characteristic
advertisement

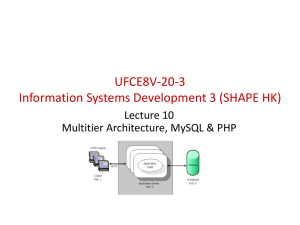
CPSC431 Lecture 10
PHP's mysqli Extension
Connecting to the MySQL Server
$mysqli = new mysqli("localhost", "siteuser", "secret", "book");
Or
$mysqli = new mysqli();
$mysqli->connect("127.0.0.1", "siteuser", "secret", "company");
Selecting a MySQL Database
$mysqli->select_db("book") or die("Can't select db!");
Closing a MySQL Connection
$mysqli->close();
PHP's mysqli Extension
Query Execution
<?php
$mysqli = new mysqli("127.0.0.1", "siteuser", "secret", "company");
$query = "SELECT productid, name, price FROM product ORDER
by name";
$result = $mysqli->query($query, MYSQLI_STORE_RESULT);
// Cycle through the result set
while(list($productid, $name, $price) = $result->fetch_row())
echo "($productid) $name: $price <br />";
// Free the result set
$result->free();
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
$mysqli->real_query() and $mysqli->store_result()
<?php
$mysqli = new mysqli();
$mysqli->connect("127.0.0.1", "siteuser", "secret", "company");
$query = "SELECT productid, name, price FROM product ORDER
by name";
$mysqli->real_query($query);
$result = $mysqli->store_result();
while(list($productid, $name, $price) = $result->fetch_row())
echo "($productid) $name: $price <br />";
$result->free();
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
$mysqli -> fetch_array()
$query = "SELECT productid, name FROM product
ORDER BY name";
$result = $mysqli->query($query);
while ($row = $result->fetch_array(MYSQLI_ASSOC))
{
$name = $row['name'];
$productid = $row['productid'];
echo "Product: $name ($productid) <br />";
}
PHP's mysqli Extension
$mysqli -> fetch_object()
$query = "SELECT productid, name, price FROM
product ORDER BY name";
$result = $mysqli->query($query);
while ($row = $result->fetch_object()) {
$name = $row->name;
$productid = $row->productid;
$price = $row->price;
echo "($productid) $name: $price <br />";
}
PHP's mysqli Extension
$result->fetch_row()
<?php
...
$query = "SELECT productid, name FROM product ORDER BY
name";
$result = $mysqli->mysqli_query($query);
while (list($productid, $name) = $result->fetch_row()) {
echo "($productid) $name: $price <br />";
}
...
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
$mysqli->multi_query($query)
<?php $mysqli = new mysqli("127.0.0.1", "root", "jason",
"company"); // Retrieve the userID from some session ID
$userid = $_SESSION['userid']; // Create the queries
$query = "SELECT lastname, firstname FROM user WHERE
userID='$userid';";
$query .= "SELECT product_count, CONCAT('$',total_cost) FROM
sales WHERE userID='$userid'";
if($mysqli->multi_query($query)) {
do { $result = $mysqli->store_result();
while ($row = $result->fetch_row())
echo "$row[0], $row[1] <br />";
if ($mysqli->more_results()) echo "********** <br />";
} while ($mysqli->next_result());
}
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
Executing a query with different parameters
<?php
$mysqli = new mysqli("127.0.0.1", "siteuser", "secret", "company");
$query = "INSERT INTO product SET rowID=NULL, productID=?, name=?,
price=?, description=?";
$stmt = $mysqli->stmt_init();
$stmt->prepare($query); // prepare the statement and bind the parameters
$stmt->bind_param('ssds', $productid, $name, $price, $description);
$productidarray = $_POST['productid']; $namearray = $_POST['name'];
$pricearray = $_POST['price']; $descarray = $_POST['description'];
$x = 0;
while ($x < sizeof($productidarray)) {
$productid = $productidarray[$x]; $name = $namearray[$x];
$price = $pricearray[$x]; $description = $descarray[$x];
$stmt->execute(); }
$stmt->close();
$mysqli->close();
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
Binding Results with the mysqli Extension
<?php
$mysqli = new mysqli("127.0.0.1", "siteuser", "secret", "company");
$query = "SELECT productid, name, price, description FROM
product ORDER BY productid";
$stmt = $mysqli->stmt_init();
$stmt->prepare($query);
$stmt->execute();
$stmt->bind_result($productid, $name, $price, $description);
while($stmt->fetch()) {
echo "$productid, $name, $price, $description <br />"; }
$stmt->close();
$mysqli->close();
?>
PHP's mysqli Extension
$stmt->affected_rows()
$stmt->free_result()
$stmt->num_rows()
$stmt->errno(mysqli_stmt stmt)
$stmt->error(mysqli_stmt stmt)
PHP's mysqli Extension
Database Transactions
$mysqli->autocommit()
mysqli_commit(): commit the present transaction
to the database
$mysqli->rollback(): roll back the present
transaction
Stored Routines – the Proc table
Column
Datatype
Null
Default
db
char(64)
Yes
No default
name
char(64)
No
No default
type
enumtype
No
No default
specific_name
char(64)
No
No default
language
enum('SQL')
No
SQL
sql_data_access
enumdataaccess
No
CONTAINS_SQL
is_deterministic
enum('YES', 'NO')
No
NO
security_type
enumsecurity
No
DEFINER
param_list
blob
No
No default
returns
char(64)
No
No default
body
longblob
No
No default
definer
char(77)
No
No default
created
timestamp
Yes
Current timestamp
modified
timestamp
Yes
0000-00-00 00:00:00
sql_mode
setsqlmode
No
No default
comment
char(64)
No
No default
Stored Routines – the Procs_priv table
Column
Datatype
Null Default
Host
char(60)
No
No default
Db
char(64)
No
No default
User
char(16)
No
No default
Routine_name
char(64)
No
No default
Routine_type
enumroutine
No
No default
Grantor
char(77)
No
No default
Proc_priv
procset
No
No default
Timestamp
timestamp
Yes
Current timestamp
Stored Routines
Creating a Stored Routine
mysql>CREATE PROCEDURE get_inventory()
->SELECT 45 AS inventory;
That's it. Now execute the procedure using the following command:
mysql>CALL get_inventory();
Executing this procedure returns the following output:
+---------------+
| inventory |
+---------------+
|
45 |
+---------------+
Stored Routines
Creating a routine syntax
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name
([parameter[, ...]]) [characteristics, ...] routine_body
Three types of parameters:
IN: intended solely to pass information into the procedure.
OUT: intended solely to pass information back out of the
procedure.
INOUT: can pass information into the procedure, have its
value changed, and then be called again from outside of
the procedure
Stored Routines
Characteristics of routines
LANGUAGE SQL
| [NOT] DETERMINISTIC
| { CONTAINS SQL | NO SQL | READS SQL
DATA | MODIFIES SQL DATA }
| SQL SECURITY {DEFINER | INVOKER}
| COMMENT 'string'
Stored Routines
Multistatement Stored Routines
DELIMITER //
CREATE FUNCTION calculate_bonus (employee_id CHAR(8))
RETURNS DECIMAL(10,2) COMMENT 'Calculate employee
bonus'
BEGIN
DECLARE total DECIMAL(10,2);
DECLARE bonus DECIMAL(10,2);
SELECT SUM(price) INTO total FROM sales WHERE employee_id
= employee_id;
SET bonus = total * .05;
RETURN bonus;
END;
//
DELIMITER ;
mysql>SELECT calculate_bonus("35558ZHU");
Stored Routines
BEGIN and END
BEGIN
statement 1;
statement 2;
...
statement N;
END
IF-ELSEIF-ELSE
IF years_employed < 5 THEN
SET bonus = total * .05;
ELSEIF years _employed >= 5 and years_employed < 10 THEN
SET bonus = total * .06;
ELSEIF years _employed >=10 THEN
SET bonus = total * .07;
END IF
Stored Routines
CASE
CASE state
WHEN "AL" THEN: SET tax_rate = .04;
WHEN "AK" THEN: SET tax_rate = .00;
...
WHEN "WY" THEN: SET tax_rate = .04;
END CASE;
Stored Routines
LOOP
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE service_info (client_id INT, services varchar(20))
BEGIN DECLARE comma_pos INT; DECLARE current_id INT;
svcs: LOOP
SET comma_pos = LOCATE(',', services);
SET current_id = SUBSTR(services, 1, comma_pos);
IF current_id <> 0 THEN
SET services = SUBSTR(services, comma_pos+1);
ELSE SET current_id = services; END IF;
INSERT INTO request_info VALUES(NULL, client_id, current_id);
IF current_id = 0 THEN LEAVE svcs; END IF;
END LOOP;
END//
DELIMITER ;
mysql> call service_info("45","1,4,6");
Stored Routines
REPEAT
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_data (rows INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE val1 FLOAT;
DECLARE val2 FLOAT;
REPEAT
SELECT RAND() INTO val1;
SELECT RAND() INTO val2;
INSERT INTO analysis VALUES(NULL, val1, val2);
SET rows = rows - 1;
UNTIL rows = 0 END REPEAT;
END//
DELIMITER ;
Stored Routines
WHILE
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE test_data (rows INT)
BEGIN
DECLARE val1 FLOAT;
DECLARE val2 FLOAT;
WHILE rows > 0 DO
SELECT RAND() INTO val1;
SELECT RAND() INTO val2;
INSERT INTO analysis VALUES(NULL, val1, val2);
SET rows = rows - 1;
END WHILE;
END//
DELIMITER ;
Stored Routines
Calling a Routine from Within Another Routine
DELIMITER //
CREATE PROCEDURE process_logs()
BEGIN
SELECT "Processing Logs";
END//
CREATE PROCEDURE process_users()
BEGIN
SELECT "Processing Users";
END//
CREATE PROCEDURE maintenance()
BEGIN
CALL process_logs();
CALL process_users();
END//
DELIMITER ;
Stored Routines
Modifying a Stored Routine
ALTER (PROCEDURE | FUNCTION) routine_name [characteristic
...]
mysql>ALTER PROCEDURE calculate_bonus SQL SECURITY
invoker;
Deleting a Stored Routine
DROP (PROCEDURE | FUNCTION) [IF EXISTS] sp_name
mysql>DROP PROCEDURE calculate_bonus;
Viewing a Routine's Status
SHOW (PROCEDURE | FUNCTION) STATUS [LIKE 'pattern']
mysql>SHOW PROCEDURE STATUS LIKE 'get_products'\G
Stored Routines
Integrating Routines into Web Applications
<form action="viewbonus.php" method="post">
Employee ID:<br />
<input type="text" name="employeeid" size="8" maxlength="8"
value="" />
<input type="submit" value="View Present Bonus" />
</form>
<?php // Instantiate the mysqli class
$db = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "jason", "corporate");
$eid = $_POST['employeeid'];
$result = $db->query("SELECT calculate_bonus('$eid')");
$row = $result->fetch_row();
echo "Your bonus is \$".$row[0];
?>
Stored Routines
Retrieving Multiple Rows
CREATE PROCEDURE get_employees()
SELECT employee_id, name, position FROM employee ORDER by
name;
This procedure can then be called from within a PHP script:
<?php
$db = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "jason", "corporate");
$result = $db->query("CALL get_employees()");
while (list($employee_id, $name, $position) = $result->fetch_row()) {
echo "$employeeid, $name, $position <br />";
}
?>