Introduction to Flow Cytometry
advertisement
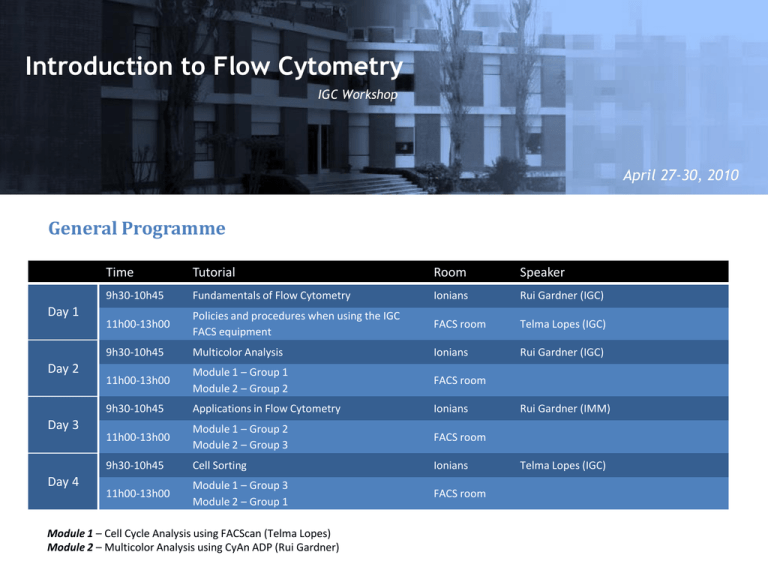
Introduction to Flow Cytometry IGC Workshop April 27-30, 2010 General Programme Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Time Tutorial Room Speaker 9h30-10h45 Fundamentals of Flow Cytometry Ionians Rui Gardner (IGC) 11h00-13h00 Policies and procedures when using the IGC FACS equipment FACS room Telma Lopes (IGC) 9h30-10h45 Multicolor Analysis Ionians Rui Gardner (IGC) 11h00-13h00 Module 1 – Group 1 Module 2 – Group 2 FACS room 9h30-10h45 Applications in Flow Cytometry Ionians 11h00-13h00 Module 1 – Group 2 Module 2 – Group 3 FACS room 9h30-10h45 Cell Sorting Ionians 11h00-13h00 Module 1 – Group 3 Module 2 – Group 1 FACS room Module 1 – Cell Cycle Analysis using FACScan (Telma Lopes) Module 2 – Multicolor Analysis using CyAn ADP (Rui Gardner) Rui Gardner (IMM) Telma Lopes (IGC) What is Flow Cytometry? Introduction to Flow Cytometry IGC Workshop Flow Cytometry uic Fundamentals of Flow Cytometry IGC – April 27, 2010 Overview • Definitions: What is flow cytometry and what does it measure? • Fluidics: Hydrodynamic focusing • Optics: Light, fluorescence, emission and detection • Electronics: pulse, data acquisition • Analysis: Data handling 3 Resources Purdue Univ. Cytometry Labs: all you need to know about Cytometry! • http://www.cyto.purdue.edu Tutorials: • http://probes.invitrogen.com/resources/education Spectra Viewers: • http://www.bdbiosciences.com/spectra • http://probes.invitrogen.com/resources/spectraviewer • http://www.mcb.arizona.edu/ipc/fret/ Books: • Shapiro, H. “Practical Flow Cytometry”, 4ed, Online version. http://probes.invitrogen.com/lit/practicalflowcytometry/toc.html http://www.coulterflow.com/ History of Flow Cytometry: • Shapiro, H. (2007) “Cytometry and Cytometers: Development and Growth”, in Flow Cytometry with Plant Cells (Eds, J. Dolezel, J. Greilhuber, J. Suda), WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim 4 What is Flow Cytometry? Cytometry: Measurement of physical and chemical properties of cells. Flow Cytometry: Characterization of cells flowing in a stream of fluid Fluidics Cells in suspension flow in single file through Optics an illuminated volume where they scatter light and emit fluorescence that is filtered, collected and Electronics converted to digital values that are processed and analyzed in a computer FACS: Fluorescence Activated Cell Sorting 5 Key Advantages of Flow Cytometry • Population data • Measure thousands of cells/particles per second • Measure multiple parameters simultaneously. • Detection and sorting of extremely rare populations 0.02% • Cell sorting • High purity, speed, and yield. Flow Cytometers FACSCalibur FACSscan FACSCanto LSR II CyAn ADP etc FACSAria MoFlo FACS Vantage EPICS ALTRA etc 7 The Instrument 8 Interrogation point 10 Hydrodynamic Focusing Low Flow Rate Sheath Flow Sample Flow Sheath Flow Laser High Flow Rate Sheath Flow Sample Flow Sheath Flow Laser Less cells pass per unit time More cells pass per unit time 11 Flow Rate High Flow Rate Low Flow Rate Laser Sheath Laser Sheath Sample Sample 3105 3105 2328 1552 Counts Counts 2328 1552 776 776 0 100 101 102 FL2 Log Comp 103 104 0 100 101 102 FL2 Log Comp 103 104 12 Lasers 488 nm Most common laser wavelengths available 14 Light Scatter Light is reflected towards all directions Low angle: Forward Scatter (FSC) High angle: Side Scatter (SSC) 16 Forward Scatter (FSC) The magnitude of Forward Scatter is roughly proportional to the size of the cell. 17 Side Scatter (SSC) Side Scatter is caused by granulosity and structural complexity inside the cell. 18 (2D) Scatter Plot 19 Fluorescence (1) Excited State Absorbed Light High Energy Emitted Light Ground State Low Energy 21 Fluorescence (2) High Energy 2 2 1 1 3 3 Low Energy Excitation Spectrum (1) 480 nm 520 nm 550 nm 590 nm Excited 23 Excitation-Emission Spectrum (1) Excitation Excitation max 550 nm Emission Excitation - Emission Excitation at different wavelengths decreases intensity of emission. Excitation-Emission Spectrum (2) Excitation maxima Emission maxima Fluorescence Charts Fluorescence Spectra Viewers Invitrogen (http:// www.invitrogen.com/spectraviewer) BD Biosciences(http:// www.bdbiosciences.com/spectra) Reactive and Conjugated Probes Cascade Blue Pacific Blue Pacific Orange Alexa Dyes Lucifer yellow NBD R-Phycoerythrin (PE) PE-Cy5 conjugates PE-Cy7 conjugates PE-Texas Red PerCP TruRed PerCP-Cy5.5 conjugate Fluorescein (FITC) BODIPY-FL TRITC X-Rhodamine XRITC Lissamine Rhodamine B Texas Red Allophycocyanin (APC) APC-Cy7 conjugates Etc… Immunohistochemistry Direct method Indirect method First dye-coupled antibody using fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) patented by Joseph Burckhalter and Robert Seiwald, in 1960 Pictures adapted from wikipedia Tandem Dyes PE-Alexa Fluor 700 PE-Cy5 PE-TxRed PerCP-Cy5.5 PE-Cy7 APC-Cy7 31 DNA and Cell Function Probes Calcium Membrane pH Cell Tracker DNA Mitocondria Fura 2 FM 1-43 SNAFLE CMRA DAPI Nonyl Acridine O Indo 1 FM 4-64 SNARF CMTPX HOECHST MitoSox Bapta/dye DiO BCECF BMQC TOPRO3 Mitotracker Calcium Green ANNINE 6 pHRodo DMFDA PI Rhodamine 123 Fluo 4 Di4ANNEPS hq lysosensor CMTMR DRAQ5 MitoProbe Fluorescent Proteins (1) GFP was first noted by Shimomura et al., in the jelly fish Aequoria Victoria, in 1962 and cloned 30 years later Fluorescent Proteins (2) San Diego beach scene drawn with living bacteria expressing 8 different colors of fluorescent proteins What is Flow Cytometry? Introduction to Flow Cytometry IGC Workshop Flow Cytometry uic Coffee Break…!