury securities is
exempt from federal taxes.
20. Convertible bonds have an embedded conversion
option that allows the bonds to be converted into
the issuer’s common stock.
47
Module 6 True/False
21. A nonrated bond means the bond has received a
22.
23.
24.
25.
poor credit rating from the rating agencies.
Preferred stock is a hybrid security that has
characteristics of both debt and equity.
The shorter the time period to the maturity of a
bond, the greater the potential for price
fluctuation.
A yield curve is a line plotted on a graph that
shows, as of a given date and for a range of
maturities, the yields on fixed-income securities of
the same quality.
The yields on a yield curve are the coupon rates
of the fixed-income securities being plotted.
48
Module 6 True/False
26. Two or more yield curves on a single graph show
what has happened to interest rates over a period
of time.
27. Yield curves can be used to predict whether
trends will continue and when they will reverse.
28. A normal yield curve is one in which the yields on
short-term securities are relatively low compared
to the yields on long-term securities.
29. A yield curve is inverted when the yields on shortterm securities are higher than the yields on longterm securities.
49
Module 6 True/False
30. When a yield curve is inverted, a financial planner
should consider recommending short-term
securities in order to lock in high rates.
31. A Yankee bond is a bond that is issued in the U.S.
by a foreign company and denominated in U.S.
dollars.
32. The principal amount on Treasury inflationprotection securities (TIPS) issued by the U.S.
government is adjusted semi-annually for inflation,
based on the CPI-U (All Urban Consumers) index.
50
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 7
Valuation & Analysis of
Fixed-Income Investments
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 7 True/False
1. An investor in a 28% marginal tax bracket who
2.
3.
4.
invests in tax-free municipal bonds yielding 10%
would require a taxable equivalent yield of at least
13.89% on an investment in corporate bonds in
order for the corporate bond to be more attractive.
The current price of a bond is the future value of
the bond’s cash flow stream.
Duration is used to calculate the expected change
in the price of a bond when interest rates change.
Duration is directly related to changes in the
market and in coupon interest rates, and it is
inversely related to changes in maturity.
52
Module 7 True/False
5. A bond’s systematic risk is reflected in the bond’s
6.
7.
8.
9.
credit rating.
The face value of a bond divided by its conversion
price is known as the conversion value.
An investment premium is the difference between
the market value of a convertible bond and its
conversion value.
The yield to maturity of a 7% coupon bond with 12
years until maturity and a current price of 980 is
7.14%.
If the current yield of a 7% coupon bond is 8%,
then the bond must be selling at a premium.
53
Module 7 True/False
10. Bond X has a 9.5% coupon, 15 year maturity, and
11.
12.
13.
14.
is callable in 10 years at a 5% premium. If the
bond is currently trading at 990, the yield-to-call
would be 9.96%.
If a bond is selling at a discount, yield-to-maturity
will be greater than the yield-to-call.
If a bond is selling at a premium, the current yield
will be greater than the yield-to-maturity.
An investor in the 33% marginal tax bracket
should purchase an 8.5% corporate bond over a
5.75% municipal bond.
The yield-to-maturity on a bond with a current
price of $1,035, a 5% coupon, 20-year maturity,
and AAA rating, is 4.80%.
54
Module 7 True/False
15. When evaluating a premium bond, yield-tomaturity is the yield an investor should focus on,
and yield-to-call is not relevant.
16. If an investment advisor anticipates that interest
rates will be increasing for the foreseeable future,
he or she would want to increase (lengthen)
durations.
17. If an investor believes interest rates are going to
fall, he or she would choose a 5% coupon bond
with a 15-year maturity over a 8% coupon bond
with a 15-year maturity.
18. As the coupon rate increases, duration will also
increase.
55
Module 7 True/False
19. If interest rates are currently 9%, and your client is
holding a zero coupon bond that matures in 17
years, the intrinsic value (present value) of the
bond would be $224.
20. The duration of a zero coupon bond matches its
maturity.
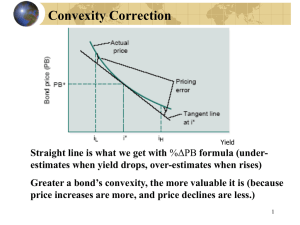
21. Straight bonds (bonds without any embedded
options or call features) have a positive convexity,
meaning that if interest rates go down, the bond
will go up in price more than duration alone
indicates.
56
Module 7 True/False
22. Credit ratings have a minimal impact on a
23.
24.
25.
26.
company’s or municipality’s cost of issuing debt.
In a bullet portfolio, maturities are concentrated in
the short- and long-term.
A substitution bond swap takes advantage of
when bonds are temporarily mispriced.
If a convertible bond is currently trading at $1,100,
has a conversion value of $1,020, and an
investment value of $950, its downside risk is $80.
If a convertible bond has a conversion price of
$45 per share, and the common stock is currently
trading at $38 per share, the conversion value is
$844.
57
Module 7 True/False
27. If a convertible bond is convertible into 35 shares,
and the stock is currently trading at $45 per share,
the conversion value is $1,285.
28. If interest rates are currently at 7% for comparable
debt, the investment value of a convertible bond
with a 6% coupon and
10-year maturity is $929.
29. If an investor’s time horizon is 15 years, then they
should choose a 25-year bond with a duration of
14 over a 15-year bond with a duration of 9.
30. Immunization means matching an investor’s time
horizon with the maturity of a bond.
58
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 8
Derivatives
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 8 True/False
1. A put is an option that grants a buyer the right to
2.
3.
4.
purchase stock from an option writer at a
specified price and within a specified time period.
Those who purchase calls are seeking profits that
result from rising stock prices.
The exercise price is that price at which the owner
of an option has the right to buy or sell the
underlying stock.
In options quotations, the numbers listed under
columns headed by names of months indicate the
last trading price of puts and calls that were
written on the listed stock.
60
Module 8 True/False
5. Warrants, just like call options, usually expire
6.
7.
8.
within one year.
The maintenance margin in futures contracts is
the amount the investor must maintain with the
broker; and if an investor’s equity falls below this
amount, then funds must be deposited to bring
the equity back up to at least the maintenance
amount.
Delivery is the typical method of settling a futures
contract.
Speculators in futures markets buy or sell
contracts to reduce the risk of adverse price
fluctuations.
61
Module 8 True/False
9. Investors who are concerned about unfavorable
short-term market prospects, but who remain
bullish for the long run, can protect themselves by
selling stock index futures.
10. Futures contracts are an obligation to buy or sell;
they are different from options, which give
individuals a right (but not an obligation) to buy or
sell.
11. To guard against a price decrease, someone who
is long in a commodity would use a long hedge
position as well.
12. Buyers, not sellers, need to meet margin
requirements.
62
Module 8 True/False
13. Options can be used as portfolio insurance to limit
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
a portfolio’s exposure to a market decline.
If you expect the S&P index to fall, you would sell
stock index futures.
All futures positions are taxed at year-end as
closed positions.
Income-oriented investors can earn additional
income by writing options that are purchased by
speculators.
A profitable call is “in the money.”
Any premium above and beyond the intrinsic
value is time value.
63
Module 8 True/False
19. Futures investors must pay a premium for each
futures contract they purchase.
20. The essence of the commodity futures markets is
its use for speculation.
21. If a client is concerned about the market declining
in the short run, but does not want to sell their
positions, a possible solution is to buy protective
puts.
22. Hedging is simply taking the opposite position of
what you have (or don’t have). If you are long a
commodity, to hedge you would short the futures;
and if you are short a commodity, you would buy
(go long) the futures.
64
Module 8 True/False
23. A jeweler needing gold in the future would be
short gold. To hedge against falling prices, he or
she could buy (go long) gold futures.
24. A gold mine would be long gold. To hedge against
falling prices, the mine could enter into a short
hedge.
25. A collar is a strategy one can use when long on a
stock. It involves selling covered calls with a strike
price above the current price of the stock, and
then taking the premium received from selling the
calls to purchase puts with a strike price below the
current price of the stock.
65
Module 8 True/False
26. As an option approaches its expiration date, the
27.
28.
29.
30.
time premium of the option will decline.
If a stock is trading at $48, and an investor holds
a $50 call option, the option is “in-the-money.”
If a stock is trading at $37, and an investor holds
a $40 put option, the option is “in-the-money.”
Futures, unlike credit default swaps, are not a
type of derivative.
Futures contracts are available on commodities,
financials, greenhouse gases, and temperature
changes.
66
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 9
Real Assets &
Foreign Investments
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 9 True/False
1. The four major types of real estate are industrial,
2.
3.
4.
commercial, residential, and land.
A disadvantage of direct investing in real estate is
the inherent management responsibility.
A due-on-sale clause in a mortgage bond means
that when the property is sold, the lender has a
right to call in the remainder of the mortgage and
renegotiate contract terms with the new buyer.
Foreclosure is described best as occurring when
the payments set forth in the mortgage agreement
are not made or when any of the covenants are
not upheld by the mortgagor.
68
Module 9 True/False
5. The various forms of real estate ownership
6.
7.
8.
include outright ownership, joint ventures, and
limited partnerships.
Real estate limited partnerships (RELPs) provide
limited liability, but marketability may be an issue.
Qualities to look for in a dealer of bullion or bullion
coins include financing fees, sales commissions,
and other fees.
In terms of investment potential, the main
difference between gold and assets such as real
estate, art, and antiques is that, as a precious
metal, gold is very marketable.
69
Module 9 True/False
9. Collectibles are bought and sold in organized
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
markets such as the New York Stock Exchange.
Anticipation of inflation is an important reason for
investing in collectibles.
Gold’s general acceptability potentially makes it a
good store of value.
Most REITs retain their earnings in order to
expand.
In a period of falling interest rates, a mortgage
REIT is a good investment.
While rental properties may operate at a loss,
they may produce a positive cash flow.
70
Module 9 True/False
15. Dividends distributed to REIT shareholders are
eligible for the preferential long-term capital gains
rate.
16. REMICs (Real estate mortgage investment
conduits) are similar in many ways to a mortgage
REIT, except that principal and interest payments
are structured into separately traded securities
classes.
17. An investor should purchase property being
offered for $3,800,000 if the net operating income
of the property is $310,000, and the capitalization
rate for similar properties is 8%.
71
Module 9 True/False
18. An investor should purchase property being
offered for $1,200,000 if the predicted gross rental
income is $125,000 and the GIM is 8.6.
19. The net operating income of a property with
$110,000 of rental income, 5% vacancy
allowance, $35,000 of operating expenses, and
$12,000 of mortgage payments is $57,500.
20. The two general classes of international funds are
developed country funds and emerging market
funds.
21. Emerging markets are not a good diversifier, since
they have a high correlation to U.S. markets.
72
Module 9 True/False
22. Investors can avoid currency risk by investing in
23.
24.
25.
26.
ADRs.
All else being equal, in order to make a profit, the
home currency needs to go up in value, and the
foreign currency needs to go down in value.
If the current exchange rate is $1.54 U.S. for each
euro, then this would mean that one euro
purchases 0.65 U.S. dollars.
ETFs are offered for many different individual
countries.
The vast majority of REITs are equity REITs.
73
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
Module 10
Mutual Funds &
Other Investments
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.
Module 10 True/False
1. A unit investment trust holds a fixed pool of
2.
3.
securities; because the pool is almost always kept
unchanged, the need for active management is
eliminated.
Investment companies must maintain a minimum
level of diversification, which requires them to
have at least 85% of a fund’s total assets invested
and to have not more than 10% of a fund’s total
assets invested in one company.
One difference between open-end and closed-end
investment companies is that shares of open-end
companies sell for net asset value (NAV), while
shares of closed-end companies sell at a discount
or a premium.
75
Module 10 True/False
4. Investment companies provide professional
5.
6.
7.
management, contain diversified portfolios having
specific investment objectives, and offer investors an
opportunity to participate with a relatively small
financial outlay.
Administrative fees charged to participants in
investment company funds are used for marketing
and distributing fund shares.
An investment company custodian purchases fund
shares for resale to brokers, selling groups, or plan
companies, or for direct resale to investors.
An automatic dividend reinvestment plan is one in
which earnings are immediately used to purchase
additional shares of the fund.
76
Module 10 True/False
8. Income mutual funds are characterized by a fixed
portfolio of municipal bonds that can be traded in
a secondary market and that provide monthly
income to the investor.
9. Growth mutual funds are characterized as having
the greatest market risk because they contain
speculative securities of small companies and
securities of companies that have fallen on bad
times.
10. Balanced mutual funds are characterized by a
proportional weighting of income and growth
securities and include stocks, bonds, and money
market instruments.
77
Module 10 True/False
11. A major advantage of money market mutual funds
12.
13.
14.
15.
is safety of principal, which is due to the shortterm maturities and the diversification in types of
securities, issuers, and maturities.
The return on money market mutual funds results
from an increase in net asset value during an
investor’s holding period.
Interest rate risk is a major type of systematic risk
in bond funds.
A target-date fund becomes more conservative in
its asset allocation over time.
Mortgage-backed securities pay both interest and
principal monthly.
78
Module 10 True/False
16. U.S. Treasury debt is free of both interest rate risk
17.
18.
19.
20.
and default risk.
Index funds are designed for investors who want
their investments to outperform the market.
Closed-end funds continuously sell new shares
and redeem shares from holders.
A Yankee certificate of deposit is a short-term,
unsecured IOU of a U.S. corporation.
In a dollar-cost-averaging approach, an equal
number of dollars are invested in a fund at each
investment period.
79
Module 10 True/False
21. Many academic studies have confirmed that past
22.
23.
24.
25.
fund performance is a reliable predictor of future
performance.
Aggressive stock funds with low portfolio turnover
tend to have high capital gains distributions.
International funds invest in both U.S. and foreign
securities.
Hedge funds strive for risk-adjusted returns as
measured against the appropriate benchmark.
One advantage of separately managed accounts
is the ability to implement tax planning.
80
Module 10 True/False
26. If a formula uses beta, it is important that the
27.
28.
29.
30.
coefficient of determination be low, indicating a
high level of systematic risk.
A negative alpha for a fund means that the
performance of the fund has been negative.
Fund size can be an advantage for a bond fund.
If an investor believes that interest rates are going
to be in an uptrend for the next few years, he or
she should invest in bonds with lower durations.
Closed-end funds often sell at a premium.
81
Module 10 True/False
31. Hedge funds often have a “lock-up period” of one
year or longer.
32. ETFs tend to have lower fees than mutual funds,
but both ETFs and mutual funds have comparable
taxable distributions at the end of the year.
82
CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER CERTIFICATION
PROFESSIONAL EDUCATION PROGRAM
Investment Planning
CFP 2
True/False Questions
End of slides
©2015, College for Financial Planning, all rights reserved.