Macro Chapter 11- presentation 2 Built
advertisement

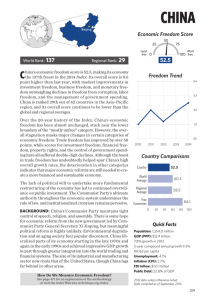
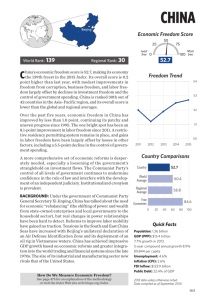
Chapter 11 Presentation 2 Quick Review #1 • Suppose consumption is $400 and that the MPC is 0.8. If disposable income increases by $1200, consumption spending will increase by • A. $1600 • B. $1360 • C. $1200 • D. $960 • E. $400 • Answer D Quick Review #2 • An increase in personal income taxes will most likely cause AD and AS to change in which of the following ways in the short run? • AD AS • A. Not change Decrease • B. Not Change Increase • C. Decrease Not Change • D. Decrease Increase • E. Increase Not Change • Answer: C Quick Review #3 • When the value of the US dollar appreciates relative to other currencies, which of the following is most likely to occur? • A. Imports into the US will decrease • B. Exports from the US will increase • C. US residents will take more vacations in foreign countries • D. More foreign visitors will travel to the US • E. Investments in US securities will increase Discretionary v. Non-Discretionary • Discretionary Spending- changes in spending and taxes that are through government action • Non-Discretionary Spending- changes that occur without Congressional action Built-In Stabilizer • Anything that increases the government’s deficit during a recession and increases its surplus during an expansion without government action • ***the tax rates are set, and as output expands, tax revenues go up Built-In Stability • As GDP increases, taxes will yield more revenue for the government • When GDP expands, individuals and businesses pay more taxes • As GDP falls, unemployment and welfare increase (transfer payments) Built-In Stability Government Expenses, G and Tax Revenues, T T Surplus G Deficit GDP1 GDP2 GDP3 Real Domestic Output, GDP Progressive Tax • The average tax rate rises as income increases, and decreases as income decreases • **as GDP rises, tax revenue rises Regressive Tax • The average tax rate falls as income and GDP rise Proportional Taxes • The average tax rate remains constant as income/GDP rise Activity • Congress has approved a new tax to fund scientific research on clones. Everyone will pay $1000. • Classify this tax as progressive, regressive, or proportional. • Who would be in favor of this tax? Opposed? • How could problems be corrected? Problems With Fiscal Policy • 1. Recognition Lag- the time between the beginning of a recession/inflation and when people become certain they are happening • 2. Administration Lag- always a lag when Congress needs to make a decision on policy • 3. Operational Lag- time between when action is decided on and when it goes into place • Ex- planning for roads, dams etc. Political Business Cycle • Politicians often increase government spending prior to an election and then slow the economy after they are in office Crowding Out Effect • An expansionary fiscal policy may increase the interest rate and reduce private spending, which weakens or cancels the stimulus of the expansionary policy 11-2 (Key Question) • Assume that a hypothetical economy with an MPC of .8 is experiencing severe recession. By how much would government spending have to increase to shift the aggregate demand curve rightward by $25 billion? How large a tax cut would be needed to achieve this same increase in aggregate demand? Why the difference? Determine one possible combination of government spending increases and tax decreases that would accomplish this same goal. Answer 11-2 Key Question • In this problem, the multiplier is 1/.2 or 5 so, the required increase in government spending = $5 billion. • For the tax cut question, initial spending of $5 billion is still required, but only .8 (= MPC) of a tax cut will be spent. So .8 x tax cut = $5 billion or tax cut = $6.25 billion. Part of the tax reduction ($1.25 billion) is saved, not spent. • One combination: a $1 billion increase in government spending and a $5 billion tax cut.