
CKD In Primary Care
Dr Mohammed Javid
Relevance
• End Stage CKD places a very significant burden
on patients quality of life.
• End Stage CKD is very expensive to manage.
• Deteriorating CKD is an independant risk
factor for an increase in mortality from
cardiovascular disease.
• QOF: CKD = 38 points
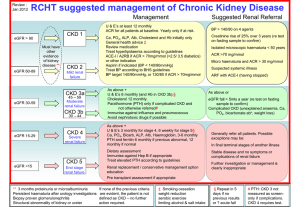
Guidelines
•
•
•
•
National Service Framework 2004 -2005
NICE guidelines 2008
PACE local guidelines
QOF
eGFR
• CKD classification is based on eGFR
• Estimates Glomerular Filtration Rate using
serum creatinine and patients Age, Sex, etc
• Cockroft-Gault formula
• MDRD formula
Creatinine 120
eGFR 31-40
eGFR 82-106
CKD stage
GFR (ml/min/1.73m2)
Description
1
>90
Normal renal function but
other evidence of organ
damage*
2
60-89
Mild reduction in renal
function with other
evidence of organ
damage*
3
30-59
Moderately reduced GFR
Insert P for proteinuria
3a and 3b
45-49 and 30-44
4
15-29
Severely reduced GFR
5
<15
End stage, or
approaching, end stage
renal failure
* Structural (eg APCKD), functional (eg proteinuria) or biopsy proven GN
Stage 5
0.2%
Stage 4: 0.2%
Stage 3: 4.3%
Stage 2: 3.0%
Stage 1: 3.3%
Risks of a low eGFR
Renal
• 1% of patients with CKD 3 will progress to ERF
in their lifetime (99% won’t)
Cardiovascular
• If you have an eGFR <60 you are at higher risk
of all cause mortality and any cardiovascular
event
100 patients with eGFR < 60
1 year later: 1 patient needs RRT, 10 patients have died (> 50% CV
death)
10 years later: 8 patients need RRT, 65 patients have died, 27 have
ongoing CKD
Proteinuria
•
•
•
•
•
Indicates poorer renal prognosis
Urine dipstick
Protein : Creatinine ratio PCR
Protein : Creatinine Index PCI
Albumin : Creatinine Ratio ACR
– Early morning sample
– <5 normal, >30 significant , >70 severe
– Check for heamaturia
Progressive CKD
• Check at least 3 eGFRs over 90 days
• Defined as a decline in eGFR of
>5 within 1 year, or >10 within 5 years
Routine management
Lifestyle modification
•
•
•
•
Smoking increases risk of progressive CKD
Lose weight if obese
Regular exercise
Reduce salt if hypertensive
Routine management
Monitor eGFR
• CKD 3
• CKD 4
• CKD 5
6 monthly
3 monthly
6 weekly
Routine management
Control BP
• NICE target <140/90
•
<130/80 if ACR >70
•
<130/80 if diabetic
• QOF
<140/85 for all
Routine management
ACEI or ARB:
• Diabetes + ACR (>30)
(irrespective of hypertension or CKD stage)
• Non-Diabetic with CKD + HT + ACR >30
• Non-Diabetic with CKD + ACR >70 (irrespective of
presence of HT or CVD)
Routine management
Routine anti-hypertensive treatment
• Non-diabetic + CDK + HT + ACR <30
(See NICE Hypertension guideline 34)
Routine management
CVD risk assessment
• treat with a statin if CVD risk >20%
(SystmOne CVD risk calculator does NOT include adjustment
for chronic renal disease, but QRISK2 does)
Immunizations
• Influenza - annually
• Pneumococcal - 5 yearly, due to declining antibody
levels
Routine management
Drugs
• Check BNF Appendix 3: Renal Impairment
Test for anaemia
• If Hb <11 first consider other causes of anaemia
• Determine iron status – if serum ferritin <100 start
oral iron
Consider renal USS
•
•
•
•
•
If CKD 4 or 5
Progressive CKD
Visible or persistent microhaematuria
Symptoms of urinary tract obstruction
FHx polycystic kidney disease and >20yrs of
age
Consider referral
•
•
•
•
•
•
CKD 4 or 5
Proteinuria ACR >70
Proteinuria ACR>30 with haematuria
Progressive CKD
CKD and poorly controlled BP on 4 agents
Suspected genetic renal disease or renal
artery stenosis
QOF indicators
• CKD points total = 38 points = £££
•
•
•
•
•
CKD1 (register)
CKD2 (bp checked)
CKD3 (bp controlled)
CKD5 (acei started)
CKD6 (acr checked)
= 6 points
= 6 points
= 11 points
= 9 points
= 6 points
Take Home Message
• CKD is an independant risk factor for
cardiovascular mortality which far outweighs
the risk of developing end-stage renal disease
• CKD 3 is managed in primary care with ACE-i
and cardiovascular optimisation.
– Monitor eGFR
– Blood pressure control with ACE
– Check for proteinuria




![Risk Adjustment Factor [RAF]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005748329_1-97f04b2983127ae4930cafa389444167-300x300.png)





