1._hypertension
advertisement

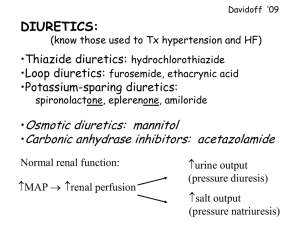
Pharmacotherapy of hypertension Systemic hypertension • long-lasting, usually permanent increase of systolic and diastolic blood pressure primary (essential) hypertension – unknown cause; usually coincidence of more factors – neural, hormonal, kidney dysfunction, ... secondary (symptomatic) hypertension – symptom (sign) of other disease Isolated systolic hypertension • increased systolic blood pressure at normal or decreased diastolic BP • pseudohypertension ← rigid arteries in old age “white coat hypertension “ – induced by stress at physical examination „masked hypertension“ - false finding of normal blood pressure during the examination; opposite of white coat hypertension Secondary hypertension essential hypertension – 90 to 95 % of high blood pressure prevalence: • children...about 4 %, mostly secondary • middle age ... 11-21 % • 50-59 years old ... approximately 44 % • 60-69 years old ... approximately 54 % • more than 70 years old ... ≥ 64 % (Standard guidelines, 2nd edition) Classification of hypertension JNC 7 7th report of Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure Classification of adult´s hypertension • Previous classification of hypertension (JNC 6, WHO) Reasons for actualisation of classification JNC 6 (1997): • Completing of more new clinical studies with substantial consequences for the treatment of hypertension. • Need for less complicated classification of hypertension. • Need for new and clear guidelines suitable for physicians. • Previous reports didn´t bring expected benefits. Classification of adult´s hypertension • New classification of hypertension according to JNC 7 Hypertenzia 3. štádia • in Europe partly remains classification of hypertension to 3 stages • ESH a ESC (European Society of Hypertension / E. S. of Cardiology) didn´t adopt JNC 7 classification without comments Risk of cardiovascular diseases • relationship between BP and CVD (cardiovascular disease) risk is continual, consistent and not dependent on other risk factors • the higher BP, the higher risk of heart failure, stroke, renal diseases • each increase of systolic BP by 20 and diastolic BP by 10 mm Hg doubles the risk of CVD Benefit of BP reduction In clinical studies was during antihypertensive therapy recorded: • 35-40% incidence reduction of stroke • 20-25% incidence reduction of myocardial infarction • more than 50% share at incidence reduction of heart failure • it is assumed that among patients at first stage of hypertension (140-159/90-99 mm Hg) and with other cardiovascular risk factors, permanent reduction of BP by 12 mm Hg during 10 years prevents one death from 11 treated patients (when CVS disease or organ affection, it is one from 9) Effectivity of BP reduction • despite the fact that decreasing of BP below 140/90 mm Hg is successful among more and more patients, still their number (34%) is less than intention (50%), 30% still doesn´t know about their disease Evaluation of patients All of these datas influence the prognosis and therapy selection. Evaluation of patients with diagnosed hypertension has importance to: evaluate the way of living + reveal other CVS risk factors and/or associated diseases - very important is the circadian rhythm of blood pressure! - physiological profound nocturnal decline, mostly around 4 a.m. ("dipping"), acts as a protection against pathological lesions of blood vessels, resp. reduces them - also hypertensive patients with significant nightime BP decrease have a more favorable prognosis ,as patients whose blood pressure at night compared to daytime values doesn´t decrease (worse prognosis) - → according to it are patients diveded to „dippers“ versus „non-dippers“ - ≅ improvement of diagnosis ← broader application of 24-hour blood pressure monitoring Circadian rythm of BP (dippers vs. non-dippers) We gain information about patient from : • anamnesis • physical examination (BP measurement, eyeground examination, BMI calculation, listening to murmurs at large arteries, detailed examination of heart, lungs, stomach, searching for enlarged kidneys, palpation of glandula thyroidea, resistency and abnormal pulsation of aorta, palpation of lower extremities to search for oedemas and pulsations, neurologic examination) • laboratory examinations (ECG, urine, blood glucose, haematokrit, kallium, calcium, creatin in serum, lipid spectrum of serum) Treatment • The final goal of antihypertensive therapy is reduction of mortality and morbidity to CVS and renal diseases. • Primary goal is reduction of systolic BP. We wamt to reach BP less than 140/90 mm Hg (Torr), or less than 130/80 mm Hg among diabetic patients and patients with kidney diseases • Needed is also increased detection! Nonpharmacological treatment Change of life-style: • intake of salt ... ≤ 5 – 6 g per day • prevention of obesity – dietetic modification • alcohol ... ≤ 30 g per day • smoking – stop • physical activity • psychical relaxation Pharmacologic treatment Antihypertensives 1st choice drugs: 1. diuretics 2. β-blockers 3. inhibitors of ACE 4. blockers of AT1 receptors (ARB) 5. calcium channel blockers 2nd choice drugs – mainly to drug combinations: α1-sympatholytics; α2-sympathomimetics; direct vasodilators; kallium channel openers; agonists of I1 receptors in CNS; other mechanisms of action Diuretics Diuretics • increase urination 1. carboanhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamid) – not used in the treatment of hypertension 2. loop diuretics (furosemide, etacrynic acid, bumetanide) – strong short-lasting effect; ability to excrete to 25 % of Na+ from filtrate • block active reabsorption of Na+, Cl-, K+ from ascending limb of Henle´s loop • at treatment of hypertension is rarely used only furosemide in low dosage – if simultaneously is very much reduced G filtration; they aren´t suitable for long-lasting application 3. thiazide diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, clopamide) • block reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- from distal tubulus • effect is weaker as at loop diuretics – they excrete about 5 % from Na+ filtrate • most suitable diuretics for long–lasting treatment of hypertension • effect also in vessel wall (↓ volume of Na and ↓ reactivity to norepinephrine; regression of media hypertrophy) • the most is used hydrochlorothiazide – daily dose 12,5 – 25 mg Mechanism of Action of Thiazide Diuretics 4. K-sparing diuretics (spironolactone (aldosterone antagonist), amiloride, triamterene) • at hypertension only assistant drugs to combinations – to correct hypokalemia 5. other diuretics • osmotic (mannitol, sorbitol) • xanthine • diuretics are suitable mainly for older patients and at simultaneous chronic heart failure • ADRs - hypokalemia, hypovolemia, hyperuricemia, metabolic ADRs (impaired glucose tolerance and dyslipidemia - mostly after high doses), erectile dysfunction Adrenergic Receptor with Agonist β-blockers Classifications: 1. non-selective (β1- aj β2-effect – propranolol, metipranolol, ...); selective (β1-effect – metoprolol, bisoprolol, atenolol, ...); hybrid substances (beside β-effect have also other effects, additional, resp. β2-mimetic effect), through which they induce vazodilation – labetalol, carvedilol, nebivolol, ...) – the most important classification 2. β-blockers with ISA (intrinsic sympathomimetic activity – pindolol, acebutolol, ...; ≈ parcial agonists) and without ISA 3. hydrophilic (atenolol, celiprolol, ...) and lipophilic β-blockers (propranolol, metoprolol, carvedilol, ...) 4. classification according to generations ....... and other different classifications.... β-blockers • preferenced are selective and hybrid substances before nonselective • don´t differ very much in antihypertensive effect, selection according to adverse effect profile • suitable for younger patients with ↑ sympathicoadrenal activity, hyperkinetic circulation, patients under psychical stress; patients with existent ischaemic heart disease and mainly after myocardial infarction • in our country are mainly prescribed : metoprolol (Vasocardin) bisoprolol (Concor) karvedilol (Talliton) and according to tradition nonselective metipranolol (Trimepranol) Main Effects of β1- a β2-blockade • β-blockers – possibilities of combinations: diuretics, Ca2+ blockers – only dihydropyridines!, α1sympatholytics, ACEI, vazodilators ADRs: • tendency to bronchoconstriction and to vasoconstriction in the periphery – mainly at non-selective βB • metabolic ADR – worsening of lipidogram; mask symptoms of hypoglycemia and can impair glucose tollerance – more at non-selective βB • sleep disturbances, bad dreams → ... depression • at very high doses can worsen heart failure; if indicated at chronic heart failure, dose should be increased step by step • erectile dysfunction ! selectivity of action is only relative! - at higher doses is dissapearing - even among β1selective agents appear β2-lytic effects • they can´t be combined with verapamilom a diltiazem! • treatment can´t be stopped abruptly – rebound effect! Indication for Self-medication with β-blockers: stage fright Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB) Classification: Ca2+ Channel Blockers (CCB) • Different chemical structures, with different haemodynamic and clinic effects • According to chemical structure divided to: - dihydropyridins (amlodipine, felodipine, lacidipine, nifedipine, isradipine) - phenylalkylamins (verapamil, gallopamil) - benzothiazepins (diltiazem) CCB – Mechanism of Action Block influx of calcium to cell through slow L-type channels, lower its intracellular concentration what causes relaxation of smooth muscle in vessel wall, decrease of contractility, decrease of electrical irritability and conductivity Selectivity of CCB Blood vessels vasodilation of arterial vasculature Heart: decrease of Heart AV rate conduction Strenght of contraction Calcium channel blockers • at treatment of hypertension are mostly used dihydropyridines; verapamil only at present tachycardia • prototype short-acting DHP nifedipine is contraindicated! - it reduces BP too rapidly, so induces reflex activation of sympaticus with subsequent increase of BP and such a repeated BP fluctuation causes worse vessel damage as untreated hypertension → instead of mortality decrease its increase! • pharmacokinetic explanation: effect fluctuates for fluctuation of level in blood – has low T/P (trough to peak ratio) • for antihypertensive to reduce mortality and morbidity, it has to reduce BP slowly and successively, without reflex activation of sympathicus → more steady level and higher T/P → FDA approves as antihypertensives only drugs, that have T/P more than 50 % • this applies for the 2nd generation of dihydropyridines (isradipine, felodipine, nitrendipine) and 3rd generation of dihydropyridines (amlodipine, lacidipine, lercanidipine). • Ca2+ blockers are suitable to treat hypertonic patients with DM, metabolic syndrome, at ischaemic disease of lower extremities • particularly advantageous are for isolated systolic hypertension • possibilities of combinations: ACEI, βB (only dihydropyridines), diuretics • ADRs: headache, red face, perimalleolar edemas, constipation, tachycardia (dihydrop.), severe bradycardia (non-dihydropyridins), steal phenomen • nimodipine (1st generation) affinity to brain vasculature → ... effectively relieves spasms of cerebral arteries → used at subarachnoid bleeding • lercanidipine has high T/P ratio • in our country for the treatment of hypertension are prescribed mainly following dihydropyridines: 2nd generation: felodipine (Presid, Plendil), isradipine (Lomir), nitrendipine (Nitresan, Lusopress) 3rd generation: amlodipine (Amlopin, Agen, Tenox, Norvasc), lacidipine (Lacipil), lercanidipine (Lercal) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Pharmacologic Interference to AT Cascade Inhibitors of AC enzyme • block the change of angiotensin I to angiotensin II and at the same time block inactivation of bradykinin • vazodilation in both resistant and capacitance vessels • accented indication: - hypertonic people with heart failure (vasodilating therapy of cardial insuficiency), also after myocardial infarction - hypertonic people with DM and different forms of diabetic nephropathy starting with mikroalbuminuria (nephroprotective effect of ACEI) • excessive initial fall in BP → postural hypotension or syncope; treatment should be started in bed from the lowest doses • reaction of airways is often strong and irritating cough → intollerance of the whole group → replacement to AT1 receptor blockers • they are administered as “prodrug“, to effective substance are changed in liver • effect to reduce BP is in the whole group similar; they differ only in pharmacokinetic dependent from structure → division to hydrophilic (“blood“) and lipophilic (“tissue“) ACEI • hydrophilic act only inside vessels and in endothelium; lipophilic also on the outer side of vessels (on “adventicial“ angiotenzinconvertase) and in myocardial interstitium → probably more effectively at regression of left ventricule hypertrophy and vessel media • typical hydrophilic ACEI: captopril (prototype substance – has SH-group; nowadays used only in hypertension crisis, Tensiomin) enalapril (Enap, Ednyt), lisinopril (Dapril, Diroton) • typical lipophilic ACEI: perindopril (Vidotin, Stopress, Prestarium) trandolapril (Actapril, Gopten) quinapril (Quinpres, Accupro) • ADRs: impaired renal function, hyperkalemia, hypotension, dry cough, angioneurotic edema • contraindications: pregnancy!, high concentration of potassium and creatinine, stenosis of a. renalis on both sides, severe aortal stenosis, angioneurotic edema in anamnesis Main Benefits of ACE inhibition AT1 receptor blockers • the most often replacement of ACEI in case of cough • losartan (prototype; Cozaar), valsartan, kandesartan, irbesartan (Aprovel) α1-sympatholytics • beside BP reduction they reduce benign prostatic hyperplasia → indication mainly older man with simultaneous BPH • in combination at severe resistant hypertension • positively influence lipidogram • strong 1st dose phenomenon! → postural hypotension, syncopes • prazosin (prototype; Deprazolin), doxazosin (Cardura), terazosin α2-sympathomimetics • central effect – stimulation of central α2 receptors through negative feedback inhibit release of norepinephrine on periphery → reflex BP reduction • α-metyldopa (Dopegyt), clonidine • ADR: central depression – sleepiness, bad dreams • clonidine has significant rebound phenomenon • α-metyldopa is advantageous during pregnancy – doesn´t influence negatively blood circulation of fetus Direct vazodilators hydralazines • specific mechanism of action is unknown; probably directly influence contractile system of vessel wall myocytes • ADR: tachycardia, palpitations, fluid retention → necessary combinations dihydralazine, hydralazine • suitable in pregnancy • hydralazine – genet. polymorphism of biotransformation → at slow acetylators can develop as syndrome similar to lupus erythematodes Kallium channel openers • opening of K+ channels on the top of myocytes → hyperpolarisation → induction of relaxation minoxidil • vazodilation in the area of arterioles • retention of Na+, hirsutism, hypertrichosis → used in the treatment of alopecia • expensive diazoxide • only short-term use – at hypertension crisis • induces hyperglycemia – at short-term use not matters Central I1 receptor agonists • I1 – imidazoline receptors type 1 in medulla oblongata • stimulation → reflectory decrease of peripheral resistency • without serious hemodynamic, metabolic ADR; are metabolically neutral → promising to future moxonidin (Physiotens, Moxostad, Cynt), rilmenidin (Rilmex, Tenaxum) Other antihypertensives • magnesium (MgSO4) – natural antagonist of calcium • sodium nitroprusside – simple molecule releasing NO; only i.v. at severe hypertension crisis, patient must lie, cyanide is formed; max. lenth of therapy 3 days • ketanserin – blocks S2 receptors for serotonin → prevents effect increase of catecholamines on symp. receptors Direct renin inhibitors (PRI) • absolutely new group • in many tissues is present own renin system with individual receptors → (pro)renin is bind to cell surfaces; system acts pressorically and proliferatively • it is activated when stimulation of AT1 receptors decreases → negative feedback • this signal way apparently decreases benefit of ACEI! → inhibition of the level of renin → ... better control of the whole RAAS → ... possible better prevention of organ damage Aliskiren • first available peroral PRI • ↓ plasmatic renin activity • indication in 2-combination aliskiren + ACEI or aliskirén + ARB → dual inhibition of RAAS system • product Rasilez ? - clinical results below expectations Selection of pharmacotherapy • Results gained in clinical studies show that BP reduction with using following antihypertensives – inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme(ACEI), blockers of angiotensin receptors(ARB), betablockers (βB), calcium channel blockers(Ca2+B) a diuretics, can reduce complications of hypertension. Reaching BP improvement at specific patients • Among most patients is necessary combination of 2 and more antihypertensives. • Adminastration of other drug should start when monotherapy in required dose doesn´t reduce BP to intended value. • If the BP is by 20/10 mm Hg higher than intended value, therapy should be started with combination of 2 antihypertensives. • recently is a growing trend to use combination of 2 antihypertensive drugs already in stage I hypertension • convincing evidence from relevant clinical trials → combinations perindopril-amlodipine perindopril-indapamide Other factors influencing selection of antihypertensives Potentially prosperous effects: • Tiazide diuretics slower the process of bone demineralisation at osteoporosis • βB can have positive influence at ventricular tachyarrhythmias and fibrilations, at migraine, short-termly at thyreotoxicosis, at essential tremor, perioperational hypertension • Ca2+B can be applied at Raynaud syndrome and some arrhythmias Other factors influencing selection of antihypertensives Potentially negative effects: • tiazide diuretics at patients with gout and hyponatremia in anamnesis • βB at patients with asthma, allergic diseases of airways and with A-V blocks of 2nd and 3rd stage • ACEI and ARB should not be given at probability of getting pregnant, are contraindicated in pregnancy, ACEI at angioneurotic oedema • aldosterone antagonists and K-sparing diuretics can cause hyperkalemia