Subatomic Particles and Isotopes
advertisement

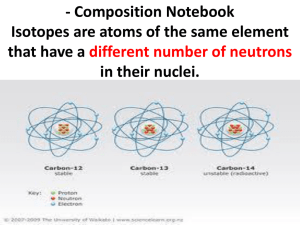
Subatomic Particles and Isotopes Subatomic Particles Protons- Positively Charged Located in the nucleus Have the same mass as a neutron Have same but positive charge of an electron Atomic number tells number of protons in an atom of that element Atomic Number = # protons Example- Carbon atomic number= 6 Has 6 Protons Neon- Atomic Number ? # protons ? Electrons Negative charge In the electron cloud Smaller than protons and neutrons Has the same charge as protons, but it is negative In a neutral atom, # protons= #electrons Electrons In a neutral atom, # protons= #electrons If electrons ≠ protons, the atom has a charge Known as an ion If more protons- atom has a positive charge If more electrons- atom has a negative charge To find the charge: charge= protons - electrons Neutrons Neutrally charged Located in nucleus Have the same mass of protons For most atoms, # protons=#neutrons However, for some atoms #protons ≠ #neutrons These are called isotopes Isotopes #protons ≠ #neutrons Mass number= #protons + #neutrons What is the mass number of carbon with 8 neutrons? Answer: 14 Written: carbon- 14 Isotopes How many neutrons does hydrogen-3 have? Answer: 2 mass #= #protons + #neutrons 3 = 1 + # neutrons 3–1 = #Neutrons Why are isotopes important? They contribute to the mass of the atom. Why? Most of the mass of the atom is from protons and neutrons If there is an additional neutron the mass increases Also, they have properties different from other isotopes Carbon-14 The Average Atomic Mass The average of the masses of all the isotopes of an atom That’s why the average atomic mass is a decimal! Average Atomic Mass Tells you the most abundant isotope of an atom. Example- Iron (Fe) Average atomic Mass: 55.845 Round the mass to the nearest whole number 55.845 round to 56 Iron- 56 is the most abundant isotope of iron Determine the Most Abundant Isotopes for the Following Elements 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Lithium (Li) Carbon Oxygen Hydrogen Neon Chlorine •Lithium- 7 •Carbon- 12 •Oxygen- 16 •Hydrogen- 1 •Neon- 20 •Chlorine- 35 and Chlorine36