Leg Ulcers
advertisement

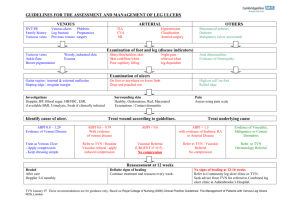
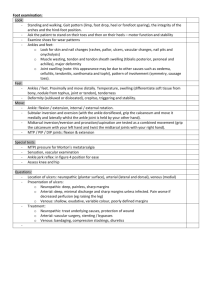
Barry Gibson-Smith Anniesland Medical Practice A 63year old presents with an 8 week history of a non healing area on her shin. She describes that it started after she bumped her leg on a chair. She has been dressing it herself. What more from her history do you want to know? Ulcer – painful, discharge, smell, itchy, change in size, PMHx –Venous disease, previous DVT, Arterial disease – IHD, PVD, CVA Diabetic Auto-immune – RA, SLE, Inflam BD, Cancer – general health Renal disease Medication – new? immunosuppressants Established from Hx • Venous veins • Obesity • Poor mobility Your working diagnosis is Venous Ulceration. What signs in the leg would support this? Signs may include: Common site is the medial lower aspect of the calf especially over the malleolus. Varicose veins Chronic lymphoedema Pigmentation Stasis dermatitis (scratched, dry or weeping patches) Atrophie blanche (scarring with prominent tortuous capillaries) Lipodermatosclerosis (firm to hard induration) Multiple ulcers may occur. What are you going to do for this lady who you suspect has venous ulceration of her lower leg? •Ankle Brachial Pressure Index (ABPI) by using a Doppler probe to measure pressure in the arm and the ankle. The normal value 0.92 to 1.3. •Peripheral pulses not reliable •ABPI is less than 0.9, there is likely to be arterial disease. Levels of less than 0.5 indicate severe arterial disease. • Caution in diabetics Treatment of/with •Cellulitis •Oedema •Leg elevation •Improve mobility •Dermatitis •Compression bandaging •Aspirin and pentoxyphyline •Avoid – sensitisers, antimicrobials, swabbing, fancy dressings •Heavy Smoker •Hx of IHD •Hx of intermittent claudication •Ulcer for 5 weeks on toe. •Suspect Arterial Ulcer •What signs would support this? SignsUsually feet, toes, heels involved and painful Punched out appearance Associated with cold white or bluish, shiny feet. Poor peripheral pulses. Do ABPI His ABPI is 0.8 What will you do for him? Referral CVS risk assessment – aspirin, BP, CKD, cholesterol, ?diabetes Exercise – collateral circulation Simple dressings Analgesia Warning advice - gangrene A 47 year old lady with 5 year Hx of Rheumatoid arthritis currently on DMARDs therapy. Develops ulcer on lower leg after simple knock. What type of ulcers present in this group? Ulcers in RA Pyoderma gangrenosum Vasculitis Risk of arterial ulcers Cellulitis and associated ulceration Skin cancer ulcers from use of DMARDs Pyoderma gangrenosum Vasculitis Importance of prompt referral and secondary care involvement Likely to require high dose steroids Admission required if progressing rapidly An elderly lady presents with a relatively painless ulcer on her lower leg that has been slowly enlarging over several months. What are your differential diagnoses? Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Amelanotic melanoma Requires referral for biopsy and excision Beware of non-healing ulcers A 22year old single mother girl presents with 8 week history of ulcerated area on shin. Lesion is an unusual shape, what diagnosis should be considered and what signs would support it? Bizarre shape depending on methods used to injure the skin Linear or geometric pattern Lesions at different stages and range from red patches, swelling, blisters, denuded areas, crusts, cuts, burns, and scars. Lesions emerge quickly (overnight) without any prior symptoms or signs Accessible sites such as hands, arms, buttocks, lower legs A 52 year old diabetic patient presents with a painless ulcer on the sole of his foot. What type ulcers can diabetics suffer from? Neuropathic ulcers Arterial Venous Necrobiosis lipoidica Importance of ABPI and examination Involvement of diabetic specialist nurses and podiatrist at early stage. Leg ulcers are a common presentation in practice and require a multi-disciplinary approach Importance of careful history and examination Importance of ABPI assessment Importance of biopsy for non healing ulcerated lesions