Basic Clinical Audit MHC Workshop
advertisement

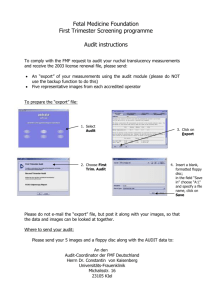
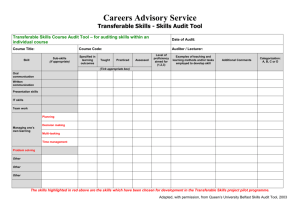
Nor is it… • Buying computers • Buying software • Having others put in all the data and you pushing the button • Extra work • Optional work If only we had that package Can’t you do it for me I’m too busy We don’t need to do that What is quality? Best patient care More efficient Least risk Satisfaction Least strife Smooth running Best care Rescue principle Responsive Empathic Quick Patient Best safest care Continual improvement Satisfied patient Advanced research Clinical freedom Responsive support Managerial Professional Safe Best Smooth / No gaps Patient centred Gap models of service quality Expected service Gap 5 Perceived service Gap 1 Service delivery Gap 3 Service standards Gap 2 Company perceptions of customer expectations Gap 4 External communications Improve patient outcomes Release money to provide better patient care Improve professional practice Promote MDT working Professional education Identify and eliminate waste Select and support only highest quality care Identify and stop bad practice Identify and promote good practice Clinical Audit Implementation of CA Define Measure Analyse Traditional improvement projects Improve Control Effectiveness Information for research Detailed, focussed and minutiae Info not usually collected Information for monitoring Technical data Lot of energy in getting agreement Information for quality improvement Quickly gathered Rapid cycle Some misconceptions…… It is not about cook book medicine Identify Standard Make appropriate changes Measure activity Validate against standard ACT Check ACT ACT Check Check Do Plan Do Plan Plan Do Framework for clinical audit Physical attributes of health care Structure •Tangible, easily counted •Presence increases the chance of good quality care but does not ensure it (appropriate use…..) •Examples: equipment; medical records Care given by a practitioner / service •Health professionals identify process with quality Process Outcome –It describes what they do –Reflects their attitudes, knowledge & skills •Examples: prescribing habits, hospital referral rates, lab & x-ray use Changes in patient’s current & future health status as result of intervention •Describe effectiveness of care •Difficult to measure…… •Example – lower incidence of specific disease; lower mortality; improvement of level of function, patient satisfaction Continuous vs. Big Bang Feedback Intervention Theory Emphasis on clinical performance task Specifying performance target Presenting information on how target can be reached Information on progress since last target Emphasis on recipient Discouragement Praise ??? Audit and Feedback +70% Change in practice after clinical audit – measured by adherence to specific guideline 0% -16% Jamtvedt et al 2006, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Why audit • Measuring for compliance • Win over the sceptics • Measuring for research • Sharing the experience • Measuring for improvement • True short cycle improvement Good audit • The right processes – Prescribing practice • The right objectives – Continual self improvement • The right measures – Logistics of the prescribing actions • The right actions – Reinforcing concept / reinforming stakeholders Challenges • Understanding • Good audit • Professional competence • Measurement of audit • Sustaining audit Joining up the dots • Building CA into a central plank of monitoring • Understanding context of CA • Matching CA to strategic goals • Making CA comfortable Motherhood and apple pie More education More forms More awareness More research Recommendations “We (I) will do x, y and z in the next 6 weeks and we will know we have succeeded Implementation of CA Define Measure Analyse Traditional improvement projects Improve Control