Student will learn: Relationship between light & electrons What produces color
advertisement

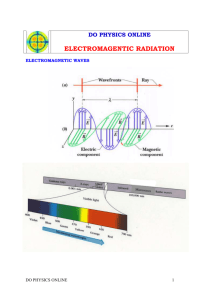
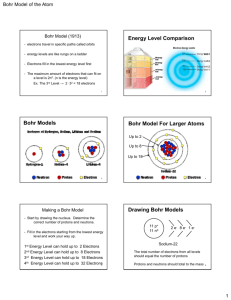
Student will learn: Relationship between light & electrons What produces color Electromagnetic Spectrum Readings Neils Bohr Model of Hydrogen Readings Atomic theory = Dalton Electron discovery = JJ Thomson Electron charge = Millikan Nucleus discovery = Rutherford Neutron = Chadwick Neils Bohr What keeps the negative electrons from falling toward the positive nucleus? Neils Bohr What keeps the negative electrons from falling toward the positive nucleus? The emission of light is related to the behavior of the electrons. Light as a Wave Light as a stream of photons Tiny little packets of quantum energy Light: travels in waves, made up of photons Photons : zero mass, contain a quantum energy Glasses Light = electromagnetic radiation energy from light affects electrons • Ground State: lowest energy state of an atom. • Excited State: an atom has absorbed energy higher than ground state. • Electromagnetic radiation: The energy given off when an excited atom returns to its ground state. “production of colored light / luster of a metal” Absorption / Emission of Photon An excited atom returns to a lower energy level. Excited State Photon emitted Ground State The color of the photon emitted depends on the energy change that produces it. Excited state two Excited state one Each photon emitted corresponds to a particular energy change. 4 excited states… each one may emit a different color ? What is the principal number of electrons that produces the 1094 infared wavelength? ? A Red light is produced when the electrons fall back from energy level 3 to energy level_________. ? A Violet light is produced when the electrons fall back from energy level __________ to energy level_________. ? For hydrogen to produce a UV wavelength the electron must fall back from what to what? Student will learn: Relationship between light & electrons What produces color Electromagnetic Spectrum Readings Neils Bohr Model of Hydrogen Readings