Course Description: CE205: This course will present the theory and
advertisement

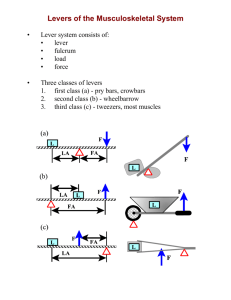
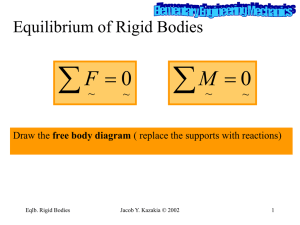
Course Description: CE205: This course will present the theory and applications of basic engineering mechanics, including a review of vectors, the computation of resultant forces, the equations for equilibrium of particles and rigid bodies, the computation and diagramming of internal shear and moment forces, and dry friction. Corequisite: PHYS 151L Fundamentals of Physics I: Mechanics and Thermodynamics (4 units) Textbook: R.C. Hibbeler, Engineering Mechanics: Statics (10th ed.), Prentice-Hall, 2003. (highly recommended) The MATLAB Student Edition, The MathWorks, 2003. Topics: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Forces and vectors, cartesian vector notation and operations Particle equilibrium Moments and force system resultants Rigid body equilibrium Structural analysis of trusses and frames/machines Internal forces, shear/moment diagrams Dry friction Course Objectives: 1. To study and analyze forces on a static particle Outcomes: The student will be able to: 1. Express force and position vectors in Cartesian vector form, determine unit vectors, vector sums, dot products, and cross products 2. Draw and label free-body diagrams 3. Determine the resultant force acting on a particle 4. Determine the forces necessary for a particle to remain static using equations of equilibrium 2. To study and analyze forces and moments on a static rigid body Outcomes: The student will be able to: 1. Determine the moments of forces in two or three dimensions 2. Determine force and moment resultants 3. Determine point loads statically equivalent to distributed loads 4. Replace supports with equivalent reaction forces 5. Write and solve equations of equilibrium of a rigid body 3. To study and analyze forces/moments on/between multiple static rigid bodies Outcomes: The student will be able to: 1. Use the methods of joints and sections to analyze truss structures 2. Determine the forces acting between members of frames and machines composed of pin-connected members 4. To study and analyze internal forces/moments in a static rigid body Outcomes: The student will be able to: 1. Use the method of sections to determine internal forces 2. Determine internal shear and bending moments using loading equations 3. Understand and draw shear / bending moment diagrams 5. To use computer programming to solve statics problems Outcomes: The student will be able to: 1. Use MATLAB(R) to compute forces and moments 2. Use MATLAB(R) to solve systems of equations in statics problems Class Schedule: Two lectures (MW, 50 minutes each), 1 discussion (Tu, Th or F, 50 minutes) Laboratory projects: none Computer usage: Approximately one-eighth of the homework problems must be solved using MATLAB; this allows for exploration of the effects of varying parameters in realworld problems. Relation of Course to Program Objectives: The course provides the students with basic knowledge of forces and moments on and between components of a structure. It also emphasizes the fundamental steps (e.g., setup, analysis, solution, discussion) of engineering problems. It contributes to the following program outcomes: a, d, e, g, and l Prepared by: Erik A. Johnson