Access Network Planning and Technologies BY ZOU JIAN
advertisement
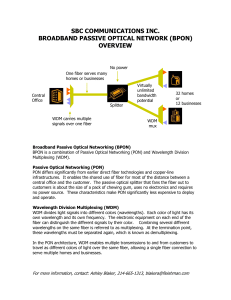
Access Network Planning and Technologies Part1 structure of Access Network Conception of Access Network Access Network(exchange) is the subscriber part of the telecommunications network. The basic idea of telecommunication is the exchange of information. •Voice •text •data •image •video If you are a telecommunications service provider and you have set up you first switch. You just need to link the customer premises equipment(CPE) to you witch with a pair of copper conductors . Simple interconnection of subscribers to exchange Structure of the Access Network DP1 2000 pairs 400 pairs DP2 DP3 SCP To other SCPs PCP EXCHANGE Part2 New Technologies in the Access Network Limitation of the copper network •limited bandwidth and there are problems in overcoming. •Inflexibility: both in time and types of service provisioning. •Reliability is limited. •Installation time is long. •Possible cable damages and maintenance costs were high. •Difficult to manage •Loop length limitations(~ 5km) •Has problem of security •Uneconomical in remote •Prone to electromagnetic interference New technologies in the copper Access Network Name Meaning DSL Digital Data Connection Distance Rate type to exchange 160kb/s Symmetrical ~5 km Subscriber Application ISDN series, voice, data communication line HDSL SDSL ADSL VDSL High Data 2Mb/s Symmetrical 4-5km No POTS, E1, LAN/ Rate Digital WAN, Internet Service Subscriber line access Single Line 2Mb/s Symmetrical 3-4km Same as HDSL+POTS Digital Sub- Work at home, scriber line internet access Asymmetric Downstream Asymmetrical Digital Sub- 2-8Mb/s, Up- emand, remote LAN access scriber line stream 128kb/s-768kb/s interactive multimedia Very High Downstream 13- Data Rate 52Mb/s, Digital Sub- Upstream 1.5- scriber Line 2.3Mb/s Asymmetrical 3-6km 0.3-1.5km Internet access, video on d- Same as ADSL HDTV Fiber based new technologies in the Access Network Methods of deployment of fiber •Fiber to the Curb(FTTC) •Fiber to the Building(FTTB) •Fiber to the home/office(FTTH/FTTO) Fiber in the loop architectures •Point-to-point •Point-to-multipoint/star •Tree •Ring Technological options 1. PDH(plesiochronous digital hierarchy) • fiber optic cabinet • PON(passive optical network) • AON(active optical network) 2. SDH(synchronous digital hierarchy) Basic PON system components • OLT(optical line terminal) • Splitter • ONU(optical network unit) Typical implementation of PONs ONU Management Up to 4 PONs ONU 1 ONU Switch 2 OLT 3 Capacity: 4B-120B 4 Splitting up to 32 Capacity: OLT 1920B, PON 480B B: 64Kb bearer channel Advantages of PON/AON • Sharing of fiber and equipment as in case of PONs •Increase in range at the cost of an additional active component(splitter) •High flexibility in structures •Higher capacity •Management Future of PON systems ATM-PON(APON): One fiber is passively split up to 64 times. Serve more customers. Can savings 20%-40% over circuit based access systems. Future of PON systems ATM-PON(APON): One fiber is passively split up to 64 times. Serve more customers. Can savings 20%-40% over circuit based access systems.