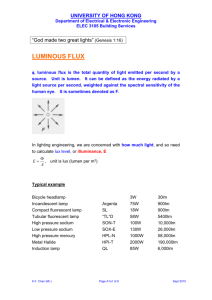
Luminous flux光通量
advertisement

6 Principles of Light 光学原理 Light and the effects of light are a major element in the human sense of the environment. Both artificial and natural sources of light are used in buildings and these sources can be supplied and controlled in many ways. 6.1 Natural of Light 光的性质 what is light? Light is energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation 光是以电磁波形式传播的(辐射)能。 electromagnetic spectrum 电磁辐射波谱 UV:紫外线 is the short of (ultraviolet) IR: 红外线 is the short of (infra-red) how do light travel? Light travel in straight lines but can be affected by the following effects. Reflection 反射 Refraction: 折射 Diffraction: 衍射 Light travel in straight lines Reflection 反射 Refraction: 折射 Diffraction: 衍射 what is Visible radiation 可见光 nm_ nanometre 纳米10-9m The wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation that are visible to the eye range from approximately 380nm to 760nm . 380nm 760nm What is white light? 什么是白光? If all the wavelengths of light are seen at the same time the eye cannot distinguish the individual wavelengths and the brain has the sensation of white light. 380nm 760nm White light can be separated into its component wavelengths using a glass prism棱镜, Monochromatic and color light 单色光 is light of one particular wavelength what is Non-visible radiation 不可见光 Electromagnetic radiations with wavelengths outside the range of visible wavelengths cannot be detected by the human eye. Ultra-violet Infra-red Infra-red radiation 红外线 Infra-red radiation has wavelengths slightly greater than those of red light and can be felt as heat radiation from the Sun and from other heated bodies. Infra-red radiation is made use of in radiant heating devices, for detecting patterns of heat emission, for “seeing ” in the dark, and for communication links. Ultra-violet 紫外线 Ultra-violet radiation has wavelengths slightly less than those of violet light. It is emitted by the Sun and also by other objects at high temperature. Ultra-violet radiation helps keep the body healthy but excessive amounts can damage the skin and the eyes. Ultra-violet radiation can be used to kill harmful bacteria in kitchens and in hospitals. Certain chemicals can convert UV energy to visible light and the effect is made use of in fluorescent lamps荧光灯. 6.2 Nature of vision 视觉特征 retina视网膜 the structure of the eye Cone vision 锥体细胞 is adapted to normal levels of light and is used to for seeing details and distinguish colour Rod vision杆状细胞 is adapted to very low levels of light and is very sensitive to light but cannot distinguish colour terminology of vision视觉术语 Visual field视野 Is the total extent in space that can be seen when looking in a given direction Visual acuity视觉敏锐度 Is the ability to distinguish between details that are very close together. Adoption视觉适应 Is the process occurring as the eyes adjusts to the relative brightness or colour of objects in the visual field. Contrast视觉对比度 is the different in brightness or colours between two parts of the visual field. 180 6.3 how to measure lighting 光的度量 Light is one form of energy and could be measured by the standard units of energy. But the effect of light on the human environment also depends upon the sensitivity of the eye and a special set of units has been developed for the measurement of light and its effects. Luminous flux 光通量 Solid angle 立体角 Luminous intensity 发光强度 Illuminance照度 Luminance 亮度 which one can give more light? Luminous flux光通量 is the rate of flow of Incandescent lamps light energy 辐射体单位时间内以电磁辐射的形式向外 辐射的能量称为辐射功率或辐射通量 其中被人眼感觉为光的那部分成为光通量。 Unit : lumen (lm) 1lm= 1/683 W fluorescent lamps what is Solid angle 立体角 light can radiate in all three dimensions the space around a point can be divided into “solid angles” ds d 2 r The ds r 2 1steradian 2 2 1 r r standard SI unit of solid angle is the steradian球面度(立体 角单位 A complete sphere contains a total of 4 steradians ds d 2 r which one would you choose? F Luminous intensity发光强度 Unit : candela (cd) The candela is one of the base units in the SI system. I Illuminance 照度 When luminous flux falls on a surface it illuminate that surface. Illuminance is the density of luminous flux reaching a surface Unit : lux (lx) 1lx=1lumen/(meter)2 If light is falling a surface at right angles to the surface then the illuminance is given by the following formula. F E A Illuminance 照度 in several different cases 22 Figure 5.3 Summary of lighting measurements McMullan Inverse square law of illumination 照度的平方反比定律 The llluminance produced by a point source of light decreases in inverse proportion to the square of the distance from the source. May be expressed by the following formula I E 2 d Worked example 6.2 A lamp has a luminous intensity of 1200cd and acts as a point source. Calculate the illuminance produced on surfaces at the following positions a) At 2m distance from the lamp, and b) At 6m distance from the lamp Know: I=1200cd Using I E 2 d d1=2m and d2=6m, E=? E1=1200/22=300lx E2=1200/62=33.33lx Cosine law of illumination照度的余弦定律 light strikes many surfaces at an inclined angle and therefore illuminates larger areas than when it strikes at a right angle. I Can be calculated using E 2 cos d Angle between direction of flux and the normal Worked example 6.3 2.5m 2m 1.5m A lamp acts as a point source with a mean spherical intensity of 1500cd. It is fixed 2m above the centre of a circular table which has a radius of 1.5m. Calculate the illuminance provided at the edge of the table, ignoring reflected light. know: I=1500cd, E=? Using :triangle laws三角形定律 d=2.5m 2 2 cos d 2.5 Note: you do not need to know the actual value of the angle in degrees Using I 1500 2 E 2 cos 192lx 2 d 2.5 2.5 Reflection 反射 Diffusere Specular flection 镜面反射 flection 漫反射 Reflectance 反射率is the ration of the luminous flux reflected from a surface to the flux incident upon the surface Worked example 6.4 A point source of light with a luminous intensity of 1800cd is set 3m above the floor and 1m below the ceiling which has a reflectance of 0.5. calculate the direct and reflected component of the illuminance on the floor beneath the light Know I=1800cd d=3m E=? Using Reflectance of 0.5 1m I 1800 E 2 2 200 lx d 3 3m So direct component = 200 lx d=1+1+3=5m I 1800 E 2 reflectanc e 2 0.5 36 lx d 5 which one is brighter ? a fluorescent tube a spot lamp聚光灯 have the same luminous intensity; Self-luminous The sources 自发光光源 luminance is given by the following formula Luminous intensity in a given direction L Area of source as seen from that direction unit: cd/m2 亮度和照度有何区别?照了不一定亮! Luminousflux reflected Reflecting surface 反射表面 L Area of reflectingsurface unit: apostilb 阿波熙提(应用于扩 散表面的亮度单位) where 1asb=1lumen/m2 反光材料,亮度高 吸光材料,亮度低 31 Self-luminous sources 自发光光源 Reflecting surface 反射表面 cd/m2 1asb=1lumen/m2 the candela per square metre is the correct SI unit of luminance. The apostilb is an alternative unit of luminance which is convenient for some calculations 1 apostilb =1/ cd/m2 Draw out a list to compare these parameters Solid angle 立体角 Luminous intensity 发光强度 Steradian candela (cd) 球面度 ds d 2 r Luminous Illuminance Luminance flux 照度 亮度 光通量 lumen (lm) lux (lx) I I E F cd/m2 F E A L I I E 2 E 2 cos d d F 1lm= 1/683 W 1lm/m2 1 apostilb = 1/ cd/m2 Self-luminous The sources 自发光光源 luminance is given by Luminous intensity in a given direction L Area of source as seen from that direction Reflecting surface 反射表面 Luminousflux reflected L 2 1asb=1lumen/m Area of reflectingsurface 1 apostilb =1/ cd/m2 unit: cd/m2 A good light environment requires a suitable light distribution what is Glare 眩光 Glare is the discomfort or impairment 损害of vision caused by an excessive range of brightness in the visual field. Glare can be caused by what? lamps, windows and painted surfaces appearing too bright in comparison with the general background. Glare Can be further described as Disability glare 失能眩光 Discomfort glare不舒适眩光 how to measure Light? A Photometer 光度计is an instrument that measures the luminous intensity of a light source by comparing it with a standard source whose intensity is known. A photocell light meter 光电仪 is an instrument that directly measures the illuminance on a surface. The electrical resistance of some semiconductors , such as selenium硒, changes with exposure to light and this property is used in an electrical circuit connected to a galvanometer检流计. This meter may be calibrated in lux. Does light has Directional quality ? 光有方向吗? We can describe its directional property using the following parameters Illumination vector 照明矢量 Scalar illuminance 照明标量 Vector/scalar ratio 矢量/标量比 Because of the limited time, we won’t talk too much about these parameters 6.4 Color 色彩 please read this part by yourself after class Spectral energy distribution figure 5.12 Colour systems CIE color coordinates Munsell system Colour reproduction Additive colour Additive primary colours Application of additive colour Stage lighting Colour television Colour printing 6 Principles of Light 5.1 what is light? 5.1.1 how is light travel? 5.1.2 what is Visible radiation 可见光 5.1.3 what is Non-visible radiation 不可见光 5.2 Nature of vision 视觉特征 Cone vision 锥体细胞 Rod vision杆状细胞 Visual field视野 Visual acuity视觉敏锐度 Adoption视觉适应 Contrast视觉对比度 Inverse square law of illumination 5.3 Measure of lighting 光的度量 I Solid angle 立体角 E 2 d Luminous intensity 发光强度 Cosine law of illumination Luminous flux 光通量 I Illuminance照度 E 2 cos d Luminance 亮度 5.4 Colour 色彩 P122 Exercise in the class 1 Cone vision 锥体细胞 ( ) A is adapted to normal levels of light B is adapted to very low levels of light C is used for seeing details D is used for distinguish E is very sensitive to light F cannot distinguish colour 2 rod vision 锥体细胞 ( ) A is adapted to normal levels of light B is adapted to very low levels of light C is used for seeing details D is used for distinguish E is very sensitive to light F cannot distinguish colour 3( ) is the rate of flow of light energy A solid angle B luminous intensity C luminous flux D illuminance E luminance 4 Link the following two columns by lines 1 Solid angle 2 Luminous intensity 3 luminous flux 4 illuminance 5 luminance A cd/m2 B steradian C apostilb D lm E cd F lx G lumen/m2