Document
advertisement

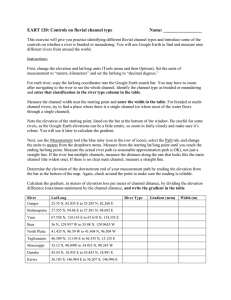
River Systems Four types, braided, meandering, anastamosing and straight Grand Canyon, erosion River incision in Indus Suture Zone River types Links between sinuosity and slope Anastomosing river stratigraphy Braided rivers • Typically developed in mountainous terrain on higher gradients. Typified by high degree of seasonality. Permanent channels with ripple crossed bedded sands develop during periods of low flow. These channels meander between sand bars that are active only during flood stage, these develop larger scale cross beds. Sediments are typically sandy and pebbly, usually moderate to well sorted, texturally moderately mature. Ancient example- Devonian Old Red Sandstone. Modern example - Saskatchewan River. Braided River Model Braided River Model and stratigraphy Braided River Braided geometry, Matanuksa River, Alaska Braided River, Nubra, India Braided River, Shyok River, India Anastomosing River, Indian foreland Channel sandstone facies Meandering Rivers Typically developed in coastal plain areas, lower gradient. More continuous flow, finer grained sediment than braided. Channel sediment is marked by the deep stream migration of meanders and the construction of cross laminated sands on point bars in the inner bends of meanders. Channels are separated by levees from flood plains that are comprised of finer grained muds and sands deposited after breach of levee during flood stage, usually vegetated. Flood stage can lead to cut-off of meanders and breakthrough of river. Meandering Rivers, contd. Abandoned meanders become Ox-bow lakes, filled by clays. Meandering river deposits typified by finingupward stratigraphy. Sediments are typically sandy, silty and clayey. Well sorted. Sandstones form isolated channels in finer background. Ancient example- Jurassic, Brent Group of North Sea. Modern example - Brazos and Mississippi Rivers. Meanders in the Amazon Basin McKenzie River meanders and glacial lakes Ox Bow Lake/meanders Point bar deposits Braided versus meandering river type sections Impact of sinuosity on stratigraphy Channel migration-Ganges Ganges and Himalaya thrust front Indus River and tectonic uplift, Kohat Plateau Effect of tectonism on location of rivers Fluvial facies examples Indus Molasse, fluvial sandstone Slumped sediment, modern Indus River Climbing wave ripples, Indus River