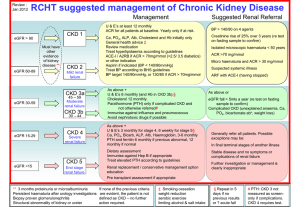
Chronic Kidney Disease
Jacqueline Annand – CKD Nurse
Mary Simpson – CKD Nurse
Joyce Mackie – Pre Dialysis/Transplant
liaison Sister
What is CKD?
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), is a
progressive loss of renal function over a
period of months or years.
Chronic Renal Failure/Established Renal
Failure (CRF/ERF) is complete, or almost
complete failure of the kidneys to function.
Stages of CKD
Stagea
GFR
(ml/min/1.73 m2)
Description
1
90
Normal or increased GFR, with other evidence of
kidney damage
2
60–89
Slight decrease in GFR, with other evidence of
kidney damage
3A
45–59
3B
30–44
Moderate decrease in GFR, with or without other
evidence of kidney damage
4
15–29
Severe decrease in GFR, with or without other
evidence of kidney damage
5
< 15
Established renal failure
a
Use the suffix (p) to denote the presence of proteinuria when staging CKD
(recommendation 1.2.1).
Causes of CKD
Hypertension
Diabetic nephropathy
Glomerulonephritis
Hereditary disease – APKD
Analgesic – nsaid
Mechanical obstruction – ie prostate
Ageing process
Scope and Range
The Renal Service provides 24hr specialist Renal
care to patients from Grampian, Orkney & Shetland.
It caters for those suffering from Acute Renal
Failure (ARF) and Chronic Renal Failure (CRF),
together with other nephrological problems, during
investigation, diagnosis, treatment of their condition
and offers specialist palliative care.
The main Dialysis Unit and Renal Medical Ward are
situated within Aberdeen Royal Infirmary and there
are Satellite Dialysis Units at Elgin, Peterhead,
Portsoy & Inverurie. There are also satellite
facilities on Orkney & Shetland
Pre-Dialysis & Transplant Clinics are held at within the
main Dialysis Unit & Satellite Units and other Renal /
Nephrology clinics are held at Woolmanhill
The Renal Transplant Service is provided by NHS
Lothian. Joint Pre–transplant assessment clinics are held
at Aberdeen Royal Infirmary, approximately every 6
weeks in conjunction with colleagues from NHS Lothian.
Conservative treatment and support is offered to
patients, families and carers of those who decide not to
undergo Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT).
Local Demographics
ARI
Elgin
Peterhead
Inverurie
Banff
Orkney
Shetland
Home
Total
208
PD
Pre-RRT
Transplant
36
106
222
Haemodialysis
Peritoneal Dialysis
Diabetic
Transplant
Pre Dialysis
Diabetic
Diabetic
Diabetic
CKD Facts & Figures
1 in 10 people in the UK have CKD. Patients
with CKD are more likely to die than go on
to have dialysis.
Early recognition of CKD permits
intervention to alter the natural history of
the disease – nephro-protection,
cardiovascular protection.
30% of patients with advanced CKD are
referred late to nephrology services from
primary and secondary care.
Referral rate doubled in some areas.
Why Role Came About
2006 National Service Framework
– Renal recommended that…
eGFR (estimated glomerular
filtration rate) based on serum
Creatinine level, age, sex, and
race.
….be the recommended formula
used to detect CKD
Job Purpose
To improve outcomes for patients with CKD,
by improving service and quality
Education of patients re BP/glycaemic
control, medication compliance,
supporting lifestyle changes
To enhance links with primary care in
managing the CKD population in the
community
Primary care visits, educational
sessions, meet the team sessions
To provide education to those in primary care
who are dealing with this patient group
GP practice visits, awareness sessions,
contactable resource
Job Purpose
To support medical personnel
Back to back clinics with Nephrologists
To develop clinical expertise
Participate in delivery of research and
evidenced based care
To be proactive in developing the role
Teaching/supervising members of MDT
including medical students, pre/post
registration nurses with regard to the
complexities of CKD patient
management
Our Background
Mary
25 yrs renal variety of
posts from staff
nurse, sister, clinic
nurse to research
nurse
7 yrs urology
research
CKD Nurse
Jacqui
1 year assessment &
rehabilitation
14 years renal (ward,
outpatients
haemodialysis,
research and
anaemia)
7 months
secondment – clinical
educator
Here & Now!
Case presentation 1
78 yr old woman
Hypertensive. Treated with amlodipine
BP 160/80
Creatinine 119 (eGFR 42)
Urinalysis: trace of blood
Clinic review
BP 140/80
Creatinine 170 (eGFR 27)
Ramipril stopped
4 weeks later creatinine 127 (eGFR 38)
All patients with CKD should have urinalysis:
if proteinuria is detected it should be
quantified by PCR. I suspect the patients she
refers to "with CKD 4 or 5 who are reviewed
at the renal clinic seem to have urinalysis
done" are patients with no (or minimal)
proteinuria on urinalysis, and hence the
consultant does not quantify it at each clinic
visit; or they are already maintained on
appropriate treatment and the level of
proteinuria is stable; or no other
intervention is possible and the consultant
therefore does not measure it.
2) Quantifying proteinuria. As we discussed this is
not straightforward. Our Lab gives an upper limit
for a "normal" PCR of 20mg/mmolcr - other
hospitals may use 30 or 50. Therefore "proteinuria"
is any level above an arbitary cut-off. In practice
the higher it is the more significant, and I am
happy to consider >50mg/mmol as "significant".
All patients with CKD & proteinuria should be
considered for an ACE-I (but not appropriate for
all). The key target should be BP reduction.
As always the level of proteinuria must be taken in
clinical context. I would want to see a 30-year-old
with a PCR of 80; but would not want to see a 80year-old diabetic with a stable PCR of 80, without
other relevant renal problems.
Some facts regarding
CKD
GFR is inversely related to hypertension and
cardiovascular risk
Symptoms are unusual until GFR is less than
30mls/min/1.73m2
Complications including renal anaemia and bone disease
are
unusual until GFR is less than 30 mls/min/1.73m2
Early CKD is very common
Advanced CKD is relatively uncommon
The epidemiology and natural history of CKD is still largely
unknown


![Risk Adjustment Factor [RAF]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005748329_1-97f04b2983127ae4930cafa389444167-300x300.png)