Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理
advertisement
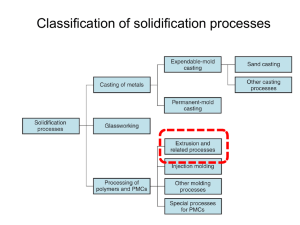
Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Plastic Forming: Extrusion and Injection Molding Similar to plastic forming technique, suitable for large scale, continuous production Need quite some polymer additives, to make bahaviour similar to plastic materials Extruded products: tube, paltes (tile), brick, insulator (ring shape), catalyst extrudate (pellet) etc. Injected products: mostly small objects, and small, complex shape with thin walls 1 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Extrusion of Ceramics Usually mix ceramic powder with polymer binder first, then add solvent to make slurry, then to remove some solvent (e.g. by filtration) to get cake for extrusion High shear mixer is often needed; screw feeder also has good mixing effect 2 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Extruded Shapes Honeycomb shape is a common shape in recent years; say 200 channel/cm2, wall thickness 0.1 mm; Often contain high quantity of binder, e.g. 35%, often become melt during processing, to solidify after leaving mold and cool down 3 From JS Reed, 1995; sequence of extrusion: (a) feed, (b) consolidation and flow in the barrel, (c) pass barrel head to enter die; (d) pass die-land; (e) ejection; [in some cases, die-land is not necessary] 4 pressure of extrusion system: 4 – 15 M Pa Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Flow in Extruder extruder: piston type or screw (single or twin) type flow from 3 parts: (a) drag flow by screw surface; (b) pressure flow induce by axial gradient; and (c) leakage flow through clearance between barrel and outside diameter of screw ceramic paste rheology is quite complex, difficult to simulate. Unless to use Newtonian fluid model In die, simple pressure flow After die, relaxation of stress may cause small change in objects (in terms of thickness; depending on its yield strength of course). Gravity may have some effect 5 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Extrusion Mechanics Slippage at wall may be due to lubrication effect; often in the die-land region; at high speed, friction effect from wall can not be neglected, e.g. die entry region 6 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 A Few Equations When feed is compressed into “saturation state”, one can use Herschel-Bulkley equation for description n : shear thinning index; b yield strength of the plastic body In die-land region, assume slippage at wall, m & f refers to corresponding properties of slippage film A land = cross section area of this region, A = other surface area n Y K P Pdie entry Pdie land P ln( Abarrel / Aland )[ b k b v ] ( A friction / Aland )[ n kfv ] m f 7 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Empirical Parameters Slippage film’s yield strength: much lower, higher index meaning more fluid in film 8 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Pressure distribution inside extrusion machine Major part: die land region 9 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 More Comments As extrudate pass tapered die, it will receive pressure and shear force; this value will increase while the die entrance angle becomes smaller; angle increase shear stress at wall decrease, after some critical angle , shear occur within body to occur static zone around the periphery of the die; dead zone will cause defect in product 10 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Twin Screw Extruder Twin screw better mixing than single screw; can be used for mixing purpose Gas-aided process: air can be pumped into to help forming (e.g. small hollow fiber) 11 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Control of Defects Insufficient strength and stiffness: cohesive strength closely related to binder, strength affect processing afterwards Cracks and laminations: caused by differential shrinkage; fundamental reasons: inclusion effect, e.g. agglomerates; poor mixing, liquid migration during extrusion, differential drying rate between inclusion and body, etc surface craters and blisters: dissolved gas become bubble after pressure release; vacuum before pressure may help Periodic surface laminations: extrusion pressure high, insufficient surface lubrication, more elastic springback 12 Crack produced by inclusion (due to differential shrinkage); Bird-foot crack: small inclusion of low drying rate; 13 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Control of Effects (2) Curling of the extrudate: more often for un-symmetric objects; or extruding hollow items through core rod, symmetry is important; Laminations from unjoined flow streams: S-shaped flow by screw extruder Poor skin: insufficiently developed slippage film, cause rough surface, need polishing afterwards; or dispersing more uniformly colloids, fines, more lubricants, liquid etc.; Gradient in extrudate stiffness: liquid migration (bleeding); Tearing during cutting: due to frictional drag, change cutting tool; Curling on drying: due to differential drying 14 Development of S crack during auger extrusion 15 conventional injection molding: mixing of raw materials (ceramic powder, binder, lubricant, solvent) granulation or pelletization feed to the molding machine injection molding debinding, de-waxing etc. sintering to get product Uniformity: very important factor; recycled parts may join; often use extrusion to make pellets; 16 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Plunger Type Injection Molding Machine 17 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Compositions Many binder system contains more than one compound for better rheology; viscosity < 105 mPa.s on molding Burning off these organics is an important work afterwards 18 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Material Variables Materials into the mold, may through multiple cavities; temperature control may be important Uniformly packed green body is important to perfect product (without defect) Hardness of tool surface: important 19 本圖取自JS Reed, 1995; 填料行為: 物料黏度, 溫度, 固化溫度, 填料速度, 填料口 選擇, 物件的大小形狀, 氣體 排出等因素影響 如圖, 在中間的開口比較好 些 Plunger motion與die motion 必須配合, 形成一個cycle; 物料被射入mold後, 多仍需 要維持在一定壓力, 溫度時間 後才脫模. 20 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Mechanics of Flow 對於射出成型的配料, 一般用capillary viscometer零測 其黏度與流變行為 (similar to injection molding) Basically , shear thinning fluid for the mixture 物料被射入mold後, shear rate & temperature都會下 降, 將造成黏度上升很多; 體積收縮也許需要考慮 固化時, 應該先由mold牆壁開始, 會有收縮, 所以此時 仍須維持 mold壓力以彌補之 系統內溫度不均, 易造成thermal stress, 也會形成產品 缺陷 21 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Defects and Control 許多工程上需要改進的地方, 需要許多經驗, 不完全可 以模擬預測 大致來說, 進料必須均勻混合, 選對組成, 粒子沒有大 凝聚體, 其他許多屬於模具設計的工程問題; 藉助於高 分子加工的知識與技術 溫度與壓力的控制 是得到理想填料關 鍵之一 22 23 24 25 Che5700 陶瓷粉末處理 Removal of Organics Due to large quantity, a critical step, related closely to cost, may become rate-determining step; 也因為量多, 所以出現缺陷機會也大 一般採用方法 (機制): Liquid flow Solvent extraction High pressure extraction Vaporization or sublimation Thermal or oxidative decomposition 前兩者技術多針對low viscosity liquid (low MW polymers); capillary flow by gravity or capillary suction force Solvent extraction可以產生一些連通孔洞, 有助於後續 燒除高分子量的物質 26 移除有機物, 除了加溫外, 也多需要抽真空 27 28 29 30