2B.3.5: Electromagnetic Waves
advertisement

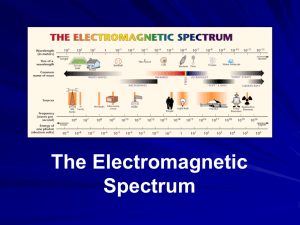
State Assessment Review Physical Science S.HS.2B.3.5 subatomic particles – the three main particles that exist in an atom (proton, neutron, and electron) proton – a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and is found in the nucleus of an atom electron – a subatomic particle that has a negative charge and is located outside the nucleus in the electron cloud, much smaller than the proton and neutron Two charged particles exert a force on one another. These forces become stronger with an increased magnitude of charge and are decreased when the distance between the charges becomes greater. Opposite charges attract each other. Like charges repel each other. When charged particles accelerate, a magnetic field is produced. In the presence of a magnetic field, an electric current can be produced (moving charged particles). Every electron is moving around the nucleus of an atom, so every electron is a tiny magnet. Not all objects are magnetic because the electrons are spinning in different directions and their magnetic fields cancel each other out. The electric field given off by the charged particle combined with the magnetic field given off by its motion produces an electromagnetic wave. electromagnetic wave – a transverse wave composed of alternating electric and magnetic fields arranged in order of their wavelength and frequency Electromagnetic waves include: (low frequency, high wavelength) Radio Waves – Microwaves – Infrared Waves (Heat) – Visible Light (Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet) – Ultraviolet Rays – X Rays – Gamma Rays (high frequency, low wavelength) The energy of electromagnetic waves are carried in packets which have a magnitude that is inversely proportional to the wavelength. Questions 1. Stars emit wave energy as electromagnetic radiation. Which statement best explains the origin of these waves? A. Accelerated electrons give off energy of various wavelengths. B. Electrons that maintain constant kinetic energy give off waves with constant energy. C. Accelerated neutrons give off energy at constant wavelengths. D. Neutrons that maintain maximum kinetic energy give off waves with maximum wavelengths. Questions 1. Stars emit wave energy as electromagnetic radiation. Which statement best explains the origin of these waves? A. Accelerated electrons give off energy of various wavelengths. – correct answer B. Electrons that maintain constant kinetic energy give off waves with constant energy. C. Accelerated neutrons give off energy at constant wavelengths. D. Neutrons that maintain maximum kinetic energy give off waves with maximum wavelengths. Questions 2. An electron will attract A. a proton. B. a neutron. C. another electron. D. An electron does not attract any other subatomic particles. Questions 2. An electron will attract A. a proton. B. a neutron. C. another electron. – correct answer D. An electron does not attract any other subatomic particles. Questions 3. Which of the following electromagnetic waves carries the most energy? A. B. C. D. radio waves infrared waves ultraviolet waves X-rays Questions 3. Which of the following electromagnetic waves carries the most energy? A. B. C. D. radio waves infrared waves ultraviolet waves X-rays – correct answer Questions 4. What is the source of a magnetic field? A. B. C. D. moving neutrons stationary protons moving electrons stationary neutrons Questions 4. What is the source of a magnetic field? A. B. C. D. moving neutrons stationary protons moving electrons – correct answer stationary neutrons