Centre of Gravity, Moments & Levers
advertisement

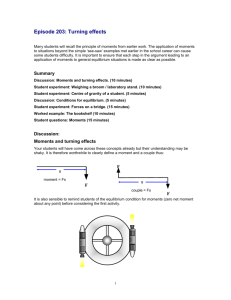
Centre of Gravity, Moments & Levers Levers A lever is a simple machine that involves moving a load around a fulcrum (pivot) using a force. Examples 1.The handle of a door 2.A wheelbarrow 3.A revolving door How a lever works There are 3 terms associated with levers • Effort • Load • Fulcrum Moment A Moment is a force that would tend to make a lever turn. A moment equals force times perpendicular distance from the fulcrum. M=Fxd M=Fxd Moment = (40)(0.2) = 8 Nm A wrench 30 cm long is used by a mechanic to turn a nut. If the force he exerts on the end is 5 Newtons, calculate the moment of the force. The Law of the Lever If a lever is balanced then the sum of clockwise moments equals the sum of anti-clockwise moments. Exp:To investigate the turning effect of forces on a lever Method: 1. Suspend a metre stick from a stand at its centre of gravity. 2. Arrange the weights at each end until the stick balances. 3. Calculate the turning effect (weight x distance from fulcrum) on each side. Result: When the metre stick is balanced the turning effect on the right hand side is equal to the turning effect on the left hand side. Conclusion: When the stick is balanced the total of the turning effects on one side is equal to the total of the turning effects on the other side. This is the law of the lever. Clockwise Moments = Anti-clockwise Moments M=Fxd or F1 x d1 = F2 x d2 ? 39 Find the missing force? Clockwise Moments = Anti-clockwise Moments F(39) + 8(12) = 13(7) + 6(18) + 2(46) F(39) + 96 = 91+ 108+ 92 F(39) = 195 F=5 •Edward weighs 500 N and is sitting at one end of a see-saw which is 4 m long and balanced in the middle. •John is 2000 N. Where should he sit in order to balance the see-saw? The centre of gravity of an object is the point through which the weight of the object appears to act. Exp:To find the centre of gravity of a thin lamina. Method: 1.Hang the card as shown. 2.Draw a line under the plumbline. 3.Reposition and repeat. Result: Where all the lines meet is the centre of gravity. Conclusion: The centre of gravity of the card is the centre and it should balance on the base of a pencil. Stability A body is more stable if: (a) its centre of gravity is close to the ground (b) it has a wide support base. In physics the term equilibrium is used when talking about stability. Equilibrium If something is in equilibrium it is balanced A body can have 3 different states of equilibrium A.Stable C.Neutral B.Unstable • Stable Equilibrium – A body is in stable equilibrium if it returns to its equilibrium position after it has been displaced slightly. • Unstable Equilibrium – A body is in unstable equilibrium if it does not return to its equilibrium position after it has been displaced slightly. • A body is in neutral equilibrium if it stays in the displaced position after if has been displaced slightly. Equilibrium?