PPT
advertisement

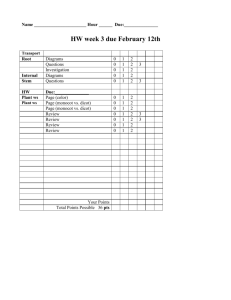
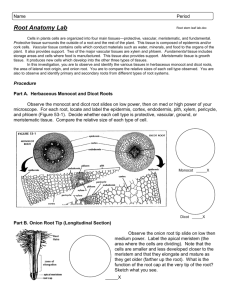
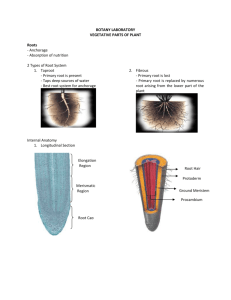
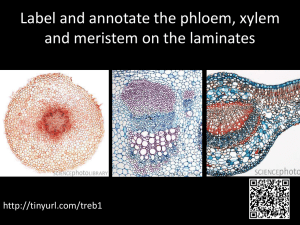
Principles of Biology By Frank H. Osborne, Ph. D. Lab 6 - Green Plant II Monocotyledonous Seed Structure A. Monocot seeds 1. Monocot seeds have one cotyledon. 2. The cotyledon stores food for the embryonic plant. 3. The embryonic plant is located next to the cotyledon. 2. Dicotyledonous seeds 1. Dicot seeds have two cotyledons. 2. The cotyledons have the embryonic plant between them. Root Structure A. Monocot roots 1. Monocot roots have xylem tissue scattered in a ring. 2. Phloem tissue is scattered in a ring. It alternates with the xylem. 3. There are very few xylem cells in each location. Monocot Root Structure Root Structure B. Dicot roots 1. Dicot roots have xylem tissue concentrated in the center in a star-shaped pattern. 2. Phloem is found between the points of the star. 3. Large numbers of xylem cells are concentrated in the star. Dicot Root Structure Stem Structure A. Monocot stems 1. Vascular bundles are scattered in the pith. 2. Vascular bundle structure a. a few xylem cells b. air space c. phloem opposite the air space d. surrounded by sclerenchyma fibers Monocot Stem Structure Monocot Stem Structure Xylem Air Space Phloem Sclerenchyma Stem Structure B. Dicot stems 1. Xylem and phloem are concentrated in a circle. 2. Xylem is on the inside. The phloem is on the outside. The cambium is in between the xylem and the phloem. 3. Larger stems have xylem in rings. 4. There are always large numbers of xylem cells present. Dicot stem structure Dicot Stem Cross-section Leaf Structure Leaf Structure A. Monocot leaves 1. Monocot leaves have parallel veins 2. Each vein has only a few xylem cells. 3. Monocot xylem cells always appear circular in cross section. Monocot leaf structure Leaf Structure B. Dicot leaves 1. The veins of dicot leaves form a netted pattern. 2. Dicot veins always have xylem on top and phloem underneath. 3. Each vein has large numbers of xylem cells. 4. The veins do not all appear circular in cross-section. Dicot leaf structure The End Lab 6 Green Plant II