Introduction
advertisement
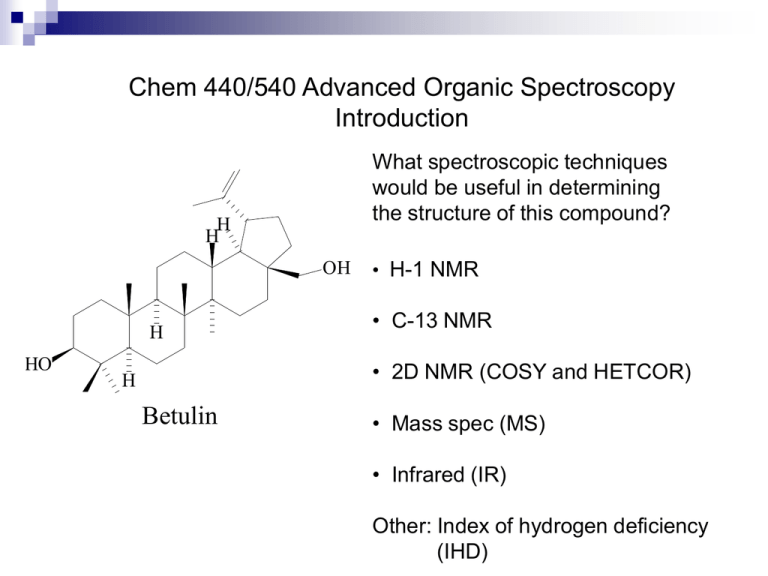
Chem 440/540 Advanced Organic Spectroscopy Introduction What spectroscopic techniques would be useful in determining the structure of this compound? H H OH H HO • H-1 NMR • C-13 NMR • 2D NMR (COSY and HETCOR) H Betulin • Mass spec (MS) • Infrared (IR) Other: Index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) H-1 NMR Spectrum H H OH H HO 4.8 4.6 4.4 4.2 H 4.0 3.8 3.6 3.4 3.2 3.0 2.8 2.6 2.4 2.2 2.0 1.8 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 C-13 NMR Spectrum CDCl3 H H OH H HO 170 160 H 150 140 130 120 110 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 General Principles of Absorption Spectroscopy A spectroscopic transition converts a molecule from a lower to a higher energy state. E = h = frequency of the electromagnetic radiation h = Planck’s constant E2 Energy E = E2 - E 1 E1 = c c = speed of light E = h = hc/ Types of Spectroscopy Radiation Type E (kJ/mol) Technique Time (sec) -rays, x-rays 105-103 X-ray diffraction (nuclear transitions) 10-18 Ultraviolet-visible 103–101 UV-vis (electronic transitions) 10-15–10-14 Infrared 101–10-1 IR (vibrational transitions) 10-13 Microwaves 10-3 Electron spin resonance (ESR- rotational motion) 10-4–10-8 Radiowaves 10-7 NMR (nuclear spin transitions) 10-1-10-9 Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) The degree of unsaturation can be calculated for any organic compound containing C, H, N, O, S, or the halogens. Use three steps: 1. Using the molecular formula, replace all halogens with hydrogens. 2. Remove all oxygen and sulfur atoms. 3. For each nitrogen remove the nitrogen and one hydrogen. The molecular formula is now reduced to CnHm IHD = n - m/2 + 1 Calculate the IHD for each of the following molecules: -sitosterol: C29H50O 3-iodothiophene: C4H3IS 5-iodouridine: C9H11IN2O6 Chloramphenicol: C11H12Cl2N2O5 Steps in Determining a Molecular Structure Determine the molecular formula (MS). Calculate the IHD. Identify the functional groups (IR, NMR, UV). Establish proton connectivities (1H-NMR) Establish carbon connectivities (13C-NMR). Determine the positions of functional groups on the carbon framework (IR, NMR, UV). Confirm the structure by synthesis or X-ray diffraction.