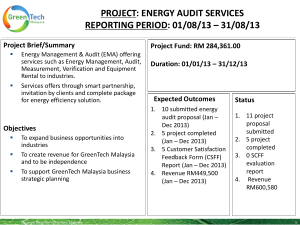
Presentation
advertisement
IRAP, RSA and METRA: The Malaysian way to Ensure Safer Road Infrastructure Prof. Dr. Ahmad Farhan Mohd Sadullah Malaysian Institute of Road Safety Research (MIROS) Malaysia CONTENTS Ensuring safer road infrastructure The dimensions Preventive vs cure Planned vs adhoc vs ignore/neglect Pre-requisite – design and construction Road Safety Audit (RSA) Operation and sustainability Road Assessment Programme (IRAP) Auditing operating facilities (METRA) ROAD INFRASTRUCTUE RELATED RISKS Poor road side protection Barrier issues Poor road design Curve Elevation Road cross section Poor access management Work/construction zone safety Poor pavement management Poor traffic management Poor road hierarchy discipline/land use issues Ending Point of the Damage Bridge Damage of the Bridge Barrier (during the crash) 1st row of bridge barrier 2nd row of bridge barrier • 1st and 2nd row of bridge barrier penetrate into the bus Source: China Press Overall Crash Dynamics 1 3 1st Impact with Barrier 2 Rail Intruded Diagonally 4 The Rail Intruded Bus entry – Principle direction of force: 12 o’clock Rail Swipes the Lower Occupants The bus tried to correct the maneuver 5 7 The Rail Bended 6 Skim the Median 8 Hit the Median The right tires on top of the median curb after the 2nd impact Come to a Rest The rest position of the bus Bus Nearside From the Rear Internal View Bus Offside Guardrail Failure POOR DESIGN WHAT IS WRONG WITH THIS DESIGN ANIMATION HOW DO WE PREVENT THESE? PREVENTION VS CURE Planned vs Adhoc vs Ignore The best way In design Road safety must be a design requirement Road safety must not be an after thought Road safety must not be compromised when price-ceiling bursts Maintenance Inspection Assessment TOOLS FOR SAFETY Internationally-known International Road Assessment Programme (IRAP) Road Safety Audit Malaysian way to complement and to close existing gaps METRA – Malaysian Guidebook for Traffic and Road Safety Audit (for operational roads) IRAP (INTERNATIONAL ROAD ASSESSMENT PROGRAMME) iRAP Project Aims Drive safety upgrading where large numbers are killed and seriously injured Global methodology to generate effective and economic countermeasure programmes Implement performance tracking methodologies for funding bodies to assess outcomes Provide the training, manuals and web tools to build and sustain national capability iRAP Background Developed countries program – AusRAP, EuroRAP, USRap, KiwiRAP Partnership of auto clubs, government, development banks, research institutes Over 40 countries worldwide Non-profit organisation with core funding from the FIA Foundation www.iRAP.net IRAP PROCESS INSPECT Video data collected using specialised equipment RATE Road attributes are recorded GENERATE Data analyses and options generated APPRAISE High return investment programmes recommended DESIGN Detailed design of schemes undertaken BUILD Safety upgrades are implemented Malaysia – 2008 Pilot Study Outline 3,700 km of peninsula Malaysia surveyed Expressways (E1, E2, E8) Federal Roads (F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F7, F8, F67 and F76) BEYOND THE PILOT: Plans for Road Improvement A 10-year Program Implementation of treatment programs Development of treatment programs Setting up of road improvements taskforce 22 Evaluation of treatment programs Malaysian Guidebook for Traffic and Road Safety Audit Malaysian Institute of Road Safety Research (MIROS) RSA: Current Practice in Malaysia “Road Safety Audit: Guidelines for the Safety Audit of Roads and Road Project in Malaysia” Published by JKR in 1997, 2nd Edition in 2002 A formal process done at various stages (5 stages) in the development of a project Auditors must be properly qualified Independent team of auditors Consideration of all road user groups Road Safety Audit: Guidelines for the Safety Audit of Roads and Road Project in Malaysia, 2002 Cycle of Road Safety Audit RSA Stage 1 RSA Stage 5 Existing Road RSA Stage 4 Pre-Opening RSA Stage 2 RSA Stage 3 The Gap Only carried out by experienced and certified auditors (inadequate numbers) Subjective guideline Unspecified task or method Guidelines are for more experienced road engineers Lack fundamental terminologies Guidelines do not provide guide for report writing For Example ? Check that:… That traffic signals are provided only where warranted for safe, efficient and equitable management of traffic flow along and across arterial roads and for the safe crossing of pedestrians. ? ? ? ? Introducing! Where MeTRA fits RSA Stage 1 Road Development & Maintenance RSA Stage 2 can be applied RSA Stage 5 Existing Road RSA Stage 3 RSA Stage 4 PreOpening MeTRA Component PART A • Chapter 1 • Chapter 2 : Road Alignment : Cross Section PART B • Chapter 3 • Chapter 4 : Un-signalized Intersection : Signalized Intersection PART C • Chapter 5 • Chapter 6 • Chapter 7 : Interchange : Bridge : Tunnel PART D • Chapter 8 • Chapter 9 • Chapter 10 : Motorcycle Infrastructure : Pedestrian Infrastructure : Public Transportation Infrastructure PART E • Chapter 11 • Chapter 12 • Chapter 13 : Visual Aid : Roadside Safety : Road Surface How MeTRA can Contribute to Road Safety? Objective and guided audit process Increase audit activities by stakeholders Inclusion of evidence based criteria Cost effective and regular maintenance work Integrated and strategic approach 31 What is MeTRA? This guidebook comprises of a road safety audit procedures specifically on operational roads which are guided through specific task. Who is MeTRA for? Any parties with interest in road infrastructure improvements, e.g. researcher, engineers, auditors, local authorities, or students. Where to use MeTRA? This guidebook is applicable to all road types regardless of condition and usage. How to use MeTRA? 33 Issue : Sets of questions that address various road safety issues. Specification and Standard : Explains or identify the relevant road safety standard and guidelines which was based on relevant references and research local and international. Task : Identify the specific instruction and assignment to be carried out in order to answer the question pertaining to road safety issues. On Site Data / Condition : Allows users to input the existing data or measurement responding to the task. Comments : Additional inputs or data that could help or assist in answering the question. How to Use - Example 1 Measure distance 2 Determine distance required from Specification & Standard 1 How to Use - Example 0.8 1.0 Success Stories Intersection & Alignment Improvement Before Improved Line of Sight After Sight Distance & Delineation Improvement Before After Visual Aid Improvement Before After • Kerbs were installed to properly segregate pedestrian from motorized traffic • Improvement of road markings The Way Forward…Supporting the Pillars of Decade of Action Vision & Target User Vehicle Road in ……… on CONCLUSIONS The Safety of mobility and road infra-structure holds a critical role to help address the road safety problems especially in the low and middle-income countries Preventive measures are critical Both at design stage as well as during operation IRAP, Road Safety Audit and METRA are useful tools BUT ABOVE ALL The “WILL” must be there. THANK YOU farhan@miros.gov.my