Metallic Bonding - Forest Hills High School
advertisement

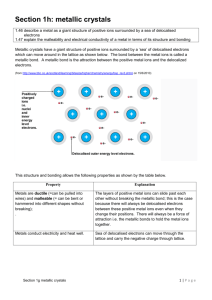
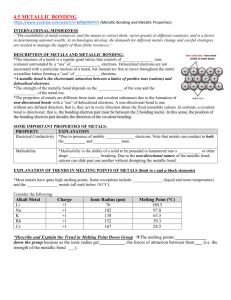
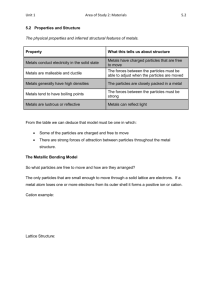
Aim: How Do Metal Atoms Bond in a Metal? DO NOW: TAKE A SHEET FROM THE FRONT AND ANSWER THE QUESTIONS. Metallic Bonding Metallic bonding consists of the attraction of the free-floating valence electrons for the positively charged metal ions Positive metal ions in a sea of electrons. Electrons are shared amongst every metal ion. Structure of Metals The metal ions are in a fixed position of a crystal lattice and the electrons are free to move throughout the lattice. A crystal lattice describes the periodic arrays of a solid. The bond results from the attraction between the free moving electrons and the atom’s positive kernel. Conductivity of Metals Metals conduct electricity because of the free moving electrons Electricity is energy due to the flow of electrons Malleability of Metals Metals are malleable When a force is applies the metal kernels move to a new location, changing the shape of a metal. Crystalline structures Metals are arranged in very compact and orderly patterns. Metal atoms crystallize in characteristic patterns. Ionic Compounds are brittle. Good conductor of electricity (in solution and when melted) Metals are malleable High melting points and boiling points Good conductor of electricity (solid and liquid) Alloys Alloys are mixtures composed of two or more elements, at least of which is a metal. Alloys are usually stronger than their individual components Steel: iron and carbon, boron, chromium, manganese, molybdenum, nickel, tungsten, vanadium. http://www.drkstreet.com/resources/metallic-bonding-animation.swf http://www.ausetute.com.au/metallic.html The ability to conduct electricity in a solid state is a characteristic of metallic bonding. This characteristic is best explained by A. high ionization energies B. high electronegativities C. mobile electrons D. mobile protons Which element consists of positive ions immersed in a “sea” of mobile electrons? A. sulfur B. nitrogen C. calcium D. chlorine