What is GPS - Yale University Library

What is GPS?
The Global Positioning System
• The Global Positioning System
(GPS) is a system of satellites maintained by the US
Department of Defense for navigational and security purposes.
• These satellites, which orbit the earth at approximately
11,000 miles, follow known orbital paths and broadcast radio signals communicating their location at a given point in time.
It’s All About Time
• In brief, the receiver is able to determine how long each signal took to travel from the satellite to the receiver
(measured as a delay in the signal’s arrival time), and translate this time interval to a distance measurement.
Trialateration
• By comparing the distances to multiple satellites the receiver is able to approximate location (both horizontal and vertical) using mathematical trialateration.
Shortcomings
• Tree canopy, nearby cliff walls, buildings, etc. all can limit the ability of a receiver to accurately determine position.
• In addition, the configuration of the satellites themselves is sometimes better or worse for a given location.
• For example, if all of the satellites are directly overhead, it is very difficult to get accurate triangulation measurements.
Accuracy
• Current consumer-grade receivers are able to determine horizontal location to within 3-20 meters, and vertical accuracy to within 50 meters.
Precision
• The Garmin Etrex is capable of recording positions with precision of .00001 decimal degrees. As shown below, this means that it is not possible to record positions at sub-meter accuracy with this equipment.
.1 degree = 11112 m
.01 degree = 1111.2 m
.001 degree = 111.12 m
.0001 degree = 11.112 m
.00001 degree = 1.1112 m
.000001 degree = .11112 m
.0000001 degree = .011112 m
GPS Data
• By default, GPS receivers record data in latitude-longitude using the WGS84 (World
Geodetic System 1984) datum
• Many GPS receivers allow the user to view their location in local coordinates as well (e.g., UTM,
State Plane, etc.), performing a translation from
WGS84 to the desired coordinate system (and datum).
• Similarly, some GPS software packages allow you to convert the coordinate system when you export your data.
Getting it into ArcGIS
• The process of getting your data out of a
GPS receiver will vary depending upon the type of receiver and/or the GPS software being used.
• For the purposes of this tutorial, it is assumed that the GPS data was collected using one of our Garmin handhelds, which are compatible with the DNR Garmin Utility.
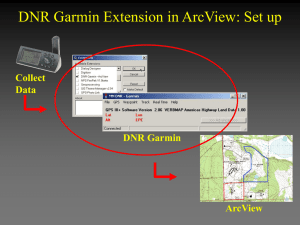
DNR Garmin Extension for
ArcView
•
This extension was built to provide users the ability to directly transfer data between Garmin GPS handheld receivers and various GIS software packages.
• Using this extension a user can use point features (graphics or shapefile) and upload them to the GPS as
WayPoints.
• Line and Polygon Graphics or shapes can be uploaded to the GPS as
TrackLogs or Routes.
•
Conversely, WayPoints, Tracklogs, and
Routes collected using the GPS can be transferred directly to
ArcView/ArcMap/Landview and saved as Graphics or Shapefiles.
Functionality Highlights
Download
Waypoints/Tracks
/Routes
Upload
Waypoints/Tracks
/Routes
Real-Time
Tracking
Waypoint to Point
Download waypoints, tracks, and routes from Garmin GPS and save as ArcView Shapefiles or Graphics
Upload waypoints, tracks, and routes to Garmin GPS
Collect real-time locational information and store as graphics or shapefile
Converts Waypoints downloaded from the GPS unit into a point shapefile or graphics
Track to
Point/Line/Polygo n
Converts a Garmin Track log to an ArcView graphic or shapefile
Point to Waypoint Convert Point shapes or graphics to a GPS Waypoint
Line/Polygon to
Track
Point to
Line/Polygon
Converts a line or polygon to a Garmin Track
Converts Point themes to Lines or Polygons
Functionality Highlights
Add Documentation to
Features
Calculate Shape
Attributes
Calculate CEP
Image Hotlinking
Adds basic documentation to ArcView themes including
Name, GPS Model, Date, Agency, etc. Arcview 3.x only
Calculates Area, Perimeter, Length attributes for features.
Arcview 3.x/8.x/9.x
Determine Circular Error Probability rings for Error estimation.
Arcview 3.x/8.x/9.x
Create hotlinks between images and GPS data.
Garmin ETREX Menus
• The first screen you will see is the Satellite
Page
• In this case, the unit is trying to lock onto the satellites
Garmin ETREX Menus
• It is possible to use various datums
• It is generally best to use WGS84
Garmin ETREX Menus
• These units are Wide
Area Augmentation
System (WAAS) compatible, allowing some degree of differential correction of the GPS signal as it is used.
Garmin ETREX Menus
• “Waypoints” can be recorded
• “Waypoints” can also be uploaded to the
GPS Unit.
• Using the GoTo feature, “Waypoints” can be navigated to.
Garmin ETREX Menus
• Various parameters of the movement of the unit can be displayed in realtime.