Supplemental_material_LCMO_JAP
advertisement
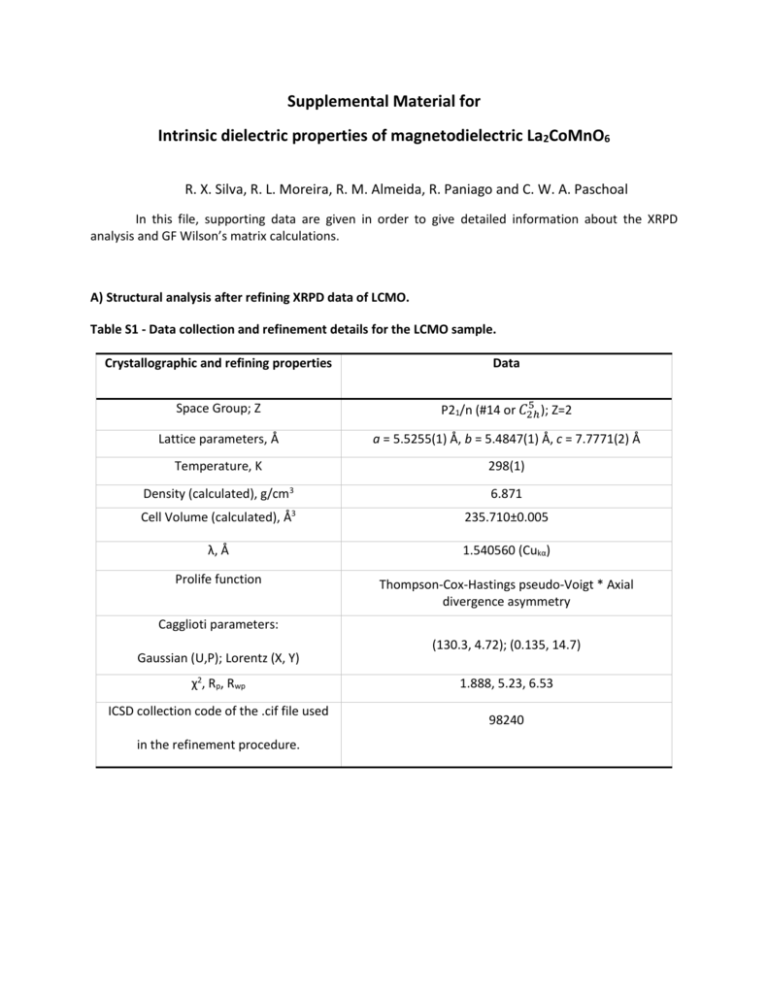
Supplemental Material for Intrinsic dielectric properties of magnetodielectric La2CoMnO6 R. X. Silva, R. L. Moreira, R. M. Almeida, R. Paniago and C. W. A. Paschoal In this file, supporting data are given in order to give detailed information about the XRPD analysis and GF Wilson’s matrix calculations. A) Structural analysis after refining XRPD data of LCMO. Table S1 - Data collection and refinement details for the LCMO sample. Crystallographic and refining properties Data Space Group; Z 5 P21/n (#14 or 𝐶2ℎ ); Z=2 Lattice parameters, Å a = 5.5255(1) Å, b = 5.4847(1) Å, c = 7.7771(2) Å Temperature, K 298(1) Density (calculated), g/cm3 3 6.871 Cell Volume (calculated), Å 235.710±0.005 λ, Å 1.540560 (Cukα) Prolife function Thompson-Cox-Hastings pseudo-Voigt * Axial divergence asymmetry Cagglioti parameters: Gaussian (U,P); Lorentz (X, Y) χ2, Rp, Rwp ICSD collection code of the .cif file used in the refinement procedure. (130.3, 4.72); (0.135, 14.7) 1.888, 5.23, 6.53 98240 Table S2 – Refined atomic coordinates in the monoclinic structure of the LCMO sample. Coordinates Ion Site Symmetry x Y z La 4e C1 0.00210 0.02090 0.25200 Co 2c Ci 0 ½ 0 Mn 2d Ci ½ 0 0 O(1) 4e C1 0.27390 0.22570 0.03300 O(2) 4e C1 0.27420 0.30370 0.47280 O(3) 4e C1 0.56830 -0.00300 0.24750 B) Lattice dynamics - GF Wilson Matrix analysis The lattice dynamic calculations of the normal modes of LCMO were performed based upon the GF matrix Wilson’s method. In this method, in order to obtain the force constants from the vibrational frequencies, the material has been treated as a system of point masses connected by springs obeying Hooke’s law. Thus, the system can be taken into the harmonic approximation with the secular equation |𝐺𝐹 − 𝐸𝜆| = 0 , where 𝐹 is a force constant matrix corresponding to the vibration potential energies that arise from the interaction between the atoms (and hence, provides valuable information about the nature of interatomic forces); 𝐺 is a matrix related to the kinetic energies, which depends on the masses of the individual atoms and their geometrical arrangement; 𝐸 is an unit matrix and 𝜆 is the eigenvalue connected to the frequency through the follow equation 𝑙 = 4𝑝2 𝑐 2 𝑢2 , where 𝑐 is the velocity of the light. To determine the force constant set that gives the best description of the structural and vibrational of LCMO data, we started from reported data of Iliev et al1. The modeling was optimized by applying a least square route to Raman spectroscopic data1,2. The initial force constants were modified in order to model the observed phonons. The final force constant values are given in the Table S3. Table S3 - Interatomic force constant values obtained in this work. No off-diagonal interaction terms were applied. Force constant reference K1 K2 K3 K4 K5 K6 K7 K8 K9 F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 Considered bond Distance (Å) La - O (3) La - O (2) La - O (1) Co - O (3) Co - O (2) Co - O (1) Mn - O (3) Mn - O (2) Mn - O (1) 2.4186 2.4608 2.4959 2.0311 2.0144 2.0707 1.9350 1.9334 1.8836 2.8142 2.9617 2.8782 2.9227 2.8421 2.8790 2.6927 2.7058 2.6841 2.7167 2.7304 2.7403 O(1) - O(2) O(1) - O(3) O(2) - O(3) O(1) - O(2) O(1) - O(3) O(2) - O(3) Force constant value (N/cm) 2.151 2.518 1.632 0.419 0.633 0.167 0.548 0.231 0.404 0.167 0.614 0.024 0.329 0.547 0.323 0.330 0.597 0.249 0.343 0.395 0.402 Table S4 - Assignment of the LCMO Raman-active modes based on the GF Wilson matrix analysis. P21/n Calculated Observed* (cm-1) (cm-1) Symmetry Calculated Observed* (cm-1) (cm-1) Symmetry 636.9 31.7 Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag Ag 23.7 Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg Bg 16.4 Ag 17.7 Bg 650.2 645.0 633.2 596.6 493.1 498.0 425.0 422.0 387.9 387.0 328.3 267.7 209.2 84.5 260.0 640.0 610.7 548.1 537.8 485.7 404.5 549.0 483.0 408.0 368.3 207.3 176.0 170.0 84.9 99.0 Table S5 - Calculated infrared-active modes based on the GF Wilson matrix analysis. P21/n Calculated (cm-1) 632.0 608.3 582.4 518.2 488.4 451.1 291.3 257.1 210.0 171.1 149.0 134.0 125.7 107.3 96.5 67.6 61.4 Symmetry Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Au Calculated (cm-1) 643.7 642.6 560.6 547.0 450.2 433.4 275.5 257.0 222.4 168.4 157.9 140.3 116.9 102.3 75.8 55.4 Symmetry Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu Bu ObservedThis Work ωj,TO (cm-1) 634.0 599.0 558.2 470.2 433.8 406.4 385.6 284.4 262.9 173.0 163.4 127.6 References *,1 M. Iliev, M. Abrashev, A. Litvinchuk, V. Hadjiev, H. Guo, and A. Gupta, Phys. Rev. B 75, (2007). *,2 K. Truong, J. Laverdière, M. Singh, S. Jandl, and P. Fournier, Phys. Rev. B 76, 132413 (2007).