Doppler Assessment Management - The Lindsay Leg Club Foundation
advertisement

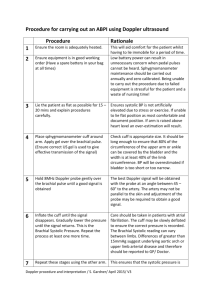
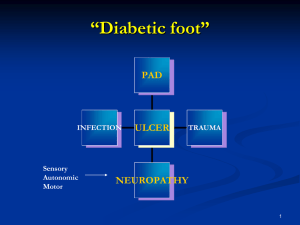
Leg Assessment and IPC Elaine Gibson BSc(Hons) DipN, RGN Aspen Medical Europe Tissue Viability Nurse Specialist East Kent University Hospitals Foundation Trust Dr Jon Evans BSc PhD MIET CEng Vascular Business Unit Manager Theresa Hanlon RN DIP HE Product Specialist Huntleigh Healthcare Jane Wigg RGN MSc Clinical Innovations Manager Haddenham Healthcare Trudie Young RGN MSc Facilitator Conference workshops in association with the Leg Club Industry Partners “Empowering patients through a unique collaboration with industry dedicated to lower limb conditions” Examination of the arterial patient Past Medical History Cardiac: angina; arrhythmias; MI Diabetes Hypertension Renal Neurological: cerebrovascular; peripheral Injuries Arthritis / collagen disease Clotting abnormalities Clinical features of the ischaemic foot • Cold • Pale colour • Glass like skin • Little callous • Pulse less • Dependent rubor • Claudication • Rest pain • Ulcers on edges © copyright Cardiff and Vale Trust Doppler Assessment • Doppler probes come in several Frequencies 2-10 MHz • It is important to use contact gel, use at 45 degree angle • 8MHz probe is ideal for measuring ABPI Doppler ABPI Measurements • Position patient supine and rest for 15-20 minutes • Measure both Brachial pressures • Measure two pedal pressures per foot • Calculate ABPI using highest ankle/highest brachial pressure ABPI > 1.0 - 1.3 Unlikely to be arterial in origin Apply compression therapy ABPI = 0.8 - 1.0 Mild peripheral Apply compression therapy with caution ABPI = 0.5 - 0.8 Moderate arterial disease disease ABPI < 0.5 Severe arterial disease ABPI > 1.3 Measure toe pressures or refer to specialist Do not compress refer to specialist Do not compress - refer urgently to vascular specialist. Other useful tests Waveform assessment (TASC2) Exercise Doppler Segmental pressures Buergers test Slow capillary return after blanching Pole test Toe pressures (TASC2) Pulse Volume Recording (TASC2) Pole Test Pole test for measurement of ankle pressures in patients with calcified vessels: the Doppler probe is placed over a patent pedal artery and the foot raised against a pole that is calibrated in mm Hg. The point at which the pedal signal disappears is taken as the ankle pressure Doppler Waveforms and Sounds Waveforms provide extra information to confirm clinical findings and ABPI’s Triphasic Waveform - Normal Biphasic Waveform – Normal with age Doppler Waveforms and Sounds Monophasic Waveform 1 - Abnormal Toe Pressures Doppler or Photoplethysmography (PPG) Toe/brachial pressure > 0.7 = normal Rest pain usually present in patients with index < 0.15 Absolute pressure in the toes of 20-30mmHg is usually associated with rest pain Problems with measuring ABPI using Doppler • Difficult to maintain vessel contact during inflation and deflation • A reasonable knowledge of anatomy is required • Difficult to locate vessels • Typical average time for ABPI is 11mins + 15-20 mins rest (Ipsilon and Get ABI Study 2006) • Clinicians must be trained and monitored (RCN Guidelines 2006) • Doppler ABPIs taken by junior doctors disagreed with vascular technicians by 30%. This improved to 15% after formal training (Ray et al 1994) Two Chamber Cuffs Specially designed two chamber cuffs are used to detect systolic pressures An Auto ABI Device Systolic Pressures and ABI PVR Waveforms Pulse Volume Recordings Grade A: Normal Sharp systolic peak with prominent dicrotic notch Grade B: Mildly Abnormal Sharp peak, absent dicrotic notch; downslope is bowed away from baseline Grade C: Moderately Abnormal Flattened systolic peak, upslope and downslope time decreased and nearly equal, absent dicrotic notch. Grade D: Severely Abnormal Low amplitude or absent pulse wave with equal upslope and downslope time Advantages of Auto ABI • Extremely easy to use and fully automatic • Rapid bi-lateral ABI measurement in < 5mins (Doppler based ABI typically takes 30mins) • No need to rest patient for 15mins • ABI can now be undertaken by less skilled staff • Only have to apply 4 cuffs • Physiologically more accurate • No need to remove socks and tights • Integral printer for documentation of results and waveforms • Automatic interpretation • Clinically validated (Lewis et al, 2010, 2012) Uses of IPC Deep veins (Johns et al 2007) Faster muscle recovery (Griffin et al 2007) Increases arterial flow (Morris et al 2002, Eze et al 1996) Wound healing (Pflzenmaier 2nd,et al 2005, Coleridge-Smith et al 1990) Enhances lymph transport (Baulieu et al 1989) Drainage to functional lymphatics aiding removal (Brennan and Miller 1998) Oedema Reduction (Partsch, 2008) Traditional IPC Sequential Cycle Starts distally and holds pressure in each chamber Releases all chambers together Useful for venous and dependency oedemas Traditional IPC Sequential Cycle Starts distally and holds pressure in each chamber Releases all chambers together Useful for venous and dependency oedemas Traditional IPC Wave cycle Applies pressure distally and inflates the next progressive chamber whilst releasing the previous It has a ‘wave’ or peristaltic effect and is useful for palliative, venous and watery oedema Traditional IPC Wave cycle Applies pressure distally and inflates the next progressive chamber whilst releasing the previous It has a ‘wave’ or peristaltic effect and is useful for palliative, venous and watery oedema New machines ‘To date, no mechanical device has been designed to mimic the technique of manual lymphatic drainage, This would essentially consist of reverse sequential compression’ (Comerota and Aziz, JOL, 2009) LymphAssist (Flowtron Hydroven 12, developed 2006) A 12 Chamber IPC System with LymphAssist cycle Designed for Lymphoedema only The first 12 chamber (overlapping) retrograde pump with this unique cycle Retrograde flow/ commences proximally 5 pulses each chamber Based on MLD (Leduc) Maximum pressure 40mmHg Completes each cycle Cycle 19.6 mins (2 cycles equivalent to MLD) Advantages Provides supervised self management/Home use Increased lymphatic drainage pathways (Furnival-Doran (2012) Treat the whole /both limbs (full leg garment) Easy to use/ does not required trained therapist Cost effective/Time/ resource saving Improved healing times Problem solving Reduced risk Assists in longevity of role Good patient experience EFFECTIVE Thank You Any Questions