Charlemagne and Feudalism
advertisement

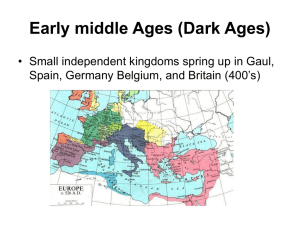
Rise of the Franks Charlemagne What happened to the Roman Empire? What was lost when Rome fell? Large cities Democratic government Centralized government Focus on law and justice Reading & writing Trade What remained? Christianity Germanic tribes converted and began to grow in power. Created monasteries – The only places that kept literacy alive. The Franks Germanic tribes that migrated into Gaul in the 5th and 6th centuries Fierce warriors – Larger than average – Battle axe The Battle of Tours Fought Oct. 10, 732 near Tours, France Charles Martel Results: – Decisive victory for Franks – Prevented Muslim conquest of Europe beyond Spain. Frankish Kings Charles Martel – The Hammer Pepin – The Short Charlemagne – Charles The Great Charlemagne Carolingian dynasty For his spread of the Christian faith, two forces were needed: – Spiritual – already existed as the Western Church – Secular – the political authority to rule Pope Leo III proclaimed him “The Consecrated Lord of Christendom” and “Emperor of the Romans” Coronation of Charlemagne Illuminated manuscript "The Coronation of Charlemagne" A New Chance for Empire Charlemagne’s Sons Mess It Up They fought over the land and eventually split it up. Lack of a single leader or administration lead to a new form of government… Feudalism Feudalism Feudalism Political and economic system based on land ownership and personal loyalty. Feudalism Fifes given out for “services and loyalty” to nobles Nobles gave out the right to work the land to serfs No central government Europeans Under Constant Attack Vikings, Magyars, and Muslims raided Europe. Lords defended the peasants. Castles Knights Knights were the warrior class. Armed and armored. Chivalry was their code of conduct. • Loyal • Brave • Courteous Manorial Economy Named after “manor,” which is where the lord lived. Self sufficient communities Peasants owed their lord three days of work each week. Also paid to grind grain, get married, or anything else that required the lord’s approval. Agriculture Three Field System • Plant two fields each year and leave third fallow (empty) • Increased food production • Increased population Medieval Life Lots of back breaking work Illness and malnutrition Average life expectancy was 35 Most people never traveled more than 25 miles from where they were born The Church was the social and cultural center of the community Medieval Medicine Poor hygiene Medical knowledge was limited People believed that disease was spread by bad odors. It was also assumed that diseases resulted from sins. Medieval Medicine First Patient Your patient has black and blue blotches all over her body. You are fairly certain it is the plague. What treatment do you prescribe? A. Apply sterile egg whites. B. Give the patient a treacle (made from over 60 ingredients including the roasted skin of vipers). C. Swaddle the patient and shave the sign of the cross into her head. Medieval Medicine Second Patient Your patient has taken to his bed with chills, a fever, and a terrible headache. When you examine him, you find pimple-like spots covering his skin. Your diagnosis is smallpox, a contagious disease common in your time. How will you treat this patient? A. Soak a piece of linen in a mixture of peony root and rose oil and apply it to the affected areas. B. Have the patient eat chicken broth. C. Wrap the patient in red cloth and drape red hangings around his bed. Medieval Medicine Last Patient You have a patient who is showing all the signs of having leprosy, what do prescribe for the treatment? A. Have the patient attend his own funeral and banish him to a colony. B. Amputate the patient's limb that is afflicted. C. Mix vinegar, sulfur, and oil and place on affected area. The Western Church The Church was heavily involved in politics. Church could threaten kings with excommunication or interdict. Constant struggle for power between church and state. Excommunication Today • • • • • Canon 1364: apostasy, heresy, or schism Canon 1367: violation of the sacred species Canon 1370: laying violent hands on the Pope Canon 1378: absolution of an accomplice Canon 1382: Episcopal consecration without authorization from the Holy See • Canon 1388: violation of the seal of Confession by a Confessor • Canon 1398: procuring an abortion The Western Church Organized under the Pope in Rome. To increase their power they: • Assumed legal authorities • Sent out their own diplomats • Collected money from tithes: everyone had to give 10% of their income to the church or else…