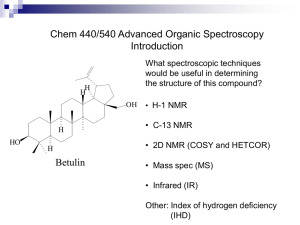
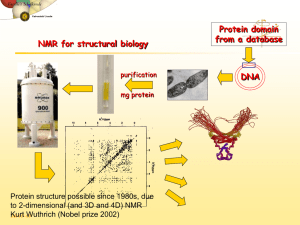
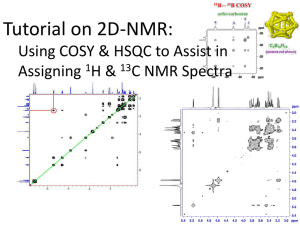
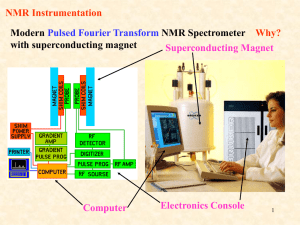
What is Multi-dimensional NMR Experiment
advertisement

How to observe NMR? Time Domain Frequency Domain t FT υ F Continuum of Frequency Excite all Resonances at the same time Short and high power pulse irradiation at Fo MHz Net Magnetization flipped to xy plane Bo 1 Excited Spin How to observe NMR? Precessing Spin 1D NMR Experiment Receiver at position x picked up a varying electromagnetic signal 2 How to observe NMR? Intensity decreases with time. Why? Free Induction Decay (FID) FT Time Domain Frequency Domain 3 Modern NMR Experiments Multi-pulses: 90 degree , 180 degree or shaped pulses Multi-channels : 1H, 15N, 13C (one channel one freq) with gradient z Multi-dimensional: t1, t2, t3 (one dimension one t) 4 What is Multi-pulsed NMR Experiments? t Short Pulse Quantum States Mz Bo Bulk Magnetization (not quantized) Excited Spin 5 Models for the description of NMR experiments: 1. Quantum Model: Density Matrix Analysis, Product operator formalism, very powerful but difficult to use. 2. Vector Model: Classical formalism, too simple but easy to visualize. Net Magnetization flipped to xy plane Bo x x y y inverted Mz 90-x My Mz 180y Spin Gymnastics! By varying the power, time length (angle) or phase (direction) of the pulse -Mz 6 Spin Gymnastics Interconversion rules between different M directions by applying 90 degree pulses Phase of pulse (thumb position of your right hand) Starting M direction Mz 90y Mx Use Right Hand Rule Mz 90z Mz Mx 90x Mx My 90y My 7 What is Multi-pulsed NMR Experiments? Magnetization can be transferred between nuclei through cross-talking by: 1. bonding: J coupling (H-H, H-C, H-N, etc…) 2. Close in space: dipolar coupling dAB HA C—H N—H HB Therefore information related to the other nuclei (e.g. chemical shifts δ, bonding, J-couplings, distances dAB) can be encoded in the NMR signals as well. 8 Mulit-Dimenstional NMR? Single pulse 1D NMR Experiment 1. Preparation: Recycle delay for relaxation 2. Applying pulse 3. Acquisition of FID Raw NMR data FID = F(t1) n1 points t1 2D NMR Experiment relaxation J or δ coding in t Exchange info get FID Raw NMR data FID = F(t1, t2) (n1 x n2 points) One dimension One t 9 Mulit-Dimenstional NMR? F(t1) F(t1,t2) 1D FT FT F(w1) F(w1,w2) 2D F(t1,t2,t3) FT F(w1,w2,w3) 3D 10 N2 points COSY: Correlation Spectroscopy F(t1,t2) FT(t2) Sine wave in t2 N1 F(t1,w2) FT(t1) F(w1,w2) Ha J-coupled to Hb δa δb 11 Homonuclear Experiment: Single channel, single resonance 2D COSY (directly J-coupled) TOCSY or HOHAHA (Total Correlation Spectroscopy) (directly or indirectly J-coupled) 2D NOESY (thru space dAB) (NOE Spectroscopy) 2D ROESY (Rotating frame NOESY) (thru space dAB) 12 Heteronuclear Experiment: Double resonance (e.g H, C) H,C-Hetero-COSY (directly H-C J-coupled) DEPT (Distortionless Enhancement via Polarization Transfer) Detecting C Inverse experiment: magnetization is transferred back to the more sensitive H HSQC (Heteronuclear Single Quantum Correlation) (directly H-C J-coupled) HMQC (Heteronuclear Multi-Quantum Correlation) (directly H-C J-coupled) 13 Heteronuclear Experiment: Triple resonance Triple resonance: H, C, N 14 Why NMR? So informative, so many applications and so much FUN! 2nd advantage of pulsed FT NMR: allow multi-dimensional NMR 15