Making life easier…

Making life easier…
Dr Michael Gordon
GP
Gleadless Medical
Centre
Sheffield michael.gordon@sheffield.ac.uk
Making life easier…
Dr Michael Gordon
Primary Care Lead
Yorkshire & The Humber Renal Network
Making life easier…
Dr Michael Gordon
(emisWeb expert…not)
Making life easier…
A Protocol for ACR interpretation
ACR measurement fiddly but important
• Measure albumin:creatinine ratio on a spot urine sample (preferably early morning)
• If the initial ACR is >30 and <70 mg/mmol, confirm by a subsequent early morning sample. If the initial
ACR is >70mg/mmol a repeat sample need not be tested
• In people without diabetes, clinically significant proteinuria is present when ACR >30mg/mmol.
• In people with diabetes microalbuminuria (ACR
>2.5mg/ mmol in men and ACR >3.5mg/mmol in women) is clinically significant
The Challenges
• NICE output
• QOF requirements
• Remembering everything v knowing where to look
• Getting excited about niche areas – e.g. CKD
• Thinking hard when tired – Lab results.
Proteinuria predicts progression of CKD
RR of progression
5
4.5
4
3.5
3
2.5
2
1.5
1
0.5
0
<0.5
0.5-
0.9
1.0-
1.4
1.5-
1.9
2.0-
2.9
3.0-
3.9
Urine protein excretion (g/day)
4.0-
4.9
5.0-
5.9
6.0+
Ann Intern Med 2003;139:244-252
Proteinuria and CV mortality
CV Deaths/100 patient-years
20
15
10
5
0
40
35
30
25 albuminuria<30mg/dl albuminuria<300mg/dl
Muntner P et al JASN 2002;13:745 albuminuria>300mg/dl
CVD the big killer
Traditional solution…
The Wall Chart
For
Brighten the room
Info at fingertips
Promotes humility
Against
Clutter
Get lost
Undermine aura of omniscience
Gathering data to check
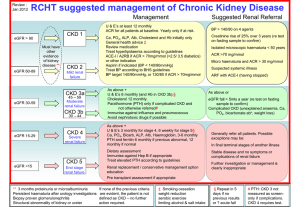
Packages of care for patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
CKD
ACR< 30 (microalbuminuria)
Stage eGFR BP target
ACE/ARB use U&E
Other
Tests to consider Refer
ACR 30-69 (proteinuria)
Read ACE/ARB
Code BP target use U&E
Other
Tests to consider Refer
ACR > 70 (proteinuria)
Read ACE/ARB
Code BP target use U&E
Other
Tests to consider Refer
Read
Code
1
> 90
& renal damage < 140/90
Not
Indicated 12m 1Z18 < 130/80
Preferred
First
Line 12m 1Z17 < 130/80
Preferred
First
Line 12m 1Z17
2
3a
3b
4
5
60-89
& renal damage < 140/90
45-59
30-44
15-29
<15
< 140/90
< 140/90
< 140/90
< 140/90
Not
Indicated 12m
Not
Indicated 6m
Not
Indicated 6m Hb
Hb
Ca/PO4
Not
Indicated 3m
PTH
US
Not
Indicated 6w
Hb
Ca/PO4
PTH
US
1Z1A < 130/80
1Z1E < 130/80
1Z1G < 130/80
Usual 1Z1J < 130/80
Usual 1z1L < 130/80
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
12m
6m
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
6m Hb
Hb
Ca/PO4
3m
PTH
US
6w
Hb
Ca/PO4
PTH
US
1Z19 < 130/80
1Z1D < 130/80
1Z1F < 130/80
Usual 1Z1H < 130/80
Usual 1Z1K < 130/80
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
12m
6m
Preferred
First
Line
Preferred
First
Line
6m Hb
Hb
Ca/PO4
3m
PTH
US
6w
Hb
Ca/PO4
PTH
US
1Z19
Usual !Z1D
Usual 1Z1F
Usual 1Z1H
Usual 1Z1K
The Basic Package for all stages of CKD
CVD risk assessment
Nephrotoxic drug avoidance
Co-morbidities e.g. Heart Failure and prostatic obstruction – optimize treatment.
Dietary & lifestyle advice. Low fat, sodium and potassium.
Stop smoking.
Progression of CKD
eGFR decline of > 5ml in 1 year (based on 3 readings over 90 days) or
10ml in 5 years – Seek advice from secondary care.
Anaemia
Hb < 11g may be considered as renal anaemia when other causes have been excluded.
African/Carribean patients
eGRF correction factor x 1.21 should be applied.
Diabetes & CKD
BP target <130/80 applies to all with microalbuminuria i.e.
Male > 2.5mg/mmol, Female > 3.5g/mmol. (2 or more measurements)
ACE/ARB use is indicated as first line treatment at all CKD stages .
Haematuria – see http://www.baus.org.uk/Resources/BAUS/Documents/PDF%20Documents/BA
US%20in%20general/haematuria_consensus_guidelines_July_2008.pdf
This table is based on NICE CKD 2008 guidelines. © Michael Gordon 2011
When the ACR is 3
• What do you need to know about the patient to make sense of the result?
• What else do you need to know to care for the patient optimally?
Facts (Concepts)
• Gender
• Diabetic?
• CKD already?
• Latest and previous eGFR
• Coded for microalbuminuria already
• Previous ACR readings
• BP – latest
• BP – appropriate target
• ACE/ARB use
• ACE/ARB allergy
emisWeb Protocols
• Check the facts (concepts)
• Follow user defined flowchart
• End in user specified output
• Applicable in a wide range of clinical situations
emis Web protocols – building blocks
1. Concepts
– Something asked of the recorded data
– e.g. gender, Lastest BP < 140/90, coding present
2. Questions
– Posed to the operator
– e.g. has the patient got specific symptoms
3. Outputs
– Guidance for the operator
– e.g. a text box saying repeat in 1 year
emisWeb protocols – construction process
• Pencil, paper rubber
• Build in emisWeb
• Whiteboard, post-it notes, peer scrutiny
• Attach to f12 key to run
• Engage colleagues to test
Mrs A
• Type 2 Diabetes
• Latest BP 140/82
• Not coded for microalbuminuria/proteinuria
• No recent consultation with UTI symptoms
• 2 previous ACRs > 3.5
• Allergic to ace/arb
• Latest ACR - 3.6
Mr B
• Type 2 Diabetes
• Latest eGFR 65
• Latest BP 129/79
• No recent symptoms of UTI
• On Ramipril
• Previous ACRs two > 2.5
• No microalbuminuria coded
• Latest ACR - 25
• Not diabetic
• Last eGFR 45
• CKD stage 3 coded
• Latest BP 120/78
• On Losartan
• No UTI symptoms
Mr C
• Latest ACR - 35
• Not diabetic
• CKD stage 3 coded
• Last eGFR 50
• Latest BP 130/80
• No UTI symptoms
Ms D
• Latest ACR - 50
Acknowledgements
• NHS Kidney Care – How to Guides
– Hosting videos and protocol to download
• Partners at Gleadless Medical









![Risk Adjustment Factor [RAF]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005748329_1-97f04b2983127ae4930cafa389444167-300x300.png)
