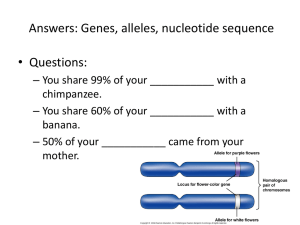
Structure Determination: MS, IR, and UV
advertisement

10.5 Spectroscopy and the Electromagnetic Spectrum The electromagnetic spectrum covers a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies, from radio waves at the low-frequency end to gamma (g) rays at the high-frequency end 10.6 Infrared Spectroscopy Infrared (IR) region • Ranges from 7.8 x 10-7 m to 10-4 m • 2.5 x 10-6 m to 2.5 x 10-5 m used by organic chemists • Wavelengths given in micrometers (1 mm = 10-6 m) • Frequencies given in wavenumbers • Wavenumber • Reciprocal of wavelength in centimeters • Expressed in units of cm-1 Infrared Spectroscopy Molecules stretch or bend at specific frequencies • Energy is absorbed if the frequency of the radiation matches the frequency of the vibration IR spectrum → What molecular motions? → What functional groups? 10.7 Interpreting Infrared Spectra Most functional groups have characteristic IR absorption bands that don’t change from one compound to another Interpreting Infrared Spectra Fig. 13-5, p. 509 Fig. 13-6, p. 510 Fig. 13-7, p. 510 Fig. 13-9, p. 512 Fig. 13-10, p. 513 Fig. 13-11, p. 513 Fig. 13-12, p. 514 Fig. 13-13, p. 515 Table 13-2, p. 522 Fig. 13-8, p. 511 Fig. 13-15, p. 523 Fig. 13-18, p. 526 Fig. 13-19, p. 527 Fig. 13-20, p. 528 Infrared Spectra of Some Common Functional Groups Characteristic aldehyde and ketone IR absorptions Infrared Spectra of Some Common Functional Groups Characteristic ester IR absorptions Fig. 13-22, p. 529