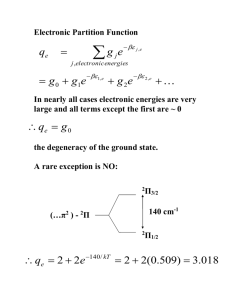
abstract - eScholarShare
advertisement
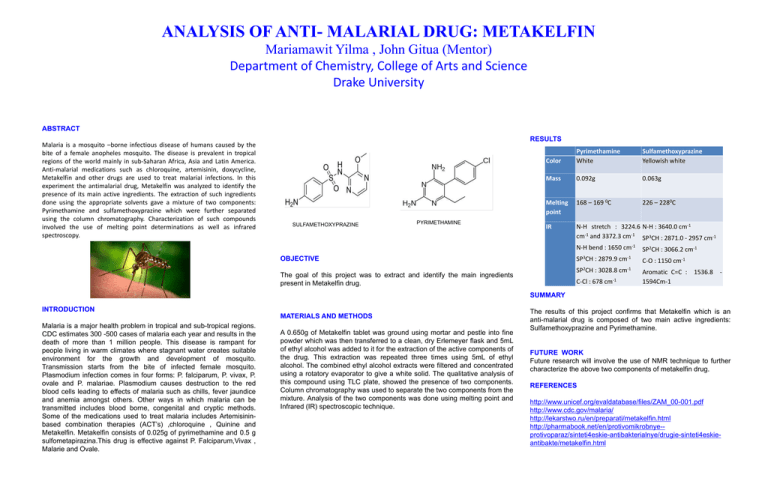
ANALYSIS OF ANTI- MALARIAL DRUG: METAKELFIN Mariamawit Yilma , John Gitua (Mentor) Department of Chemistry, College of Arts and Science Drake University ABSTRACT Malaria is a mosquito –borne infectious disease of humans caused by the bite of a female anopheles mosquito. The disease is prevalent in tropical regions of the world mainly in sub-Saharan Africa, Asia and Latin America. Anti-malarial medications such as chloroquine, artemisinin, doxycycline, Metakelfin and other drugs are used to treat malarial infections. In this experiment the antimalarial drug, Metakelfin was analyzed to identify the presence of its main active ingredients. The extraction of such ingredients done using the appropriate solvents gave a mixture of two components: Pyrimethamine and sulfamethoxyprazine which were further separated using the column chromatography. Characterization of such compounds involved the use of melting point determinations as well as infrared spectroscopy. RESULTS SULFAMETHOXYPRAZINE PYRIMETHAMINE Color Pyrimethamine White Sulfamethoxyprazine Yellowish white Mass 0.092g 0.063g Melting point 168 – 169 0C 226 – 2280C IR N-H stretch : 3224.6 N-H : 3640.0 cm-1 cm-1 and 3372.3 cm-1 SP3CH : 2871.0 - 2957 cm-1 N-H bend : 1650 cm-1 SP2CH : 3066.2 cm-1 OBJECTIVE The goal of this project was to extract and identify the main ingredients present in Metakelfin drug. SP3CH : 2879.9 cm-1 C-O : 1150 cm-1 SP2CH : 3028.8 cm-1 Aromatic C=C : 1536.8 1594Cm-1 C-Cl : 678 cm-1 SUMMARY INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS Malaria is a major health problem in tropical and sub-tropical regions. CDC estimates 300 -500 cases of malaria each year and results in the death of more than 1 million people. This disease is rampant for people living in warm climates where stagnant water creates suitable environment for the growth and development of mosquito. Transmission starts from the bite of infected female mosquito. Plasmodium infection comes in four forms: P. falciparum, P. vivax, P. ovale and P. malariae. Plasmodium causes destruction to the red blood cells leading to effects of malaria such as chills, fever jaundice and anemia amongst others. Other ways in which malaria can be transmitted includes blood borne, congenital and cryptic methods. Some of the medications used to treat malaria includes Artemisininbased combination therapies (ACT’s) ,chloroquine , Quinine and Metakelfin. Metakelfin consists of 0.025g of pyrimethamine and 0.5 g sulfometapirazina.This drug is effective against P. Falciparum,Vivax , Malarie and Ovale. A 0.650g of Metakelfin tablet was ground using mortar and pestle into fine powder which was then transferred to a clean, dry Erlemeyer flask and 5mL of ethyl alcohol was added to it for the extraction of the active components of the drug. This extraction was repeated three times using 5mL of ethyl alcohol. The combined ethyl alcohol extracts were filtered and concentrated using a rotatory evaporator to give a white solid. The qualitative analysis of this compound using TLC plate, showed the presence of two components. Column chromatography was used to separate the two components from the mixture. Analysis of the two components was done using melting point and Infrared (IR) spectroscopic technique. The results of this project confirms that Metakelfin which is an anti-malarial drug is composed of two main active ingredients: Sulfamethoxyprazine and Pyrimethamine. FUTURE WORK Future research will involve the use of NMR technique to further characterize the above two components of metakelfin drug. REFERENCES http://www.unicef.org/evaldatabase/files/ZAM_00-001.pdf http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/ http://lekarstwo.ru/en/preparati/metakelfin.html http://pharmabook.net/en/protivomikrobnye-protivoparaz/sinteti4eskie-antibakterialnye/drugie-sinteti4eskieantibakte/metakelfin.html