Moment of a Force

Centre of Gravity
& Moments
Stability
• Two factors determine the stability of an object
– Centre of Gravity
– Base
• If the Centre of Gravity of an object acts through its base an object will remain stable
– For stability a line perpendicular from the Centre of Gravity must fall inside the base
Stability
• Which object will topple over?
• Explain why the bottle rack doesn’t topple over.
Equilibrium
• Stable Equilibrium
– Returns to its position after a small disturbance
• Unstable Equilibrium
– Will not return to its position after a small disturbance
Two Laws of Equilibrium
1. The vector sum of the forces in any direction
is zero.
– forces up = forces down
– forces left = forces right
2. The sum of the moments about any point is zero.
– Sum of the clockwise moments about a point is equal to the sum of the anti-clockwise moments about a point
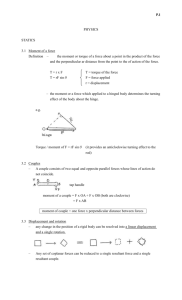
Moments
• Force causes a body to change its velocity or accelerate.
• A force can also cause a turning effect or a rotation.
• The Moment of a Force is the turning effect of a force.
Moment of a Force
Moment
=Force x Perpendicular distance
Fulcrum
FORCE
Perpendicular distance
Moments
=Force x Perpendicular distance
= 10N x 5m = 50Nm
FORCE
=10N
Perpendicular distance=5m
Couples
• A couple is two parallel forces acting in opposite directions
Torque
Sample Question 1
• A cyclist applies a force of 8N on the handlebars toward himself with his right hand and the same size force away from himself with his left. Each hand is 13cm from the fulcrum. What is the torque of the couple on the handlebars?
• Ans 2.08 Nm
Sample Question 2
• A 6m long plank of wood rests on a fulcrum 2m from the left. A boy of weight 500N stands on the left edge of the plank, while a girl weighing 400N stand 2m from the right end.
– If the system is in equilibrium, calculate the weight of the metre stick.
– What is the reaction on the fulcrum?
– If the boy was replaced by a man of weight 800N standing on the same point, where would the girl need to position herself for the system to be in equilibrium again?
Experiment: Investigation of the laws of equilibrium for a set of co-planar forces