Management of nutrition problems in pregnancy and lactation
advertisement

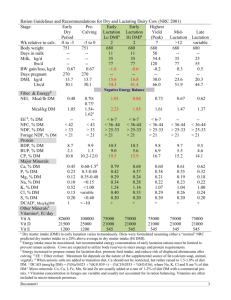
MANAGEMENT OF NUTRITION PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Prof. Sudha Salhan NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Cherished occasion for all women Anatomical and physiological changes occur in the body Nutrients essential for the growth of the foetus Al parts of the foetus synthesized from nutrients in the mother’s diet The baby’s growth similarly determined by maternal nutrition during lactation NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Extra calories during pregnancy to build tissues: enlarged uterus, placenta, breast development, foetal growth Similarly increased nutritional needs during lactation Gut absorbs nutrients better The body used them more efficiently If maternal intake of nutrients insufficient, foetal malnutrition manifesting as intrauterine growth restriction, premature delivery, still birth. Adequate quantity and quality of nutrition assures an adequate supply of good quality breast milk NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION IN A 50KG WOMAN Net energy (kcal) Protein (gm/day) Fat Sedentary work 1850 50 20 Moderate work 2225 50 20 Heavy work 2925 50 20 Pregnant woman +300 65 30 Lactation (0-6 mo) +550 75 45 Lactation (6-12 mo) +400 68 45 NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Vitamin A, β-carotene, thiamine, riboflavin, nicotinic acid, pyridoxine, ascorbic acid, folic acid and vitamin B 12 requirements also increase However, pregnant women don’t have to eat for two. Foods like whole-grain bread, cereals, legumes, dark green vegetables, citrus fruit, non-fat milk and milk products and lean meats, fish, poultry and eggs. Around 100 gm of extra carbohydrate Fat content of food 30% NUTRITIONAL REQUIREMENTS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Calcium for bone formation of the foetus. Milk and milk products and calcium supplementation ~ 600 mg/day Fibres in cereals, vegetables, fruit Iodized salt Fluid intake to be increased by about 30 ml/day. Baseline requirement: 100 ml/kg for the 1st 10kg, 50 ml/kg for the next 10 kg and 20ml/kg for every kg beyond that. COMMON NUTRITIONAL PROBLEMS OF PREGNANCY AND LACTATION Hyperemesis gravidarum Anemia Malnutrition Constipation HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM Slight nausea is felt by most pregnant women due to high levels of hormones. About 60-70% women experience nausea with onset at 4-7 weeks and lasting till 14 weeks of gestation. Harmless in them However, it is termed hyperemesis gravidarum when there is persistent viomiting with loss of 5% weight.compromised fluid.electrolyte &nutritional status with ketoneuria. HYPEREMESIS GRAVIDARUM: GENERAL MANAGEMENT Frequent small semisolid food Foods causing vomiting to be avoided Foods of the pregnant woman’s choice (do not be strict about caloric intake or about protein/carbohydrate/fat content) Avoidance of oily or spicy foods Drinking ginger tea If bothersome, an obstetrician needs to be consulted ANEMIA A condition of low hemoglobin (Hb < 11 gm/dl, hematocrit <33%) Common finding in Indian women. The incidence is 68.8-96.8% The most common type of anemia is nutritional deficiency anemia, due to deficiency of iron, folic acid, vitamin B12 Causes pre-eclampsia, preterm labour, PPH, cardiac failure, puerperal sepsis, subinvolution, etc in the mother In the foetus it causes low birth weight, intrauterine death, iron deficiency during infancy (as the inadequate iron stores are rapidly used up during growth), cognitive and affective dysfunction PREVENTION OF ANEMIA Pre-pregnancy raising of hemoglobin levels by dietary modification is helpful Consumption of iron-rich food such as green leafy vegetables (spinach, mustard leaves), jaggery, sprouted pulses Cooking foods in iron utensils Avoidance of excessive tea and coffee and overcooked foods Do not use calcium with iron rich foods. It will prevent absorption High protein diet as hemoglobin includes globin (protein) and heme (iron) PREVENTION OF ANEMIA Cereals, milk and milk products Two eggs per day with fish, poultry or meat if non-vegetarian Ingestion of citrus fruit such as orange enhances the absorption of iron CONSTIPATION Constipation is due to progesterone-induce relaxation of the intestinal smooth muscles and slow peristalsis Troublesome in some patients It can be overcome by: Adequate fluid intake High fibre diet e.g. cucumber, papaya, apple, beans HEMORRHOIDS Avoid constipation with a high fibre diet with plenty of fluids