Studies on Capacity Fade of Spinel based Li
advertisement

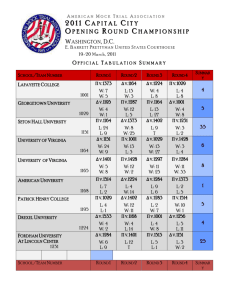
Studies on Capacity Fade of Spinel based Li-Ion Batteries by P. Ramadass , A. Durairajan, Bala S. Haran, R. E. White and B. N. Popov Center for Electrochemical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering, University of South Carolina Columbia, SC 29208 C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Motivation To characterize the capacity fade phenomena of Liion batteries. To decrease the capacity fade on both positive and negative electrode by optimizing the DC and pulse charging protocol. To develop mathematical model which will explain the capacity fade in the spinel system. C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Objectives To study the change in capacity of commercially available spinel based Li-ion Cells (Cellbatt cells). Study the performance of Li-ion cells under DC charging at different rates. Use impedance spectroscopy to analyze the change in cathode and anode resistance with cycling. Determine experimentally which electrode is more important in contributing to capacity fade. Do material characterization to study changes in electrode structure with cycling. C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Capacity Fade may Result from Overcharge Phenomena Lithium deposition on negative electrodes Electrolyte oxidation on positive electrode Passivation (Interfacial film formation) Self discharge Electrolyte Reduction Active Material Dissolution Phase Change C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Physical Characteristics of Cellbatt Lithium Ion Battery Electrodes Characteristics Positive Spinel Negative Carbon Mass of the electrode material (g) 9.592 5.0865 Geometric area (both sides) (cm 2) 436 498 Loading on one side (mg/cm 2) 22 10.2 Thickness of the Electrode (m) 91 70 54.5 x 4 58.5 x 4 Dimensions of the electrode (cm x cm) Cellbatt is a ‘Prismatic’ type cell C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Electrode Reactions At anode Li xC δLi ch arg e δe d isch arg e Li xδ C At cathode Li (M n 2 -γ Li γ )O 4 Li (M n Li )O δLi δe δ 2-γ γ 4 discharge charge Non-Stoichiometric Spinel Cell Reaction Li L i (M n 2 -γ L i γ )O 4 L i x C δ (M n 2-γ L i γ )O 4 L i x δ C discharge charge C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Charging Protocols Constant current - Constant voltage Total charging time fixed Constant voltage Charging done completely at constant voltage Constant current - Constant voltage Charging stopped when the current reaches a value of 50 mA during the CV part Charging done to different cut-off potentials C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Change in discharge capacity for Li-ion cells charged to different potentials 4.0 4.3 3.8 Cel l V o l t ag e (V ) 4.17 3.6 3.4 3.2 4.05 4.0 3.0 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 4.10 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 C ap aci t y (A h ) 4 . 0 , 4 . 0 5 , 4 . 1 0 , 4 . 1 7 , 4 . 3 V P ro t o co l C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Experimental Full Cell studies on CellBatt® Li-ion Cells Galvanostatic charge-discharge • 0.25 A, 0.5 A, 0.75 A, 1 A - (3.0-4.17 V) Cyclic Voltammograms - 0.05 mV/s, 2.5-4.2 V T-cell (half cell) studies Glove Box - Disk electrodes – 1.2 cm Counter, Reference electrodes – Li metal Cyclic Voltammograms - 0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 mV/s, 3-4.5 V vs. Li/Li+ for spinel and 0-1.2V vs. Li/Li+ for carbon Impedance Analysis - 100 kHz ~ 1 mHz ±5 mV. XRD studies of spinel electrode at various cycles. C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Charge curves for CC-CV Protocol 1.2 1 A 0.75 A 0.5 A 0.25 A Cu rren t (A ) 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 4.2 0.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 C h a rg e C u rv e c o m p a ri so n 1 0 0 c y c l e s Po t en t i al (V ) 3.9 C ap aci t y (A h ) 3.6 1 A 0.75 A 0.5 A 0.25 A 3.3 3.0 0.00 C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina 0.25 0.50 C ap aci t y (A h ) 0.75 1.00 Charge and Discharge curves for Liion Cell at various Cycles 0.6 4.17 V 0.5 4.1 0.4 3.9 0.3 1 C y cl e 3.7 0.2 V o l t ag e (V ) Cu rren t (A ) 0.5 A 3.5 0.1 800 500 200 3.3 0.0 0.18 0.36 C/2 Rate 0.54 0.72 0.90 1.08 3.8 C ap aci t y (A h ) 0 . 5 C P ro t o co l Capacity Fade 15.4% for C/2 rate C ell V o ltag e (V ) 0.00 3.6 3.4 1 cy cle 3.2 Capacity Fade 19% for 1 C rate 800 0.0 C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina 500 200 3.0 C/2 Rate 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 C ap acity (A h ) 0.7 0.8 0.9 1.0 Change in CC-CV Profiles with Cycling 1.2 4.2 1 A 0.8 0 .2 3 A h C urre nt (A ) 4.0 0.5 A 3.8 0 .2 5 A h 0.6 3.6 0 .5 6 A h 0.4 0 .5 2 A h 3.4 200 cycles V olta ge (V ) 1.0 4.17 V 0.2 3.2 500 cycles 0.0 3.0 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 C apacity (Ah) C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Nyquist plots for Cellbatt cell charged at 0.5 A at different states of charge Imag i n ary Z ( ) 0.03 100 ( Cha r ge d) 35 20 10 0 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.25 0.26 0.27 0.28 0.29 0.30 0.31 0.32 R eal Z ( ) C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Nyquist plots for Cellbatt cell charged at 0.5 A during different cycles 0.03 Z Im ( ) 0.02 F res h -0 -S O C 2 0 0 -0 -S O C 6 0 0 -0 -S O C F res h -1 0 0 -S O C 2 0 0 -1 0 0 -S O C 6 0 0 -1 0 0 -S O C 0.01 0.00 0.24 0.25 0.26 0.27 0.28 0.29 0.30 Z R e ( ) C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Nyquist Plots for Spinel and Carbon Electrodes at Discharged state at Various Cycles 50 2 0 0 cy cl es 6 0 0 cy cl es 8 0 0 cy cl es Z Im ( cm 2 ) 40 30 20 10 100 2 0 0 cy cl es 6 0 0 cy cl es 8 0 0 cy cl es 90 0 30 Spinel D i s ch arg e Im p ed an ce L i M n 2 O 4 60 ZRe 90 2 ( cm ) 120 80 150 70 Z Im ( cm 2 ) 0 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Carbon 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 2 Z R e ( cm ) 140 160 180 200 Cyclic Voltammograms of Spinel Electrode after 800 Cycles at various Scan rates C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Cyclic Voltammograms of Carbon Electrode after 800 Cycles at various Scan rates C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Cyclic Voltammograms of Spinel and Carbon Electrodes at Different Cycles Spinel C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Carbon XRD Patterns of Spinel after Different Charge-Discharge Cycles 111 400 311 8 0 0 cy cl es 511 440 531 331 In t en s i t y 222 4 0 0 cy cl es Cycle 0 400 800 "a" (Ao ) 8.17162 8.14257 8.12964 F re s h P. G.. Bruce et al., J. Electrochem. Soc., 146, 3649 (1999). 10 25 40 2 55 70 C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Conclusions Varying the charging rate affects the overall capacity of the cell. Impedance studies reveal no significant increase in resistance at both electrodes after 800 cycles. XRD studies of Spinel electrode reveal the formation of an additional phase with cycling. Capacity fade in the case of Cellbatt cells can be summarized as……… C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Capacity Fade in Cellbatt Li-ion cells Secondary Active Material Degradation(C6 & LiMn2O4) Mn Dissolution from Spinel SEI layer attack on Negative Electrode HF formation E. Wang et al. Structural Degradation of LiMn2O4 Accumulation of -MnO2 with Cycling 2L iM n 2 O 4 3 λ - M nO 2 (solid) + M nO (solution) + L i 2 O (so lution) J.C.Hunter et al. Salt Hydrolysis P F6 Electrolyte Oxidation (starts from 3.7 V) H 2O P O F 2 H F C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina Acknowledgements Financial support provided in part by the Department of Energy (DOE) is gratefully acknowledged. Thank you! C enter for E lectrochem ica l E ngineerin g U niversity o f S outh C arolina